(a) 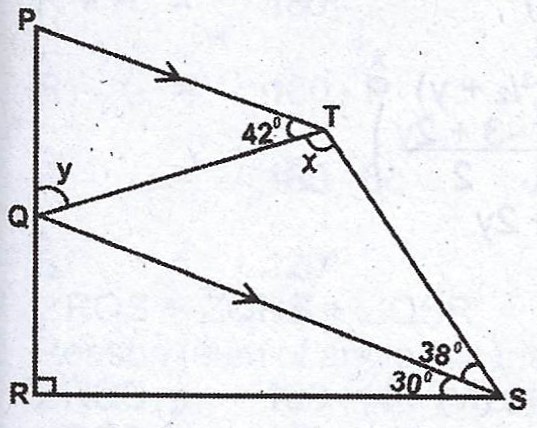
In the diagram, PQRST is a quadrilateral. PT // QS, < PTQ = 42°, < TSQ = 38° and < QSR = 30°. If < QTS = x and < POT = y, find: (i) x ; (ii) y. (SEE THE DIAGRAMS ABOVE)
(b) 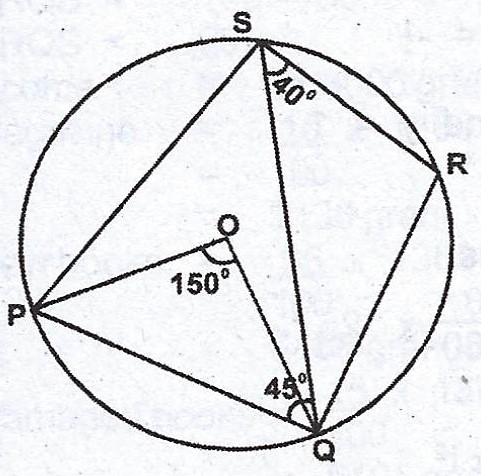
In the diagram, PQRS is a circle centre O. If POQ = 150°, < QSR = 40° and < SQP = 45°, calculate < RQS.
Explanation
(a)(i) < PTS = 38° (alternate angle)
42° + x + 38° = 180° (angles on a straight line)
80° + x = 180°
x = 180° - 80° = 100°
(ii) < SQT = 42° (alternate angle)
< SQR = 60° (sum of angles in a triangle)
y + 42° + 60° = 180° (angle on a straight line)
y + 102° = 180°
y = 180° - 102° = 78°
(b) \(< QSP = \frac{150}{2}\) (angle at the centre is twicw angle at the circumference)
\(< QSP = 75°\)
\(\hat{R} + \hat{P} = 180°\) (opposite angles in a cyclic quad are supplementary)
\(\hat{P} + 75° + 45° = 180°\) (sum of angle in a triangle)
\(\hat{P} = 180° - 120°\)
\(\hat{P} = 60°\)
\(\hat{R} + \hat{P} = 180°\)
\(\hat{R} = 180° - 60°\)
\(\hat{R} = 120°\)
\(< RQS + < QRS + < QSR = 180°\) (sum of angle in a triangle)
\(< RQS = 180° - (40° + 120°)\)
= \(180° - 160°\)
\(< RQS = 20°\)

