(a) Define the boiling it of a liquid.
(b) Describe with the a d. labelled diagram, an experiment to determire the boiling point of a small quantity of a liquid.
(c) factors that may affect the boiling point of a liquid
(d) Using the kinetic theory of matter, explain why pure water changes to steam at S.T.P. without any change in temperature, although heat is being supplied to the water.
(a) What is surface tension? Explain the phenomenon in terms of intermolecular forces
(b) Describe a simple experiment to demonstrate the surface tension of a liquid
(c) State three examples to illustrate the effects of surface tension
(d) Why does water wet a clean glass surface whereas mercury does not?
(e) State two methods by which the surface tension of a liquid may reduced.
(a) State Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
(b) Draw a labelled diagram of an induction coil and explain how it works.
(c) How is the effect of eddy currents minimized in the coil?
(d) State two reasons why a capacitor should be included in the primary circuit of the coil.
(e) State three uses of an induction coil.
(a) Explain what is meant by acceleration of free fall due to gravity, g.
(b) State two reasons why g varies on the surface of the earth
(c) A stone is projected upwards at an angle of 30° to the horizontal from the top of a tower of height 100 m and it hits the ground at a point Q. If the initial velocity of projection is 100ms\(^{-1}\), calculate the
(i) maximum height of the stone above the ground;
(ii) time it takes to reach this height;
(iii) time of flight
(iv) horizontal distance from the foot of the tower to the point Q. (Neglect air resistance and take g as 10m\(^{-2}\))
Which of the following is used for shielding radioactive fall-outs?
- A. Plastic
- B. Wood
- C. Textile
- D. Aluminium
- E. Lead
Which of the following cannot be explained by the molecular theory of matter?
- A. Conduction
- B. Radiation
- C. Convection
- D. Evaporation
- E. Expansion
Which of the following is not a product of nuclear fission?
- A. Alpha particle
- B. Beta particle
- C. Gamma ray
- D. X-ray
- E. Neutron
Which of the following are emitted from a radioactive substance without altering either the nucleon number or the proton number of the substance?
- A. Protons
- B. Neutrons
- C. Gamma rays
- D. Beta particles
- E. Alpha particles
A moving-coil meter with an internal resistance of 100 Ω has a full-scale deflection when a current of 10 mA flows through it. What value of resistance would convert it to read 10 V at full-scale deflection?
- A. 20
- B. 100
- C. 600
- D. 900
- E. 1000
A radioactive nuclide of mass 6.09 has a half-life of 8 days. Calculate the time during which 5.25g of the nuclide would have decayed
- A. 1 day
- B. 2 days
- C. 8 days
- D. 24 days
- E. 42 days.
Which of the following statements are not true of a moving-coil milliammeter? I. It can be used to measure alternating current II. It has a linear scale III. It can be adapted to read higher values of currents IV. A resistor connected in parallel with the milliammeter would convert it to a voltmeter
- A. I and IV only
- B. II and III only
- C. III and IV only
- D. I, II and III only
- E. I, III and IV only
A cell of e.m.f 1.5V and internal resistance 2.552 is connected in series with an ammeter resistance 0.50 and a load of resistance 7.00. Calculate the current in the circuit
- A. 0.15A
- B. 0.20A
- C. 2.1OA
- D. 3.00A
- E. 6.67A
Which of the following is a wind instrument?
- A. Guitar
- B. Organ
- C. Violin
- D. Piano
- E. Harp

Calculate the current in the 30 resistor in the diagram above if the battery is of negligible internal resistance
- A. 0.3A
- B. 0.4A
- C. 1.0A
- D. 1.5A
- E. 2.5A
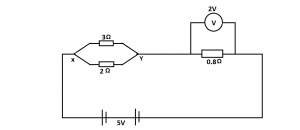
What is the potential difference between X and Y in the diagram above if the battery is of negligible internal resistance
- A. 12.5V
- B. 5.8V
- C. 5.0V
- D. 3.0V
- E. 2.0V

An alternating current, having the waveform shown in the diagram above, is represented by the equation x = Xo sinwt. Which of the following represents Xo?
- A. OS
- B. OR
- C. PQ
- D. RT
- E. OT
Calculate the quantity charge flowing through a conductor if a current of 10A passes through the conductor for 10s.
- A. 100C
- B. 20C
- C. 15C
- D. 10C
- E. 1C
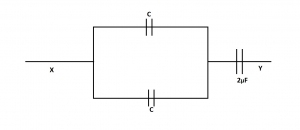
The effective capacitance between points X and Y in the diagram below is 1.0μF, What is the value of the capacitance C, measured in micro-farad?
- A. 5.0μF
- B. 4.0μF
- C. 3.0μF
- D. 1.0μF
- E. 0.5μF
The energy stored in a capacitor of capacitance 5μF is 40J. Calculate the voltage applied across its terminals?
- A. 4000V
- B. 200V
- C. 16V
- D. 6V
- E. 4V
A capacitor of capacitance 25μF is connected to an a.c. power source of frequency 200 Hz. Calculate the reactance of the capacitor
- A. 0.01
- B. 0.02
- C. 50.00
- D. 100.00
- E. 200.00.
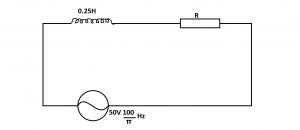
If the current in the resistor R in diagram above is 0.05A, calculate the p.d. across the inductor.
- A. 2.5V
- B. 25.0V
- C. 49.0V
- D. 50.0V
- E. 250.0V


