A trapezium PQRS is such that PQ // RS and the perpendicular P to RS is 40 cm. If |PQ| = 20 cm, |SP| = 50 cm and |SR| = 60 cm. Calculate, correct to 2 significant figures, the
(a) Area of the trapezium ; (b) < QRS.
Explanation
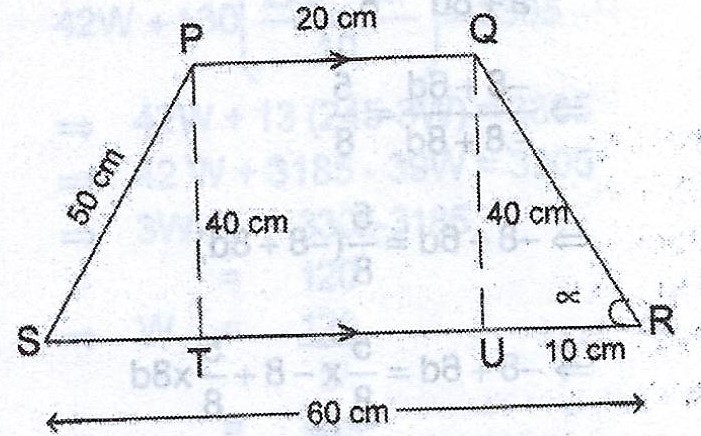
(a) Area of trapezium PQRS = \(\frac{1}{2}(PQ + RS) \times 40\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}(20 + 60) \times 40\)
= \(40 \times 40\)
= \(1600 cm^{2}\)
(b) In \(\Delta\) SPT,
\(|SP|^{2} = |ST|^{2} + |TP|^{2}\) (Pythagoras theorem)
\(|ST|^{2} = |SP|^{2} - |TP|^{2}\)
= \(50^{2} - 40^{2}\)
= \(2500 - 1600\)
\(|ST|^{2} = 900\)
\(\therefore |ST| = 30 cm\)
\(|UR| = 60 cm - (30 + 20) cm\)
= 10 cm
Let < QRS = \(\alpha\),
\(\tan \alpha = \frac{40}{10} = 4\)
\(\alpha = \tan^{-1} (4)\)
= \(75.96° \approxeq 76°\)

