A simple microscope forms an image 10cm from an eye close to the lens. If the object is 6cm from the eye, calculate the focal length of the lens
- A. 3.75cm
- B. 4.00cm
- C. 15.00cm
- D. 16.00cm
A concave mirror can be used to produce a parallel beam of light if a lighted bulb is placed
- A. between its focus and the pole
- B. at its focus
- C. at its centre of curveture
- D. between its focus and centre of curvature
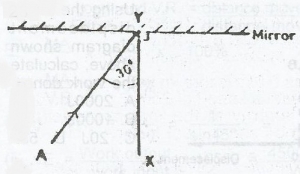
In the diagram above, an incident ray AY makes an angle of 30o with the normal XY. If the mirror is rotated anticlockwise about Y through an angle of 20o, while AY is fixed, what angle will the reflected ray now make with the incident ray?
- A. 70o
- B. 80o
- C. 100o
- D. 120o
A wave has an amplitude equal to 4.0m, angular speed \(\frac{1}{3} \pi\) rads-1 and phase angle \(\frac{2}{3} \pi\) rad. The displacement y of the wave particle is given as
- A. y = 4 sin \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)(t + 2)
- B. y = 4 sin \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)(t + \(\frac{2}{\pi}\)
- C. y = 4 sin \(\frac{\pi}{3} (2t + 1)\)
- D. y = 4 sin \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) (t + 2)
A periodic pulse travels a distance of 20.0m in 1.00s. If its frequency is 2.0 x 103Hz. Calculate the wavelength.
- A. 1.0 x 10-3m
- B. 1.0 x 10-2m
- C. 2.0 x 10-2m
- D. 1.0 x 102m
The temperature at which the saturated vapour pressure of a liquid is equal to the external atmospheric pressure is known as its
- A. dew point
- B. boiling point
- C. lower fixed point
- D. tripple point
The mass of water vapour in a given volume of air is 0.05g at 20oC, while the mass of water vapour required to saturate it at the same temperature is 0.15g. Calculate the relative humidity of the air
- A. 3.33%
- B. 5.55%
- C. 33.33%
- D. 55.55%
A piece of metal of mass 50g is cooled from 80oC to 20oC. Calculate the amount of heat lost. (specific heat capacity of the material of metal = 450Jkg-1K-1)
- A. 4.50 x 103J
- B. 2.25 x 103J
- C. 1.80 x 103J
- D. 1.35 x 103J
The volume and pressure of a given mass of gas at 27oC are 76cm3 and 80cm of mercury respectively. Calculate the volume at s.t.p
- A. 36.2cm3
- B. 72.8cm3
- C. 100.0cm3
- D. 808.9cm3
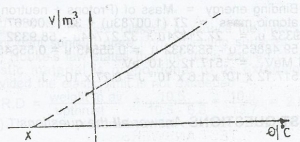
The diagram shows the variation of volume V of a glass with temperature at the point X is
- A. -32oC
- B. -100oC
- C. -273oC
- D. -373oC
The cubic expansivity of mercury is 1.8 x 10-4K-1 and the linear expansivity of glass 8.0 x 10-6K-1, calculate the apparent expansivity of mercury in a glass container
- A. 1.00 x 10-4K-1
- B. 1.56 x 10-4K-1
- C. 1.72 x 10-4K-1
- D. 2.04 x 10-4K-1
Two bodies P and Q, are in thermal equilibrium, which of the following statements about the bodies is correct?
- A. the temperature of Q is higher than that of P
- B. P and Q have the same heat capacty
- C. P and Q have the same mass
- D. P and Q are at the same temperature
A machine of efficiency 80% is used to raise a body of mass 75kg through a vertical height of 3m in 30s. Calculate the power input. (g = 10ms-2)
- A. 9.4W
- B. 60.0W
- C. 75.0W
- D. 93.8W
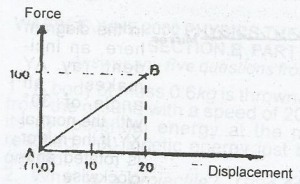
Using the force displacement diagram shown above. Calculate the work done
- A. 2000J
- B. 1000J
- C. 20J
- D. 5J
An inelastic collision takes place between ball of known masses, just before the collision one of the ball is moving with a known velocity while the other is stationary. Which of the following physical quantities can be determined from the information given?
- A. speed of each of the ball after collision
- B. kinetic energy of each ball after collision
- C. total momentum of the ball after collision
- D. total momentum of the two ball after collision
- E. mutual forces excerted by the balls
The period of oscillation of a particle executing simple harmonic motion is 4\(\pi\) seconds. If the amplitude of oscillation is 3.0m. Calculate the maximum speed of the particle.
- A. 1.5ms-1
- B. 3.0ms-1
- C. 4.5ms-1
- D. 6.0ms-1
The bob of a simple pendulum takes 0.25s to swing from its equilibrium position to one extreme end. Calculate its period
- A. 0.25s
- B. 0.50s
- C. 0.75s
- D. 1.00s
The resultant of two forces acting on an object is maximum when the angle between them is?
- A. 180o
- B. 90o
- C. 45o
- D. 0o
A uniform metre rule of mass 90g is provided at the 40cm mark. If the rule is in equilibrium with an unknown mass m placed at the 10cm mark and a 72g mass at the 70cm mark, determine m
- A. 72g
- B. 102g
- C. 298g
- D. 504g
A bus travelling at 15ms\(^{-1}\) accelerates uniformly at 4ms\(^{-2}\), what is the distance covered in 10s?
- A. 150m
- B. 170m
- C. 350m
- D. 600m
The driver of a car moving with uniform speed of 40ms-1 observes a truck approaching from the opposite direction with a speed of 20ms-1. Calculate the speed of the car relative to that of the truck
- A. .5ms-1
- B. 2.0ms-1
- C. 20.0ms-1
- D. 60.0ms-1


