With the aid of a diagram, explain the super-normal profit of a monopolist.
Explanation
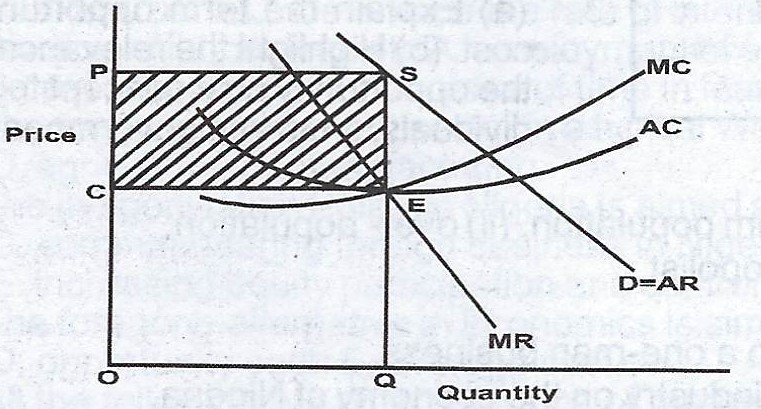
From this graph, the monopolist is at equilibrium, where his marginal cost (MC) is equal to marginal Revenue (MR). At the point of equilibrium, the quantity produced is OQ while the price is OP. At that point he is able to cover both the AC and MC. The super -normal profit can now be determined thus: Total Revenue = OPOQ
Total Cost = OCOQ
Profit = TR - TC = OPOQ - OCOQ
Quantity =PCSE or the shaded portion

