(a) Explain the following terms:
(i) viscosity;
(ii) terminal velocity.
(b)(i) Describe an experiment to determine the terminal velocity of a steel ball falling through a jar of glycerine..
(ii) State two precautions that should be taken to ensure accurate result.
(c) State two
(i) effects of viscosity
(ii) applications of viscosity.
(a) Explain what is meant by the statement: The capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is 2\(\mu\)F
(b) State: (i) three factors on which its capacitance depends
(ii) three uses of capacitors.
(c) Derive a formula for the energy W stored in a charged capacitor of capacitance C carrying a charge Q on either plate.,
(d) Two parallel-plate capacitors of capacitances 2\(\mu\)F and 3\(\mu\)F are connected in parallel and the combination is connected to a 50V d.c. source. Draw the circuit diagram of the arrangement and determine the:
(i) charge on either plate of each capacitor
(ii) potential difference across each capacitor
(iii) energy of the combinad capacitors.
(a) What is meant by dispersion of white light?
(b) State the colours in the spectrum of white light in ascending order of their wavelengths
(c) Which colour is deviated.
(i) least
(ii) most?
(d) Explain why white light is dispersed when it passes through a glass prism.
(e) Describe, with the aid of a labelled diagram, how a pure spectrum of white light can be produced on a screen.
(a) Define the apparent cubic expansivity of a liquid
(b)(i) Describe with the aid of a labelled diagram, an experiment to determine the apparent cubic expansivity of a liquid.
(ii) State two precuations that should be taken to ensure accurate results.
(c) A density glass bottle contains 44.25g of a liquid at 0°C and 42.02g at 50°C. Calculate the real cubic expansivity of the liquid. (Linear expansivity of glass = 1.0 x 10-5K\(^{-1}\))
The count rate of an alpha-particle source is 400 per minute. If the half-life of the source is 5 days, what would be the count rate per minute after 15 days?
- A. 20
- B. 25
- C. 50
- D. 200
- E. 400
Which of the following particles/rays do not originate from the nucleus of an atom?
- A. Alpha particles
- B. Beta particles
- C. Neutrons
- D. Gamma rays
- E. X-rays
Which of the following is used in a nuclear reactor to slow down fast-moving neutrons?
- A. Carbondioxide gas
- B. Liquid sodium metal
- C. Concrete shield
- D. Graphite rods
- E. Boron rods
Which of the following is used in a nuclear reactor to slow down fast-moving neutrons?
- A. Carbondioxide gas
- B. Liquid sodium metal
- C. Concrete shield
- D. Graphite rods
- E. Boron rods
Which of the following is not part of the electromagnetic spectrum?
- A. Radio wave
- B. Gamma ray
- C. Infra-red ray
- D. Alpha particle
- E. X-ray.
Which of the following substances is most viscous at room temperature?
- A. Water
- B. Alcohol
- C. Petrol
- D. Palm oil
- E. Kerosine
What is the decay constant of a radioactive element whose half-life is 3 seconds
- A. 0.132s-1
- B. 0.23s-1
- C. 0.347s-1
- D. 0.693s-1
- E. 0.924s-1
The resistance in a series R-C circuit is 5 Ω. If the impedance of the circuit is 13 Ω, calculate the reactance of the capacitor
- A. 65 Ω
- B. 18 Ω
- C. 16 Ω
- D. 14 Ω
- E. 12 Ω
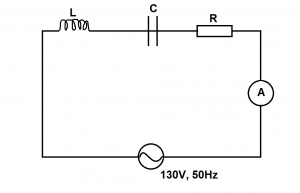
ln the diagram above, the resistor has a resistance 8 Ω while the reactances of the inductor and the capacitor are 10 Ω and 16 Ω respectively Calculate the current in the circuit
- A. 3.6A
- B. 3.8A
- C. 9.2A
- D. 10.0A
- E. 13.0A
Calculate the amount of heat generated in an external load of resistance 8Ω if an alternating current of peak value 5A is passed through for 100s.
- A. 20,000J
- B. 10,000J
- C. 5,000J
- D. 4,000J
- E. 200J
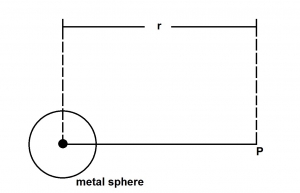
The electric potential at point P in the diagram above can be expressed as
- A. Q2/(4πεor2)
- B. Q/(4πεor2)
- C. Q/(4πεor)
- D. Q2/(4πεor2)
- E. Q/(4πεor) 2
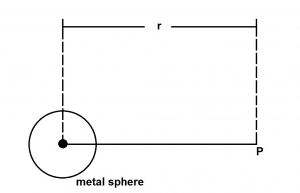
The diagram above illustrates an isolated metal sphere carrying charge W in a medium whose permittivity is so. The magnitude of the electric field intensity at P can be expressed as
- A. Q2/(4πεor2)
- B. Q/(4πεor2)
- C. Q/(4πεor)
- D. Q2/(4πεor2)
- E. Q/(4πεor) 2
Soft iron is used in making the armature of an electric bell because it
- A. retains its magnetism for a longtime
- B. Loses its magnetism readily
- C. Produces permanent magnets
- D. is not easily magnetised
- E. decreases the magnetic effect of a direct current
A cell of e.m.f. 1.5V is connected in series with a resistor of resistance 39. A high-resistance voltmeter connected across the cell registers only 0.9V. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell
- A. 1.85Ω
- B. 2.0Ω
- C. 2.4Ω
- D. 4.5Ω
- E. 5.0Ω
Lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction states that
- A. e.m.f. is induced in a circuit whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with the circuit.
- B. the induced current in a conductor is in such a direction as to oppose the change producing it
- C. the magnitude of the induced e.m.f. in a circuit is proportional to the rate of change of the number of lines of force linking the circuit
- D. a force is exerted on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic Held
- E. the induced charge is constant for a fixed change of flux.
A wire of length 100cm and cross-sectional area of 2.0 x 10-3cm2 has a resistance of 0.10 Ω. Calculate its electrical conductivity.
- A. 5.0 x 107Ω-1cm-1
- B. 5.0 x 106Ω-1cm-1
- C. 2.0 x 106Ω-1cm-1
- D. 5.0 x 105Ω-1cm-1
- E. 2.0 x 106Ω-1cm-1
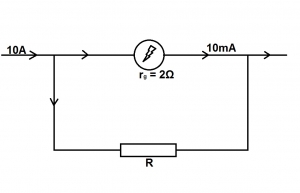
The diagram above illustrates the conversion of a galvanometer of resistance 29 to an ammeter. The galvanometer gives a full-scale deflection for a current of 10mA. Calculate the value of R.
- A. 2.0 x 103 Ω
- B. 2.0 x 102 Ω
- C. 2.0 x 10-1 Ω
- D. 2.0 x 10-2 Ω
- E. 2.0 x 10-3 Ω


