(a) Explain what is meant by photoelectric emission
(b) Draw a labelled diagram showing the structure of a simple type of a photocell and explain its mode of operation.
(c) State four applications of photoelectric emission.
(d) In a photocell, no electrons are emitted until the threshold frequency of light is reached. Explain what happens to the energy of the light before emission of electrons begins. State one factor that may affect the number of emitted electrons.
(a) Draw a simple labelled diagram illustrating the principle of a step-down transformer and explain how it works
(b) State three ways by which energy is lost in a transformer and how they can be minimized.
(c) If a transformer is used to light a lamp rated at 60W, 220V from a 4400V a.c. supply, calculate the; (i) ratio of the number of turns of the primary coil to the secondary coil in the transformer (ii) current taken from the main circuit if the efficiency of the transforme is 95%.
(a)(i) What is meant by resonance?
(ii) Outline the necessary steps taken in a simple experiment to illustrate top resonance
(iii) Explain why a vibrating tuning fork sounds louder when its stem is pressed against a table top than when held in air.
(b) Explain with the aid of diagrams, how a concave mirror could be used to: (i) Ignite a piece of carbon paper; (ii) produce an exact copy of a picture on a screen.
(a) Explain what is meant by the following statement. The specific latent heat of fusion of ice is \(3.4 \times 10^{5}Jkg^{-1}\).
(b) Describe an experiment to determine the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. State two precautions necessary to obtain an accurate result.
(c) Using the kinetic theory of matter, explain why ice can change to water at 0°C without any change in temperature.
An electric string of length l is elastically stretched through a length e by a force F. The area of cross- section of the string is A and its Young’s modulus is E. Which of the following expressions is correct?
- A. F = EA/eI
- B. F = EAI/e
- C. F = EAe/l
- D. F = EAe
The process by which a metal, heated to high temperature, gives off electrons from its surface is known as
- A. photoelectric emission
- B. thermionic emission
- C. radioactive emission
- D. Held emission
- E. secondary emission
A sheet of paper is placed in the path of a beam of radiations from a radioactive source. Which of the following radiations will pass through the paper?I. Alpha rays II. Beta rays III. Gamma rays
- A. I only
- B. II only
- C. III only
- D. II and III only
- E. I, II and III
When the nucleus of a uranium atom is split into two fragments of nearly equal mass the sum of the masses of the fragments is less than the mass of the original nucleus. This difference is a measure of the
- A. experimental error in calculating the separate masses
- B. change of momentum of each fragment
- C. potential energy lost
- D. nuclear energy released
- E. kinetic energy lost
An element whose half-life is 3 years has N atoms. How many atoms would have decayed after 9 years
- A. 1 N atoms8
- B. 1 N atoms3
- C. 2 N atoms3
- D. 5 N atoms6
- E. 7 N atoms8

A stream of alpha particles is projected into an electric field between two plates X and Y as shown in the diagram above. Which of the following is correct? The particles are
- A. accelerated and they continue in a straight line
- B. directionally reversed at the end of the plates
- C. deflected towards plate Y
- D. attracted by both plates
- E. deflected towards plate X.
Which of the following gives rise to the line spectra obtained from atoms?
- A. Kinetic energy of a moving atom
- B. Potential energy of an electron inside an atom
- C. Change of an electron from a higher to a lower energy level in the atom
- D. Disturbed proton in the nucleus
- E. Excitation of an electron in the atom
Which of the following statements is correct about cathode rays? They are fast moving
- A. atoms
- B. ions
- C. neutrons
- D. protons
- E. electrons
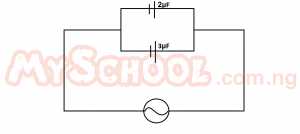
lf the frequency of the a.c. circuit illustrated is 500Hz/ π what would be the reactance in the circuit?
- A. 0.01Ω
- B. 190.91 Ω
- C. 200.00 Ω
- D. 795.46 Ω
- E. 1000.00Ω
What is the electric potential at a point distance r from a proton of charge q placed in a medium of permittivity εo?
- A. q2/4πεor2
- B. q/4πεor2
- C. q2/4πεor
- D. q/4πεor
- E. 4πεoq2r

The diagrams above show lines of force in electric fields. In which of the diagrams would a positive test charge experience the least force as it moves from x to y?
- A. I only
- B. II only
- C. III only
- D. I and II only
- E. II and III only
Calculate the energy stored in 20μF capacitor if the potential difference between the plates is 40 V.
- A. 3.2 x10-2J
- B. 1.6x102J
- C. 8.0x10-4J
- D. 4.0x10-4J
- E. 2.0x10-4J
Which of the following statements is not correct?
- A. A magnetic Held is a region where a magnetic force can be detected.
- B. Magnetic fields are scalar quantities.
- C. The magnitude of the magnetic force experienced by a moving charge depends on the speed on the charge.
- D. the angle between the direction of the earth’s magnetic held and the horizontal is called the angle of dip.
- E. Iron filings can be used to trace out the magnetic field around a bar magnet.
Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction states that
- A. electromotive force is induced in a circuit whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with the circuit
- B. the induced current in a conductor is in such a direction as to oppose the change producing it
- C. the induced e.m.f. in a circuit is proportional to the rate of change of number of lines of force linking the circuit
- D. a force is exerted on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field
- E. the induced e.m.f. is proportional to the current producing the magnetic flux.
Calculate the time in which 4.8 kJ of energy would be expended when an electric heater of resistance 1.8 x 103Ω is used on a 240 V mains supply. (Neglect heat losses to the surrounding).
- A. 150.0s
- B. 90.0s
- C. 36.0s
- D. 20.0s
- E. 2.7s.
In a domestic circuit, electrical appliances and lamps are arranged in parallel across the mains so as to enable the
- A. same current to flow through the electrical appliances and the lamps
- B. maximum energy to be consumed at least cost
- C. same fuse to be used for the electrical appliances and the lamps
- D. voltage across the appliances not to be affected when the lamps are switched on and off
- E. heat losses to be minimized
Calculate the length of a constantan wire of cross- sectional area 4 π x 10-8m2 and resistivity 1.1 x 10-6 Ω m required to construct a standard resistor of resistance 21 Ω. [Take π = 22/7]
- A. 0.42m
- B. 2.40 m
- C. 6.25 m
- D. 183.75 m
- E. 590.00 m


