Water boils at a lower temperature when heated at the top of a mountain than at sea-level because at the top of the mountain the
- A. saturation vapour pressure of water is higher than at sea-level
- B. sun adds more heat to the water
- C. temperature is lower than at sea- level
- D. relative humidity of the atmosphere is lower
- E. pressure of the atmosphere is lower
Cloud formation is the direct result of
- A. precipitation
- B. vaporization
- C. fusion
- D. sublimation
- E. condensation
The saturated vapour pressure of a liquid increases as the
- A. volume of the liquid increases
- B. volume of the liquid decreases
- C. temperature of the liquid increases
- D. temperature of the liquid decreases
- E. mass of the liquid decreases
The inside of a vacuum flask is usually coated with silver to reduce heat lost by
- A. convection
- B. conduction
- C. radiation
- D. absorption
- E. evaporation
The heating element in an electric kettle is usually located near the bottom of the kettle because
- A. water is a good conductor of heat
- B. heat can be more quickly radiated to all parts of the water
- C. no heat can be lost to the surroundings
- D. the convectional currents which are set up can carry heat to all parts of the water
- E. the molecules of the heating element can carry heat to all parts of the water.
What is the difference in the amount of heat given out by 4kg of steam and 4kg of water when both are cooled from 100oC to 80oC? (Specific latent heat of steam = 2.260,000J kg-1) (Specific heat capacity of water =4,200 J kg-1)
- A. 336,000J
- B. 672,000J
- C. 8,704,000J
- D. 9,040,000J
- E. 9,376,000J
A 400W immersion heater is used to heat a liquid of mass 0.5kg. lf the temperature of the liquid increases by 2.5oC in one second, calculate the specific heat capacity of the liquid (Neglect heat losses to the surroundings)
- A. 80 Jkg-1K-1
- B. 320Jkg-1K-1
- C. 500Jkg-1K-1
- D. 1200J kg-1K-1
- E. 2000J kg-1K-1.
Which of the following statements is not correct?
- A. Heat energy can be transformed into mechanical energy
- B. That total heat content of a body is the sum of the kinetic energies of its molecules
- C. lf a body is heated, its molecules move faster.
- D. lf a body is cooled, molecular movement remains constant.
The pressure of a fixed mass of gas is 2.0 x 105Nm-2 at a known temperature. Assuming that the temperature remains constant, what will be the pressure of the gas if its volume is halved?
- A. 1.0x105Nm-2
- B. 2.0X105Nm-2
- C. 3.0x105Nm-2
- D. 4.0 x105Nm-2
- E. 5.0 x105Nm-2
The linear expansivity of a metal P is twice that of another metal Q. When these materials are heated through the same temperature change, their increase in length is the same. Calculate the ratio of the original length of P to that of Q.
- A. 1:4
- B. 1:2
- C. 2:1
- D. 4:1
- E. 6:1
A platinum-resistance thermometer has a resistance of 5Ω at 0°C and 9Ω at l00°C. Assuming that resistance changes uniformly with temperature, calculate the resistance of the thermometer when the temperature is 45°C.
- A. 13.9 Ω
- B. 8.9 Ω
- C. 6.8 Ω
- D. 3.2 Ω
- E. 1.8 Ω
Two simple pendula x and y make 400 and 500 oscillations respectively in equal time. If the period of oscillation of x is 1.5 seconds, what is the period of oscillation of y?
- A. 0.53s
- B. 0.83s
- C. 1.20s
- D. 1.50s
- E. 1.88s.
A stationary object of mass 4kg is set in motion by a net force of 5ON. If the object attains is speed of 5ms-1 in time. Calculate the value of t.
- A. 0.20s
- B. 0.40s
- C. 0.63s
- D. 0.80s
- E. 1.30s
A body of mass 2kg is suspended from the ceiling of a lift with a light inextensible string. lf the lift moves upwards with acceleration of 2ms-2, calculate the magnitude of the tension in the string (g = 1Oms-2)
- A. 24N
- B. 20N
- C. 16N
- D. 4N
- E. 0N
A body of mass 4.2kg moving with velocity 10ms-1 due east, hits a stationary body of mass 2.8kg. If they stick together after collision and move with velocity V due east, calculate the value of V
- A. 3ms-1
- B. 6ms-1
- C. 7ms-1
- D. 15ms-1
- E. 17ms-1
The magnitude of the force required to make an object of mass M move with speed V in a circular path of radius R is given by the expression.
- A. mr/v
- B. (mr) 2/v
- C. mv2/r
- D. mv/2
- E. mv/r
Two spanners X and Y of lengths 15cm and 20cm respectively are used in turn to give a screw of pitch 2mm one complete rotation. If Rx and Ry are the respective velocity ratios of the spanners then the ratio Rx : Ry is
- A. 1 : 50
- B. 3 : 20
- C. 3:4
- D. 4:3
- E. 20:3
The velocity ratio and efficiency of a system of pulleys are 6 and 80% respectively. How much effort is required to lift a load of mass 120kg with this system? (g=10ms-2)
- A. 25N
- B. 90N
- C. 96N
- D. 250N
- E. 960N
A rocket is launched from the surface of the earth. If the radius of the earth is 6.4 x 106m and the acceleration of free fall due to gravity is 1Oms-1 calculate the escape velocity of the rocket.
- A. 2.53 x 104ms-1
- B. 1.13 x 104ms
- C. 8.00 x 103ms-1
- D. 4.23 x 103ms-1
- E. 6.41 x 104ms-1
A ball of mass 5.0kg hits a smooth vertical wall normally with a speed of 2ms-1 and rebounds with the same speed. Determine the impulse experienced by the ball
- A. 20.0kg ms-1
- B. 10.0kg ms-1
- C. 5.0kg ms-1
- D. 1.3kg ms-1
- E. 0.0kg ms-1.
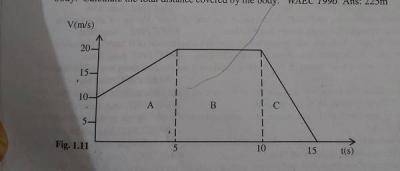
The diagram above illustrates the velocity-time graph of the motion of a body. Calculate the total distance covered by the body
- A. 50m
- B. 65m
- C. 175m
- D. 225m
- E. 300m


