(a) If \(f(x) = \frac{x – 3}{2x – 1} , x \neq \frac{1}{2}\) and \(g(x) = \frac{x – 1}{x + 1}, x \neq -1\), fing \(g \circ f\).
(b)(i) Sketch the curve \(y = 9x – x^{3}\) ; (ii) Calculate the total area bounded by the x- axis and the curve \(y = 9x – x^{3}\).
Explanation
(a) \(f(x) = \frac{x - 3}{2x - 1}, x \neq \frac{1}{2}\)
\(g(x) = \frac{x - 1}{x + 1}, x \neq -1\)
\(g \circ f = g(f(x)) = \frac{\frac{x - 3}{2x - 1} - 1}{\frac{x - 3}{2x - 1} + 1}\)
= \(\frac{\frac{x - 3 - 2x + 1}{2x - 1}}{\frac{x - 3 + 2x - 1}{2x - 1}}\)
= \(\frac{x - 3 - 2x + 1}{x - 3 + 2x - 1}\)
= \(\frac{- x - 2}{3x - 4}\) or \(\frac{-(x + 2)}{3x - 4}\).
(b)(i) \(y = 9x - x^{3}\)
If x = 0, y = 0.
If y = 0, \(9x - x^{3} = 0\)
\(x(9 - x^{2}) = x (3 - x)(3 + x) = 0\)
\(\implies x = 0, -3, 3\)
Turning points : \(\frac{\mathrm d y}{\mathrm d x} = 9 - 3x^{2}\)
\(9 - 3x^{2} = 0 \implies 9 = 3x^{2}\)
\(x^{2} = 3 \implies x = \pm \sqrt{3} = \pm 1.73\)
When x = 1.73, \(y = 9(1.73) - (1.73)^{3} = 15.57 - 5.18 = 10.39\)
Point is (1.73, 10.39).
When x = -1.73, \(y = 9(-1.73) - (-1.73)^{3} = -15.57 + 5.18 = -10.39\)
Point is (-1.73, -10.39).
Maximum or minimum ?
\(\frac{\mathrm d^{2} y}{\mathrm d x^{2}} = - 6x^{2}\)
At x = 1.73, \(\frac{\mathrm d^{2} y}{\mathrm d x^{2}} < 0 \therefore (1.73, 10.39) \text{ is a maximum point}\)
At x = -1.73, \(\frac{\mathrm d^{2} y}{\mathrm d x^{2}} > 0 \therefore (-1.73, -10.39) \text{ is a maximum point}\).
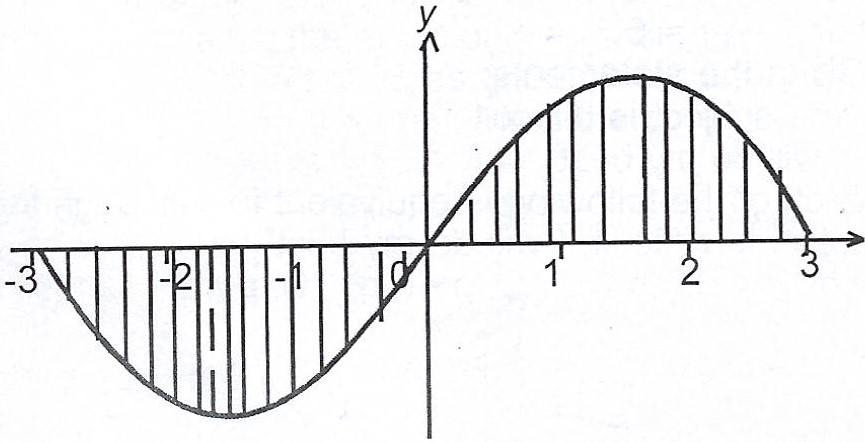
Areas between x = -3 to x = 0 and x = 0 and x = 3 are equal.
\(\therefore Area = 2 \int_{0} ^{3} (9x - x^{3}) \mathrm {d} x = 2[\frac{9x^{2}}{2} - \frac{x^{4}}{4}]_{0} ^{3}\)
= \(81 - 40\frac{1}{2} = 40\frac{1}{2} sq. units\)

