(a) Explain the following, illustrating your answer with one example in each case: (i) nuclear fusion: (ii) nuclear fission: (iii) radiation hazards.
(b) State two advantages of fusion over fission and explain briefly why, in spite of these advantages, fusion is not normally used for the generation of power.
(c) The current, I in an a.c. circuit is given by the equation: \(I = 30 sin 100\pi t\), where t is the time in seconds. Deduce the following from this equation: (i) frequency of the current (ii) peak value of the current, (iii) r.m.s value of the current.
(a) State the laws of electromagnetic induction.
(b) Draw a labelled diagram of a simple d.c. generator and explain how it works.
(c) State three methods by which higher e.m.f. could be obtained from the generator.
(a) With the aid of a labelled diagram, describe an experiment to illustrate the relationship between the volume and the temperature of a given mass of air at constant pressure.
(b) A uniform capillary tube of negligible expansivity sealed at one end, contains air trapped by a pellet of mercury. The trapped air column is 13.7cm long at 0°C and 18.7cm long at 100°C. Calculate the cubical expansivity of the air at constant pressure.
(c) Using the kinetic theory of gases, explain why the volume of a fixed mass of gas at constant pressure increases with increase in temperature.
(a)(i) Explain what is meant by a machine (ii) Define the terms: mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency as applied to a machine. Derive the equation connecting the three terms.
(b) Explain why the efficiency of a machine is usually less than 100%
(c) A screw jack whose pitch is 4.4mm is used to raise a body of mass 8000 kg through a height of 20cm. The length of the tommy bar of the jack is 70cm. If the efficiency of the jack is 80%, calcuate the: (i) velocity ratio of the jack; (ii) mechanical advantage of the jack (iii) effort required in raising the body, (iv) work done by the effort in raising the body \((g = 10ms^{-2}; \pi = \frac{22}{7}\))
Which of the following are emitted from a radioactive substance without altering either the nucleon number or the proton number of the substance?
- A. Gamma rays
- B. Alpha particles
- C. Beta particles
- D. Protons
- E. Neutrons
When an atom is in the ground state, it is said to be
- A. grounded
- B. excited
- C. stable
- D. ionized
- E. radiating
Eight or – particles and size B – particles are emitted from an atom of 92238U before it achieves stability. What is the nucleon number of the final product in the chain reaction?
- A. 206
- B. 234
- C. 238
- D. 240
- E. 252
According to the kinetic theory of gases the collision
of the molecules of a gas with the wall of the container
is mainly responsible for the l. temperature of the
gas ll. viscosity of the gas Ill. pressure of the gas
Which of the statements above is/are correct?
- A. I only
- B. II only
- C. III only
- D. II and III only
- E. I, II and III.
Which of the following is used a nuclear reactor to slow down fast moving neutrons?
- A. Carbondioxide gas
- B. Liquid sodium metal
- C. Concrete shield
- D. Graphite rods
- E. Boron rods
A radioactive substance has a half-life of 20 hours. What fraction of the original radioactive nuclide will remain after 80 hours?
- A. 1/32
- B. \(\frac{1}{16}\)
- C. \(\frac{1}{8}\)
- D. \(\frac{1}{4}\)
- E. \(\frac{1}{2}\)
The phenomenon of radioactivity was first discovered by
- A. Marie Curve
- B. Sir J.J Thomson
- C. Henn Becquerel
- D. Niels Bohr
- E. Enrico Fermi
lf Einstein’s photoelectric equation is represented by hf – W = Φ where h is Planck’s constant, f the frequency of incident radiation and W the work function of the material, what does the symbol Φ up stand for?
- A. Energy of the photons
- B. Maximum Kinetic energy of the ejected electrons
- C. Threshold frequency of the photons
- D. Stopping potential of the electrons
- E. Velocity of the electrons
| 24 Na → | 24 mg4 + X + energy |
|---|---|
| 11 | 2 |
The equation above represents a nuclear decay of sodium isotope. What is X?
- A. Alpha particle
- B. Beta particle
- C. Gamma ray
- D. X-ray
- E. Neutron
How long does it take a 750 W heater operating at full rating to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water from 40oC to 70oC? (Take the specific heat capacity of water as 4200 J kg-1 K-1 and neglect heat losses).
- A. 84s
- B. 112s
- C. 168s
- D. 280s
- E. 616s
What amount of current would pass through a 10 Ω coil if it takes 21s for the coil to just melt a lump of ice of mass 10g at 0oC if there are no heat losses? (Latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 Jg\(^{-1}\)).
- A. 16.00A
- B. 4.00 A
- C. 0.50A
- D. 0.25A
- E. 0.06 A
Electric motor primarily converts
- A. electrical energy into chemical energy
- B. electrical energy into heat energy
- C. kinetic energy into potential energy
- D. electrical energy into mechanical energy
- E. mechanical energy into light energy
When a potential difference, V is applied across the ends of a resistor of resistance, R a Current, l passes through the resistor. The heat generated in the resistor in time, t is given by the expression
- A. V2lt
- B. I2t/R
- C. l2Rt
- D. lR2tR
- E. V2Rt
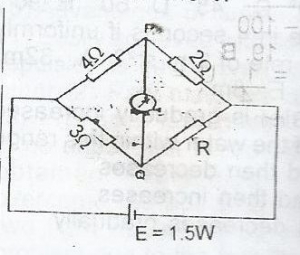
ln the diagram below, the galvanometer indicates a null-deflection. What is the potential difference between P and Q?
- A. 0.0 V
- B. 1.5 V
- C. 2.0 V
- D. 3.0V
- E. 4.0 V.
Which of the following is not a conductor of electricity?
- A. Human body
- B. Glass
- C. Silver
- D. Earth
- E. Copper
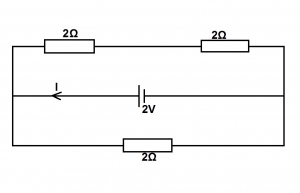
Calculate the current, I in the diagram shown above.
(Neglect the internal resistance of the cell)
- A. 4.0A
- B. 2.0A
- C. 1.0A
- D. O.5A
- E. 0.1A.
Electrical resistance is the property of an electrical conductor that causes electrical energy to be converted into
- A. mechanical energy
- B. solar energy
- C. heat energy
- D. magnetic energy
- E. chemical energy.


