
You are provided with two wires marked P and C. a resistor R\(_{s}\) = 1\(\Omega\) and other necessary apparatus.
- Connect R\(_{s}\) in the left-hand gap of the metre bridge, a length L= 100cm of wire P in the right-hand gap and the other apparatus as shown in the diagram: above
- Determine the balance point B on the bridge wire AC
- Measure and record AB =/s, and BC = /
- Evaluate R\(_{1}\) = (\(\frac{|_{p}}{|_{s}}\))Rs
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of L = 90, 80, 70 and 60cm. In each case obtain and record the value of |\(_{s}\) and |\(_{p}\) and evaluate R\(_{1}\) = (\(\frac{|_{p}}{|_{s}}\))Rs
- Repeat the experiment with the second wire, Q. Obtain the value of |\(_{s}\) and |\(_{Q}\) for equal lengths of wire as used in wire P.
- Evaluate R\(_{1}\) = (\(\frac{|_{p}}{|_{s}}\))Rs. In each case, tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph of R\(_{2}\) on the Vertical axis against R\(_{1}\) on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope S, of the graph.
- Evaluate the k = \(\sqrt s\).
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. Define the resistivity of the material of a wire.
ii. A galvanometer with a full-scale-deflection of 1.5 x10\(^{3}\). A has a resistance of 50\(\Omega\). Determine the resistance required to convert it into a voltmeter reading up to 1.5V.

Using the diagram as a out the guide carry out the following instructions:
- Place the pin O horizontally inside the cylinder provided. Pour some water on the pin in the cylinder such that the length of the water column / = SO = 10.0cm, where S place the represents the water meniscus.
- lnsert another pin, P in the cork held by the boss of the retort stand.
- Adjust the position of P vertically upward or 0 formed by refraction at S.
- Read and record the distance h = PO.
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of 1= 15, 20, 25, and 30cm.
- In each case measure and record the corresponding value of h. Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph of h on the vertical axis against l on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph
- Evaluate (i) K\(_{1}\) = 1 – S
(ii) K\(_{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{k}\) - State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. Explain the total internal reflection of light.
ii. A rectangular glass prism of thickness 6 cm and refractive index 1.5 is placed on the page of a book. The prints on the book are viewed vertically down Determine the apparent upward displacement of the print.
- Fix the 100g mass marked P at B, the 80 cm mark of the uniform metre rule, using an adhesive.
- Suspend another 100g mass marked Q at A, a distance V = 10.Ocm from the 0 cm mark of the metre rule.
- Balance the whole arrangement horizontally on a knife edge as shown in the diagram above.
- Measure and record the distance U of K from the 0 cm mark of the metre rule.
- Repeat the procedure for five other values of V = 15.0, 20.0, 25.0, 30.0 and 35.0 cm
- In each case, measure and record the Corresponding values of U. Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph of U on the vertical axis against V on the horizontal axis.
- determine the:
(1) slope, s, of the graph
(2) intercept c, on the vertical axis. - Evaluate (i) K\(_{1}\) =\(\frac{(1 – 2s)}{s}\) 100:
(ii) K\(_{2}\) = \(\frac{2c}{s}\) – 160 - State two precautions taken to ensure an accurate result
(b)i. State two conditions under which a rigid body at rest remains in equilibrium when acted upon by three non-parallel coplanar forces.
ii. Explain how the position of the centre or gravity of a body affects the equilibrium of the body.

(a) When nitrogen (atomic mass = 14, atomic number = 7) is bombarded with neutrons, the collisions result in disintegrations in which alpha particles are produced. Represent this transmutation in a symbolic equation.
(b)(i) How does a radioactive atom differ from a stable one?
(ii) Explain ‘half life’.
(iii) A sample of radioactive material has a haft life of 35 days. Calculate the fraction of the original quantity that will remain after 105 days.
(c) Light of wavelength 5.00 x 10\(^{-7}\)m is incident on a material of work function 1.90 eV. Calculate
(i) photon energy.
(ii) kinetic energy of the most energetic photo electron.
(iii) stopping potential [Plancks constant h =6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\)Js] [c= 3.0 x10\(^8\)ms\(^{-2}\), leV= 1.6 x 10\(^{19}\)J]
(a) Explain the statement the capacitance of a capacitor is 5\(\mu\)F.
(b)(i) State the factors upon which the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor depend.
(ii) State how the capacitance depends on each of these factors stated in (b)(i).
(c) A series arrangement of three capacitors of values 8uF, 12\(\mu\)F, and 24\(\mu\)F is connected in series with 90-V battery.
(i) Draw an open-circuit diagram for this arrangement.
(ii) Calculate the effective capacitance in the circuit.
(iii) On closed circuit, calculate the charge on each capacitor when fully charged.
(iv) Determine the p.d across the 8\(\mu\)F capacitor.
