(a) Copy and complete the table for \(y = 3x^{2} – 5x – 7\)
| x | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| \(y = 3x^{2} – 5x – 7\) | 35 | -7 | -9 | 5 |
(b) Using a scale of 2cm = 1 unit along the x- axis and 2cm = 5 units along the y- axis, draw the graph of \(y = 3x^{2} – 5x – 7\).
(c) On the same axis, draw the graph of \(y + 3x + 2 = 0\).
(d) From your graph, find the : (i) range of values of x for which \(3x^{2} – 5x – 7 < 0\) ; (ii) roots of the equation \(3x^{2} – 2x – 5 = 0\).
Explanation
(a)
| x | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| \(y = 3x^{2} - 5x - 7\) | 35 | 15 | 1 | -7 | -9 | -5 | 5 | 21 |
(b) 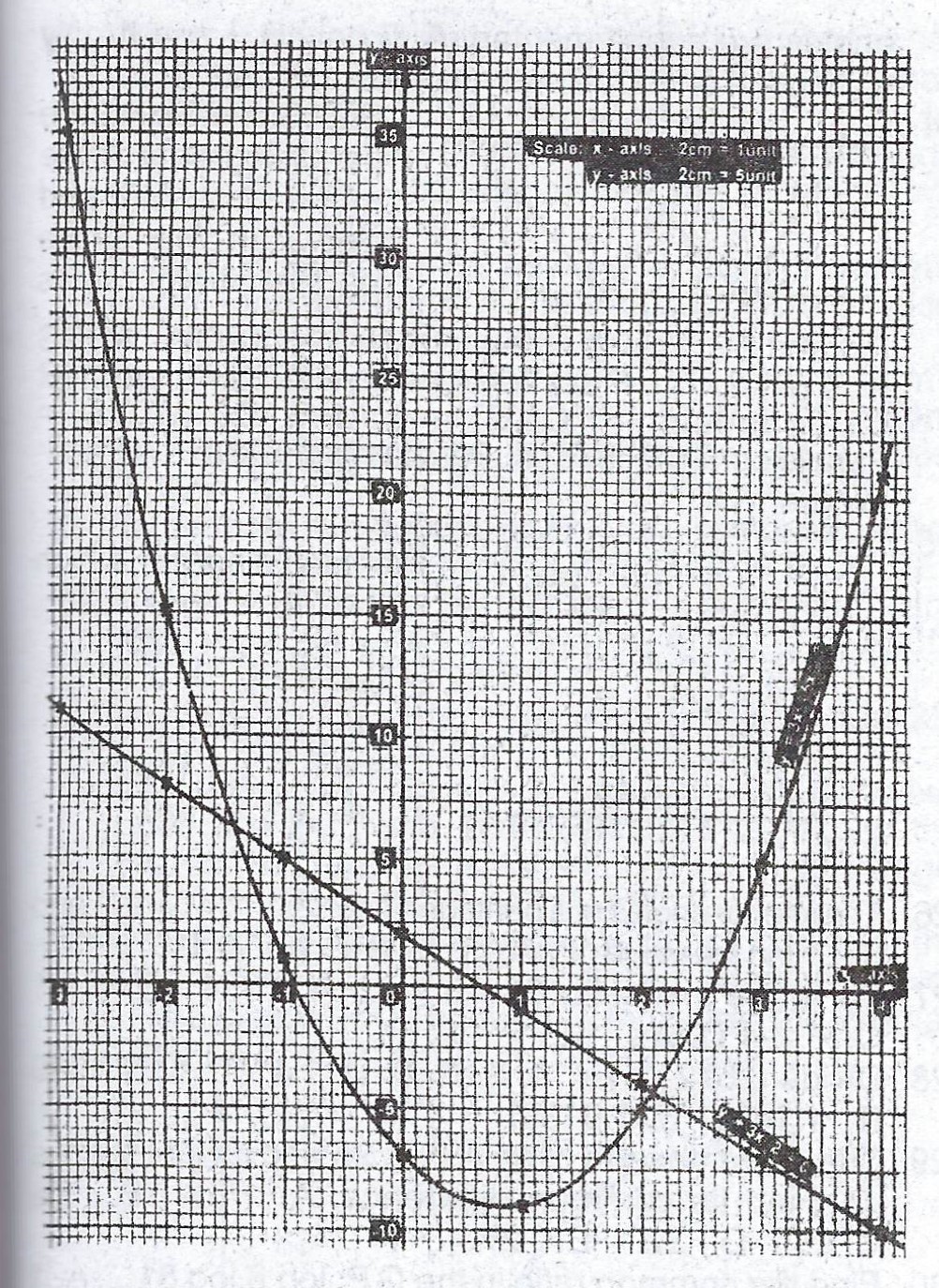
(c) \(y + 3x + 2 = 0 \implies y = -3x - 2\)
when x = -2, y = 6 - 2 = 4.
when x = 3, y = -9 - 2 = -11.
(d) \(3x^{2} - 2x - 5 = 0 = 3x^{2} - 5x - 7 = -3x - 2\)
The roots of the equation \(3x^{2} - 2x - 5 = 0\) is when the line \(y = -3x - 2\) cuts the equation i.e. x = 1.0 or 1.7.

