(a) P varies directly as Q and inversely as the square of R. If P = 1 when Q = 8 and R = 2, find the value of Q when P = 3 and R = 5.
(b) An aeroplane flies from town A(20°N, 60°E) to town B(20°N, 20°E). (i) if the journey takes 6 hours, calculate, correct to 3 significant figures, the average speed of the aeroplane. (ii) if it then flies due North from town B to town C, 420 km away, calculate correct to the nearest degree, the latitude of town C. [Take radius of the earth = 6400 km and \(\pi\) = 3.142].
Explanation
(a) \(P \propto Q\) and \(P \propto \frac{1}{R^{2}}\).
\(P \propto \frac{Q}{R^{2}} \implies P = \frac{kQ}{R^{2}}\)
When P = 1, Q = 8, R = 2
\(1 = \frac{8k}{2^{2}} \implies 8k = 4\)
\(k = \frac{4}{8} = 0.5\)
\(P = \frac{Q}{2R^{2}}\)
When P = 3, R = 5, Q = ?
\(3 = \frac{Q}{2(5^{2})}\)
\(3 = \frac{Q}{50} \implies Q = 150\).
(b) 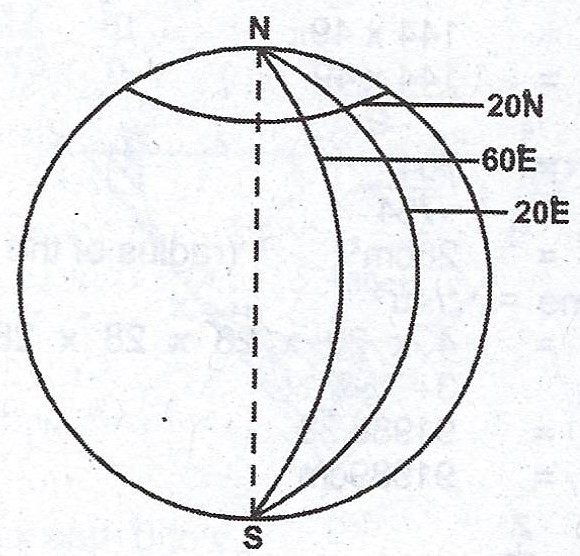
Angular difference : 60° - 20° = 40°
\(\frac{\theta}{360} \times 2\pi r \)
\(r = R\cos \theta\)
\(\frac{40}{360} \times 2 \times 3.142 \times 6400 \cos 20 = \frac{1511687.278}{360}\)
= \(4199.13 km\)
\(Speed = \frac{Distance}{Time}\)
= \(\frac{4199.13}{6}\)
= \(699.85 km/hr\)
\(\approxeq 700 km/hr\) (to 3 significant figures)
(ii) \(D = \frac{\theta}{360} \times 2\pi r\)
\(420 = \frac{\theta}{360} \times 2 \times 3.142 \times 6400\)
\(\theta = \frac{420 \times 360}{2 \times 3.142 \times 6400}\)
\(\theta = \frac{151200}{40217.6} = 3.76°\)
Latitude of C : 20° + 3.76° = 23.76°
Note that due North implies same longitude but different latitude.