(a)(i) What is an echo? (ii) State two useful applications of echoes.
(iii) Why are the walls, floors and ceilings of a recording studio heavily padded?
(b)(i) Explain timbre and overtones.
(ii) What is resonance?
(c) As a ship approaches a cliff, its siren is sounded and the echo is heard in the ship after 12 seconds. 2.1 minutes later the siren was sounded again and the echo was heard 8 seconds later. If the speed of sound in air is 340 ms\(^{-1}\), calculate the velocity at which the ship was approaching the cliff.
(a) Define specific heat capacity.
(b)(i) With the aid of a labelled diagram, describe an experiment to determine the specific heat capacity of copper using a copper ball.
(ii) State two precautions necessary to obtain accurate results.
(c) A piece of copper block of mass 24 g at 230°C is placed in a copper calorimeter of mass 60 g containing 54 g of water at 31°C. Assuming heat losses are negligible, calculate the final steady temperature of the mixture. [specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg\(^{-1}\) K\(^{-1}\)] [specific heat capacity of copper = 400 J kg\(^{-1}\) K\(^{-1}\)]
(a) In his first attempt, a long jumper took off from the springboard with a speed of 8 ms\(^{-1}\) at 30° to the horizontal. He makes a second attempt with the same speed at 45° to the horizontal. Given that the expression for the horizontal range of a projectile is \(\frac{v^2 sin \theta}{g}\) where all the symbols have their usual meanings, show that he gains a distance of 0.8576 m in his second attempt.
(b)(i) State Hooke’s law of elasticity.
(ii) Describe an experiment to verify Hooke’s law.
(iii) State two precautions you would take if you were to perform this experiment in the laboratory.
(c) A spiral spring of natural length 20.00 cm has a scale pan hanging freely in its lower end. When an object of mass 40 g is placed in the pan, its length becomes 21.80 cm. When another object of mass 60g Is placed in the pan, the length becomes 22.05cm. Calculate the mass of the scale pan. [g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\)]
(a) Distinguish between stress and strain as used in elasticity.
(b) When a force of 40 N is applied to the free end of an elastic cord, an extension of 5cm is produced in the cord. Calculate the work done on the cord.
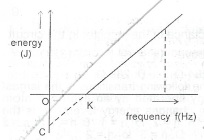
The above reprt the graph electron energy against the frequency of the radiation incident on a metal surface. lnterprete the;
(i) slope of the graph;
(ii) intercept, OC;
(iii) intercept, OK.
(a) The mass and wavelength of a moving electron are 9.0 x 10\(^{-31}\) kg and 1.0 x 10\(^{-10}\)m respectively. Calculate the kinetic energy of the electron. [ h = 6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\) Js]
(a) State two properties of cathode rays.
(b) Explain how the intensity and energy of cathode rays may be increased.
(a) Explain how a gas can be made to conduct electricity.
(b) Name the electric charge carriers in gases.
(a) What is meant by ‘a beam of polarised light?
(b) With the aid of well labelled diagrams, illustrate the action in of a polaroid spectacle on a beam of sunlight.
The value of the e.m.f of a voltaic cell, which has dilute tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid as its electrolyte and copper and zinc as its electrodes becomes less with use. Explain this observation and state how it can be corrected.
(a) What is electrolysis?
(b) A current of 2A is passed through a copper voltameter for 5 minutes. If the electrochemical equivalent of copper is 3.27 x 10\(^{-7}\) kg. Determine the mass of the corper deposited.
A lead shot is projected from the ground level with a velocity u at an angle \(\theta\) to the horizontal. Given the time, t for the lead shot to reach its maximum height as; t = \(\frac{u \sin \theta}{g}\) where “g” is the acceleration of free fall due to gravity, show that the greatest height reached by the body is h\(_{\text{max}} = \frac{u^2 \sin^2 \theta}{2g}\)
A ball thrown vertically upward reaches a maximum height of 50 m above the level of projection. Calculate the;
(i) time taken to reach the maximum height,
(ii) speed of the throw. [g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\)]
Electrons passing through crystals are diffracted because they
- A. are repelled by the atoms in the crystal
- B. are attracted by the atoms in the crystals
- C. possess wave properties
- D. are particles
A nitrogen nucleus bombarded with an alpha particle produces an oxygen nucleus and a proton. The nuclear reaction for this process is \(^4_2H + ^{14}_2N \to ^{17}_{8}O + ^1_1H + Q\). Which of the following statements about the reaction is not correct?
- A. the bombardment results into a nucleus with greater proton number
- B. it is an induced nuclear reaction
- C. it is a natural radioactive decay
- D. the sum of the final nucleon numbers
Production of x-ray tube begins with
- A. photo electric emission
- B. collision of electrons
- C. thermionic emission
- D. field emission of electrons


