(a) (i) Explain electromotive force
(ii) list two sources of electromotive force other than a chemical cell
(b) A chemical cell of electromotive force, E, and internal resistance, r, is connected in series with an ammeter, a plug key a plug key and an external load of resistance R. A volumeter is connected across the cell. Draw a circuit diagram to illustrate the arrangement,
(c) for the arrangement in (b) above, with the key opened and closed, the voltmeter readings are V\(_o\) and V respectively.
(i) Explain the physical meanings of V\(_o\) and V
(ii) Find an expression for the (I) current passing through the circuit (II) maximum power dissipated in the cell and external load respectively; (III) efficiency of the cell
Explanation
(i) E.m.f is the work doone in taking a unit electric charge round a closed circuit. H is measured in volts.
(ii) Other sources of e.m.f. are; solar cells, fuel cells, dynamo or electric generators, thermocouple etc.
(b)
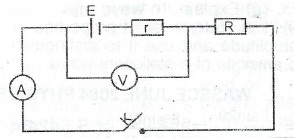
(c) (i) In open circuit Vo e.m.f of the cell.
In closed circuit V terminal p.d of the cell.
(ii) (a) I = \(\frac{E}{R + r}\)
(b) Maximum power dissipated in the cell occurs when the external resistance = the internal resistance of the cell i.e. R = r. Maximum power dissipated in the cell = IE
= \(\frac{E}{R + r} \times E = \frac{E^2}{R + r} = \frac{E^2}{2R}\)
Maximuim power dissipated in the external load
= I\(^2\)R = \(\frac{E^2R}{(R + r)^2}\)
= \(\frac{E^2R}{4R^2} = \frac{E^2}{4R}\)
(iii) Efficiency of the call = \(\frac{\text{power output}}{\text{power input}}\) x 100%
= \(\frac{2R}{E^2} \times \frac{E^2}{4R}\) x 100% = 50%

