(a)(i) Mention two modes of heat transfer other than convection.
(ii) Explain land and sea breezes.
(b) An iron rod of length 30cm is heated through 50 kelvin. Calculate its increase in length. (linear expansivity of iron = 1.2 x 10\(^{-5}\)K\(^{-1}\)
(c) An electric heater immersed in some water raises the temperature of the water from 40°C to 100°C in 6 minutes. After another 25 minutes, it is noticed that half the water has boiled away. Neglecting heat losses to the surrounding, calculate the specific latent heat of vaporisation of water.
Explanation
(a)(i) Conduction and Radiation.
(ii)

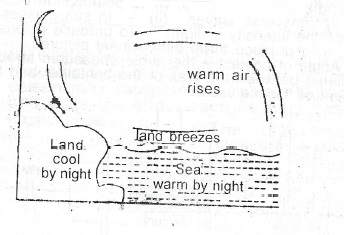
The specific heat capacity of land is less than that of sea. Land Breeze: At night land cools faster than sea, warm air from above the sea rises upward. It's place is taken by cooler air from above the land. Sea Breeze: During the day the land is hotter than the sea. Warm air above land rises, and its place is taken by cooler air from the sea.
(b) Increase in length (L\(_2\) - L\(_1\) = L\(_1 \alpha \Delta \theta = 30 \times 1.2 \times 10^{-5} \times 50 = 1.8 \times 10^{-2}\) cm
(c) Ivt = mc\(\Delta \theta\)
Power x time = mc\(\Delta \theta\)
(i) Iv x 360 = m x c 60 ----(i) Ivt = \(\frac{1}{2}\)mL
(ii) Ivx 25 x 60 = \(\frac{1}{2}\)mL ------(ii)
\(\frac{Iv \times 25 \times 60}{Iv \times 360} = \frac{\frac{1}{2}mL}{mc \times 60}\)
L = \(\frac{25 \times 60 \times C \times 60 \times 2}{360}\)
= \(\frac{25 \times 60 \times 4200 \times 60 \times 2}{360}\)
= 2.1 x 10\(^5\) Jkg\(^{-1}\)

