an electric cell with nominal voltage E has a resistance of 3Ω connected across it. If the voltage falls to 0.6E, the internal resistance of the cell is
The correct answer is: B
Explanation
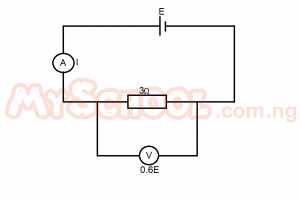
IR = 0.6 X I ( R + r )
I X 3 = 0.6 X I ( 3 + r )
3I / 0.6I = 3 + r
5 = 3 + r
r = 2 ohms


