(a) Copy and complete the following table of values for the relation \(y = 2x^{2} – 7x – 3\).
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| y | 19 | -3 | -9 |
(b) Using 2 cm to 1 unit on the x- axis and 2 cm to 5 units on the y- axis, draw the graph of \(y = 2x^{2} – 7x – 3\) for \(-2 \leq x \leq 5\).
(c) From your graph, find the : (i) minimum value of y ;
(ii) gradient of the curve at x = 1.
(d) By drawing a suitable straight line, find the values of x for which \(2x^{2} – 7x – 5 = x + 4\).
Explanation
(a) \(y = 2x^{2} - 7x - 3\)
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| \(2x^{2}\) | 8 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 8 | 18 | 32 | 50 |
| \(-7x\) | 14 | 7 | 0 | -7 | -14 | -21 | -28 | -35 |
| \(-3\) | -3 | -3 | -3 | -3 | -3 | -3 | -3 | -3 |
| \(y\) | 19 | 6 | -3 | -8 | -9 | -6 | 1 | 12 |
(b) 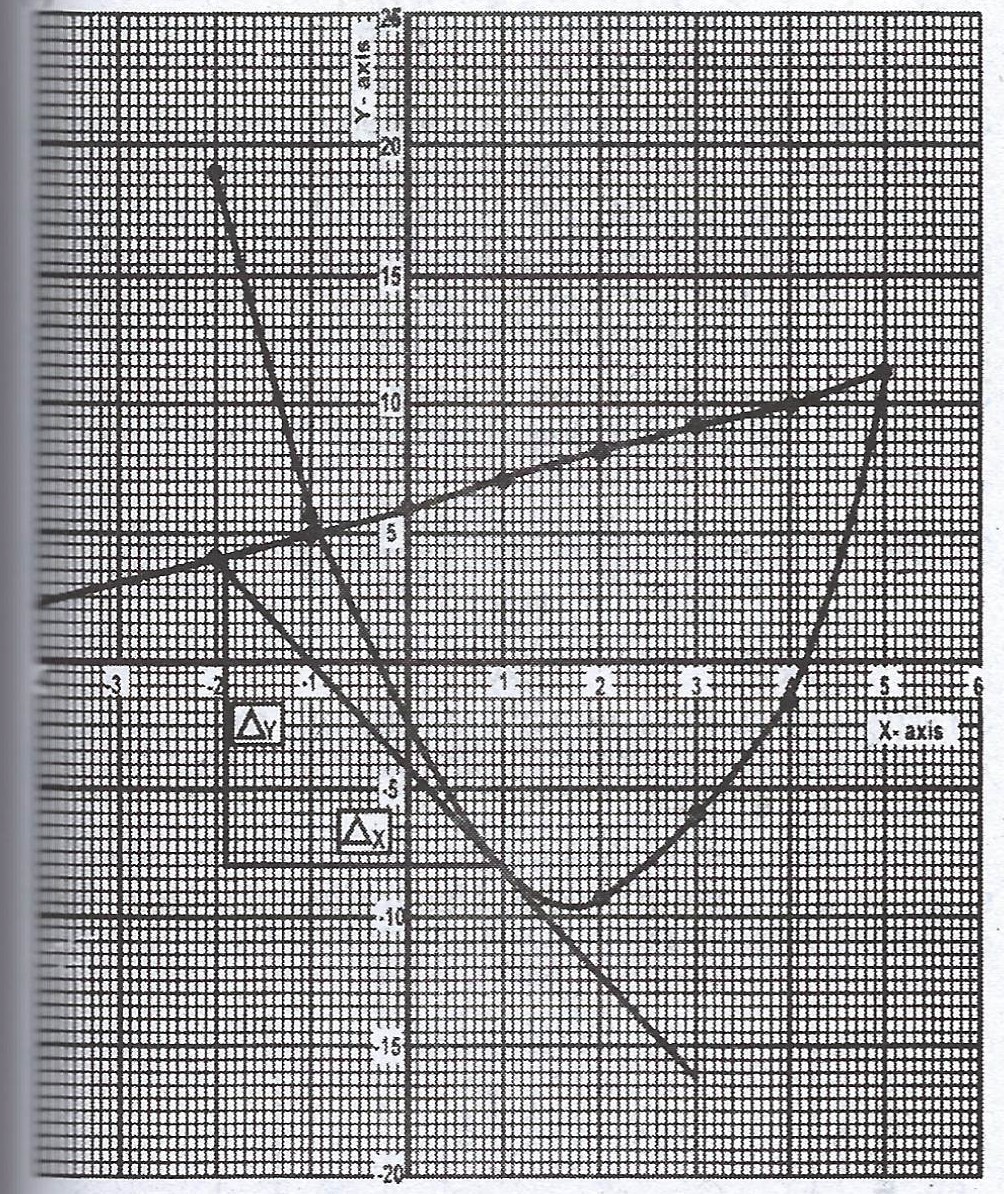
(c)(i) Minimum value of y = -9
(ii) \(y = 2x^{2} - 7x - 3\)
Gradient = \(\frac{\mathrm d y}{\mathrm d x} = 4x - 7\)
Gradient at x = 1 : \(4(1) - 7 = 4 - 7 = -3\).
(d) \(2x^{2} - 7x - 5 = x + 4\)
\(2x^{2} - 7x - 5 + 2 = x + 4 + 2\)
\(2x^{2} - 7x - 3 = x + 6\)
\(\implies y = x + 6\)
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| y | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
From the graph, x = -0.9 or 5.

