(a)(i) By means of a labelled diagram, describe the mode uf operation of a modern X-ray tube.
(ii) State the energy transformation which takes place during the operation.
(b) Explain the terms hardness and intensity as applied to X-rays
(c)(i) State three uses of X-rays
(ii) State one hazard of over-exposure to X-rays in a radiological laboratory, indicating two safety precautions.
(a) Explain the terms reactance and impedance in an a.c circuit.
(b) A source of e.m.f. 240 v and frequency 50 Hz is connected to a resistor, an inductor and a capacitor in series. When the current in the capacitor is 10A, the potential difference across the resistor is 140V and that across the inductor is 50V. Draw the vector diagram of the potential difference across the inductor, the capacitor and the resistor.
Calculate the (i) potential difference across the capacitor; (ii) capacitance of the capacitor; (iii) inductance of the inductor.
(a) Distinguish between temperature and heat. State the units in which they are measured
(ii) State two physical properties used for measuring temperature.
(b) (i) Describe, with the aid of a diagram, how the upper fixed point is determined for a mecury-in-glass thermometer. State one precaution to ensure accurate results
(ii) State one advantage which a constant-volume gas thermometer has over other thermometers and one reason why it is seldom used as an everyday laboratory instrument.
(c) Using the kinetic theory of matter explain why evaporation causes cooling.
(a) Explain the terms:- uniform acceleration and average speed.
(b) A body at rest is given an initial uniform acceleration of 8.0ms\(^{-2}\) for 30s after which the acceleration is reduced to 5.0ms\(^{-2}\) for the next 20s. The body maintains the speed attained for 60s after which it is brought to rest in 20s. Draw the velocity-time graph of the motion using the information given above.
(c) Using the graph, calculate the: (i) maximum speed attained during the motion; (ii) average retardation as the body is being brought to rest; (iii) total distance travelled during the first 50s; (iv) average speed during the same interval as in (ii).
Which of the following has the highest surface tension?
- A. cold water
- B. soapy water
- C. warm water
- D. oily water
- E. salty water
The work function of a metal is 4.65ev and the metal is illuminated with a radiation of 6.86ev. What is the kinetic energy of the electrons ejected from the surface of the metal?
- A. 1.48ev
- B. 2.21ev
- C. 4.42ev
- D. 5.75ev
- E. 11.51ev
The half-life of a radioactive substance is 2 seconds. Calculate the decay constant
- A. 0.035s-1
- B. 0.151s-1
- C. 0.347s-1
- D. 0.576s-1
- E. 1.386s-1
An electron charge 1.6 x 10-19C is accelerated in vacuum from rest at zero volt towards a plate at 40k V. Calculate the kinetic energy of the electron
- A. 4.0 x 10-26J
- B. 4.0 x 10-21J
- C. 6.4 x 10-20J
- D. 3.2 x 10-15J
- E. 2.5 x 10-20J
When a metal surface is irradiated, photoelectrons may be ejected from the metal. The kinetic energy of the ejected electrons depends on the
- A. sorce of the radiation
- B. intensity of the radiation
- C. detection device for the electrons
- D. amplitude of the radiation
- E. frequency of the radiation
plane as 63cm of HG while a ground observer records a reading of 75cm of Hg with his barometer. assuming that the density of air is constant, calculate the height of the plane above the ground. (Take the relative densities of air and mecury as 0.00136 and 13.6 respectively
- A. 120m
- B. 138m
- C. 1200m
- D. 274m
- E. 120,000m
Which of the following statements is not correct? Isotopes of an element have
- A. the same number of electric charges on the nucleus
- B. the same chemical properties
- C. different nucleon numbers
- D. different proton numbers
- E. different atomic masses
Which of the following statements above viscosity are correct? when a ball falls through a viscous liquid i. viscosity opposes the gravitational force on the ball. ii. viscosity opposes the upthrust on the ball. iii. viscosity is in the same direction as the upthrust on the ball. iv. as the ball falls faster the more viscous the liquid is
- A. i and iii only
- B. i and ii only
- C. ii and iv only
- D. iii and iv only
- E. i, ii and iv only
An induction coil is generally used to?
- A. rectify an alternating current
- B. produce a large input voltage
- C. smoothen a pulsating direct current
- D. modulate an incoming signal
- E. produce a large output voltage

The diagram above shows a current carrying wire between the poles of a magnet. In which direction would the wire tend to move?
- A. into the paper
- B. out of the paper
- C. towargs the north pole of the magnet
- D. towards the south pole of the magnet
- E. towards the top of the pages
A house is supplied with a 240V a.c mains. To operate a door bell rated at 8v, a transformer is used if the number of turns in the primary coil of the transformer is 900. calculate the number of turns in the secondary coil of the transformer
- A. 30
- B. 240
- C. 248
- D. 450
- E. 1248

In the circuit above R is a resistor whose resistance increases with an increase in temperature. L1 and L2 are identical lamps. If the temperature of R increases
- A. L1 becomes brighter and L2 becomes dimmer
- B. L1 becomes brighter and L2 does not change
- C. L2 becomes dimmer and L1 does not change
- D. L1 becomes dimmer and L2 does not change
- E. L1 and L2 becomes brighter
A 90W immersion heater is used to supply energy for 5 minutes. The energy supplied is used to completely melt 160g of a solid at its melting point. Calculate the specific latent heat of the solid.
- A. 2.81jg-1
- B. 6.25Jg-1
- C. 8.89Jg-1
- D. 168.75Jg-1
- E. 5333.33Jg-1
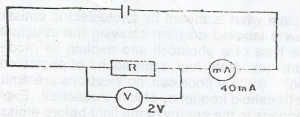
Using the data in the circuit illustrated above, calculate the value of R
- A. 0.02\(\Omega\)
- B. 0.05\(\Omega\)
- C. 5.00\(\Omega\)
- D. 20.00\(\Omega\)
- E. 50.00\(\Omega\)
Which of the following is stored by dry Leclanche cell?
- A. chemical energy
- B. nuclear energy
- C. solar energy
- D. heat energy
- E. electrical energy

In which of the points labelled A, B, C, D and E on the conductor shown would electric charge tend to concentrate most?
- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. D
- E. E


