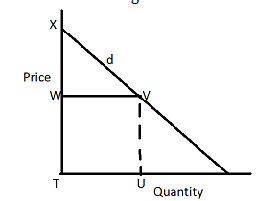
Consider the diagram below which shows a demand curve (d).
Total expenditure on a commodity is represented by the area TUVW. Consumer’s surplus is represented by___________
- A. The area VWX
- B. The area XTUV
- C. \(\frac {XW} {XT}\)
- D. \(\frac {TU} {UV}\)
If AC and MC are represented on a graph, the MC curve will cut the AC curve_______
- A. at the maximum point on the AC curve
- B. at the highest point on the AC curve
- C. at the minimum point on the AC curve
- D. at the peak
Consider the following figures which refer to a firm’s production department during one week:
Wage bill ₦6,000, Rent, Rates, Depreciation ₦200, raw materials ₦800, Power ₦300.
Total variable costs incurred during the week are
- A. ₦7,300
- B. ₦7,100
- C. ₦1,300
- D. ₦1,100
A contractionary monetary policy is used to control__________
- A. Deflation
- B. Inflation
- C. Recession
- D. Balance of Payment deficit
The term “Money at call and short notice” in a bank’s assets represents the bank’s loans to______
- A. industry and commerce
- B. overseas central banks
- C. the capital market
- D. the money markets
The second equation of exchange is__________
- A. MV = PT
- B. P = \(\frac {M}{KR}\)
- C. P = \(\frac {MV}{T}\)
- D. P=MV
The term M \(^3\) comprises M \(^1\) together with deposits on deposit account held by_______
- A. banks only
- B. discount houses only
- C. banks and discount houses
- D. banks, discount houses and stock, exchanges
The following are measures of location except________
- A. Arithmetic mean
- B. Harmonic mean
- C. Range
- D. Geometric mean
Let the quantity demanded in units of a particular commodity be represented as Qd = 80 – 2P, find the quantity demanded when P = ₦3.
- A. 70
- B. 47
- C. 74
- D. 40
Use the following information given to answer this question
Total of all expenditure incurred during the year ₤80,000 m
Indirect taxes on goods and services ₤8,000m
Capital consumption ₤6,000m
Gross national expenditure at factor cost is_________
- A. ₤ 88,000μ
- B. ₤ 82,000μ
- C. ₤ 74,000μ
- D. ₤ 72,000μ
Use the following information given to answer this question
Total of all expenditure incurred during the year ₤ 80,000m
Indirect taxes on goods and services ₤ 8,000m
Capital consumption ₤ 6,000m
National income is__________
- A. ₤ 74,000m
- B. ₤ 66,000m
- C. ₤ 60,000m
- D. ₤ 14,000m
A supply curve slopes upwards from the left to the right indicating__________
- A. a negative slope
- B. a positive slope
- C. a backward sloping supply curve
- D. short-run supply curve
When of the following matters may account for changes in supply?
I – technological advances in an industry
II – changes in labour costs
III – changes in source of supply
IV – changes in levels of taxation
- A. I, II
- B. I, III
- C. II, III, IV
- D. I, II, III, IV
An example of a vertical combination is the merger of_________
- A. a spinning firm and a wearing firm
- B. two meat retailing firms
- C. two very large wholesale textile distributors
- D. three secretarial employment agencies in one town
Whether a monopolist is able to increase his revenue by restricting his output depends on the shape of the_________
- A. marginal product
- B. marginal cost curve
- C. demand curve
- D. average cost curve
An example of a market which approaches fairly near to perfection is____________
- A. the retail market
- B. the house market
- C. the labour market
- D. the foreign exchange market
Which of the following matters may account for changes in demand?
I – changes in consumer preferences
II – changes in real income
III – changes in distribution of incomes
IV – changes in levels of taxation
- A. I, II
- B. II, III
- C. I, III, IV
- D. I, II, III, IV
A commodity is defined as normal when its demand changes in the same direction as______
- A. income
- B. price
- C. taste
- D. preferences
Effective demand for a commodity is desire for that commodity backed by_______
- A. a wish for the lowest possible price
- B. ability and willingness to pay
- C. cash in one's pocket
- D. a promise to make payment
John an apprentice, engineer and amateur trumpet player, was earning ₦30 per week before accepting Full-time employment in a top orchestra, for which he now receives ₦150 per week. ₦120 of his current weekly earnings can be described as________
- A. marginal physical productivity
- B. marginal income productivity
- C. consumer's surplus
- D. economic rent
The last link in the channel of distribution is____________
- A. Producer
- B. Retailer
- C. Consumer
- D. Wholesaler


