
- Measure and record the emf, V\(_{o}\) of the cell provided.
- Connect a circuit as shown in the diagram above.
- With the key, K closed vary the rheostat, Rh to obtain a current 1 = 0.20A. Read and record the corresponding value of the potential difference, V on the voltmeter.
- Evaluate 1\(^{-1}\) and V\(^{-1}\).
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of l = 0.25, 0.30, 0.35 and 0.40 A. Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph V\(^{-1}\) on the vertical axis against 1\(^{-1}\) on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph
- Evaluate s\(^{-1}\).
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. Explain Ohmic conductor:
ii. Explain resistivity of the material of a wire.

- Determine and record the approximate focal length f\(_{o}\) of the concave mirror provided.
- Arrange the ray box, the mirror, and the screen as shown in the diagram above.
- Adjust the ray box to a distance b = 20.0cm from the mirror.
- Adjust the position of the screen until a sharp image of the cross wire of the ray box is formed on it.
- Measure and record the distance, a, of the screen from the mirror. Evaluate \(\frac{a}{a}\) =1.
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of b = 25.0, 30.0, 35.0, and 40.0cm. Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph of l on the vertical axis against a on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope,.s, of the graph. Evaluate S\(^{-1}\).
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. An object is placed at a distance of 10cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length of 15cm. Determine the characteristics of the image formed.
ii. Briefly describe how you obtained f\(_{o}\) in (a)i) above.

Using the diagram above as a guide, carry out the following instructions.
- Place the meter rule provided on the knife edge and adjust the position until it balances horizontally.
- Read and record the balance point, G. Keep the knife edge at this point throughout the experiment.
- Suspend a mass Q= 50.0g at a point P 30cm from the 0cm end of the rule.
- On the other side of G, suspend the mass M =30g. Adjust its position until the rule settles down horizontally as shown in the diagram above.
- Read and record the position R of M.
- Record the distance, d, between G and R. Also read and record the distance, a, between P and G.
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of M = 40, 50, 60, and 70 with Q kept in the same position. Evaluate d\(^{-1}\) in each case. Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph of M on the vertical axis against d\(^{-1}\) on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope,s, of the graph.
- Evaluate k = \(\frac{s}{Q}\)
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. Explain the moment of a force about a point
ii. State the conditions necessary for a body to be in equilibrium when acted upon by a number of parallel end forces
(a) (i) Explain electromotive force
(ii) list two sources of electromotive force other than a chemical cell
(b) A chemical cell of electromotive force, E, and internal resistance, r, is connected in series with an ammeter, a plug key a plug key and an external load of resistance R. A volumeter is connected across the cell. Draw a circuit diagram to illustrate the arrangement,
(c) for the arrangement in (b) above, with the key opened and closed, the voltmeter readings are V\(_o\) and V respectively.
(i) Explain the physical meanings of V\(_o\) and V
(ii) Find an expression for the (I) current passing through the circuit (II) maximum power dissipated in the cell and external load respectively; (III) efficiency of the cell
(a) Explain;
(i) wave motion
(ii) stationary wave
(b)(i) List four physical properties of a wave
(ii) Define amplitude and use it to distinguish between the node and antinode of a stationary wave
(iii) List the factors on which the frequency of vibration in a stretched string depends
(c) The equation, y = 5 sin (3x – 4t), where y is in millimeters, x is in meres and t is in seconds represents a wave motion . Determine the;
(i) frequency
(ii) period
(iii) speed of the wave
Define upper fixed point and lower fixed point as used in thermometry
(b) The electrical resistances of the element in a platinum restistance thermometer at 100\(^o\)C, 0\(^o\) and room temperature are 75.000, 63.000 and 64.992 \(\Omega\) respectively. Use these data to determine the room temperature.
(c) (i) State Boyle’s law
(ii) A uniform capillary tube, closed at one end contained dry air trapped by a thread of mecury 8.5 x 10\(^{-2}\)m long. When the tube was held horinzontally, the length of the air column was 5.0 x 10\(^{-2}\)m, when it was held vertically with the closed end downwards, the length was 4.5 x 10\(^{-2}\)m, Determine the value of the atmospheric pressure. [g = 10ms\(^{-2}\), density of mecury = 1.36 x 10\(^4\) kg m\(^{-3}\)]
(a) Define gravitational field intensity
(b) In an experiment to determine the acceleration of free-fall due to gravity, g, using a simple pendulum of length I, six different values of I were used to obtain six corresponding values of period T. If a graph of I along the vertical axis is plotted against T\(^2\) on the horizontal axis;
(i) make a sketch to show the nature of the graph,
(ii) write down the equation that relates T, I and g hence obtain an expression for the slope of the graph
(iii) given that the slope of the graph is 0.25, determine the value for g [Take \(\pi\) = 3.142]
(c) A stone, thrown horizontally from the top of a vertical wall with a velocity of 15 ms\(^{-1}\), hits the horizontal ground at a point 45m from the base of the wall. Calculate the
(i) times of light of the stone
(ii) height of the wall [g = 10ms\(^{-2}\)]
(a) State two;
(i) properties of x-rays
(ii) reasons to show that x-rays are waves
(iii) uses of x-rays other than those in medicine;
(iv) hazards of x-rays.
(b) The potential difference between the cathode and target of an x-ray tube is 5.00 x 10\(^4\)V and the current in the tube is 2.00 x 10\(^{-2}\)A. Given that only one percent of the total energy supplied is emitted as x-radiation, determine the ospheric pressure.
(i) maximum frequency of the emitted radiation
(ii) rate at which heat is removed from the target in order to keep it at steady temperature. [Planck’s constant, h = 6.63 x 10\(^{-34}\) Js, electronic charge e = 1.60 x 10\(^{-19}\) C]
Give three observations in support of de Broglie’s assumption that moving particles behave like waves.
(a) List two properties of cathode rays
(b) Explain how the intensity and energy of cathode rays may be increased
(a) Define Young’s modulus
(b) When a force of 50 N is applied to the free end of an elastic cord, an extension of 4 cm is produced in the cord. Calculate the work done on the cord.
A Spiral spring of natural length 20.00cm has a scale hanging freely in its lower end. When an object ass 40 g is placed in the pan. its length becomes cm. When the object is replaced with another of 60g, the length becomes 22.05cm. Calculate the mass scale pan. [g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\)]
A parallel beam of unpolarised light is incident on a plane glass surface at an angle of 58\(^{o}\) to the normal. If the reflected beam is completely polarised, calculate the refractive index of the glass.
(a) For a water voltameter, identify the;
(i) electrolyte;
(ii) electrodes;
(iii) substances deposited on the electrodes
(b)State the ratio of the volume of the substances deposited in (a) (iii) above
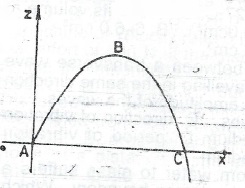
The diagram above illustrates the path ABC, in a vertical x z plane, of a bullet shot into the air at an angle above the horizontal. Copy the diagram, and, using arrows, indicate the relative magnitudes and directions of the vertical and horizontal components of the velocities of the bullet at the point A, B and C.
In his first attempt, a long jumper took off from the spring board with a speed of 8 ms\(^{-1}\) at 30° to the horizontal. He makes a second attempt with the same speed at 45° to the horizontal. Given that the expression for the horizontal range of a projectile is \(\frac{u^2 sin 2\theta}{g}\) where all the symbols have their usual meanings, show that he gains a distance of 0.8576 m in his second attempt. [g = 10ms\(^{-2}\)]
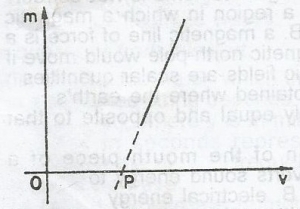
In an experiment using a converging lens to produce real images on a screen, the linear magnification m, is plotted against the image distance v, as illustrated in the diagram below. The distance OP represents the
- A. focal legth of the lens
- B. thickness of the lens
- C. radius of curvature of the lens
- D. diameter of the lens
Which of the following representations is correct for an atom X with 28 electrons and 30 neutrons?
- A. \(^{30}_{28} X\)
- B. \(^{28}_{30} X\)
- C. \(^{58}_{30} X\)
- D. \(^{58}_{28} X\)
A radioactive substance has a half-life of 3 days. If a mass of 1.55g of this substance is left after decaying for 15 days, determine the original value of the mass
- A. 49.6g
- B. 37.2g
- C. 24.8g
- D. 12.4g


