
You have been provided with an accumulator E, a standard resistor Rx, two resistance boxes RB\(_{1}\) and RB\(_{2}\), two keys K\(_{1}\) and K\(_{2}\) and other necessary apparatus.
- Measure and record the e.m.f of the accumulator.
- Connect a circuit as shown above.
- Set the resistance R, in the resistance box such that R in RB\(_{1}\) = R in RB\(_{2}\) = 1\(\Omega\).
- With K\(_{1}\) open and K\(_{2}\) closed, measure and record the potential difference V across the standard resistor Rx. (v) Close K, and K,. Read and record the potential difference V\(_{o}\) across Rx.
- Evaluate V\(_{1}^{-1}\)
- Repeat procedure (v) for four other values of R = 2, 3, 4 and 5\(\Omega\) respectively. In each case, ensure that the value of R in RB\(_{1}\) is equal to the value of R in RB\(_{2}\).
- Evaluate V\(_{1}^{-1}\) in each case. Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph of V\(_{1}^{-1}\) on the vertical axis against R on the horizontal axis starting both axes from the origin (0,0).
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph and the intercept on the vertical axis.
- Evaluate y = \(\frac{1}{s}\)
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results
(b)i. Explain what is meant by the potential difference between two points in an electric circuit
ii. A cell has an e.m.f. of 3 V. When it is connected across a resistor of resistance 4\(\Omega\), a current 0.5A passes through the circuit. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell.

Using the above diagram as a guide, carry out the following experiment:
- place the equilateral triangular glass prism on the drawing paper. Trace the outline ABC of the prism.
- remove the prism. Draw a line NO such that it makes an angle i = 25º with the normal at point O on side AB
- fix two pins R\(_{1}\) and R\(_{2}\) vertically on line N0. Replace the prism on its outline;
- place the reflecting surface of the plane mirror in contact with the face AC of the prism;
- looking through the face BC of the prism, fix two other pins at R\(_{3}\) and R\(_{4}\) such that the pins appear to be in a straight line with the images of the pins at R\(_{1}\) and R\(_{2}\);
- remove the prism, the mirror, and the pins. Draw a line to join points R\(_{4}\) and R\(_{3}\)
- produce line R\(_{4}\)R\(_{3}\) to meet line NO produced at T;
- measure and record the angle \(\theta\) at T and e at D;
- repeat the procedure for four other values of i = 30°, 35°, 40°, and 45°. In each case, measure and record the corresponding values of \(\theta\) and e. Tabulate your readings;
- plot a graph of e on the vertical axis and \(\theta\) on the horizontal axis;
- evaluate k = s\(^{-1}\)
- state two precautions taken to ensure accurate results. [Attach your traces to your answer booklet]
(b)i. State four characteristics of the image of an object formed by a plane mirror.
ii. State two Conditions necessary for total internal reflection to occur in a medium.

You are provided with a retort stand, clamp and boss, a pendulum bob, a piece of thread, and other necessary apparatus. Carry out the fo lowing experiment:
- Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram above:
- measure and record the distance = 130cm from the centre of the bob to the point of suspension of the pendulum
- displace the pendulum through a small angle and release. Allow the pendulum to oscillate freely;
- determine the time t for 20 complete oscillations;
- also, determine the period T of the oscillations
- evaluate T\(^{2}\) and L = -30;
- repeat the procedure for four other values of l = 110, 90, 70, and 50 cm
- in each case, determine t and evaluate T,T\(^{2}\) and L. Tabulate your readings.
- plot of a graph of T\(^{2}\) on the vertical axis against L on the horizontal axis, starting both axes from the origin (0,0)
- determine the slope, s, of the graph. Also determine the intercept, C, of the graph on the T\(^{2}\) axis;
- evaluate: i. k\(_{1}\) = \(\frac{4\pi^{2}}{s_{1}}\),
ii. k\(_{2}\) = \(\frac{c}{8}\) [Take \(\pi\) = \(\frac{22}{7}\)] - state two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. What is meant by the period of oscillation of an oscillating body?
i. Explain the acceleration of free fall due to gravity.
(a)(i) With the aid of a labelled diagram describe the mode of operation of a modern X-ray tube.
(ii)State the energy transformations that take place during the operation of the X-ray tube.
(b) Define, as applied to X-rays, the following terms:
(i) hardness;
(ii) intensity.
(c) State (i) four uses of X-rays;
(ii) one hazard of over-exposure to X-rays in a radiological laboratory.
(a) With the aid of a simple diagram, explain how a step down transformer works.
(b)(i) State three ways by which energy is lost in a transformer
(ii) Mention how each of the losses in (b)(i) above can be minimized
(c) A 95% efficient transformer is used to operate a lamp rated 60W, 220 V from a 4400 V a.c supply. Calculate the;
(i) ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the number of turns in the secondary coil of the transformer
(ii) current taken from the main circuit.
(a)(i) What is a wave motion?
(ii) State two differences between a radio wave and a sound wave.
(b)(i) Given that you are provided with a tuning fork, a burette and other necessary apparatus, describe with the aid of a diagram, an experiment to determine the frequency of a note emitted by a source of sound. [assume the velocity of sound in air is known]
(ii)State two precautions necessary to obtain accurate result in the experiment described in (b)(i) above
(c) A pipe closed at one end is 100 cm long. If the air in the pipe is set into vibration and a fundamental note is produced, calculate the frequency of the note. [ velocity of sound in air = 340 ms\(^{-1}\)]
(a) Define the boiling point of a liquid.
(b) With the aid of a sketch diagram, describe an experiment to determine the boiling point of a small quantity of a Iiquid
(c) A piece of copper of mass 300 g at a temperature of 950°C is quickly transferred into a vessel of negligible thermal capacity containing 250 g of water at 25°C. If the final steady temperature of the mixture is 100°C, calculate the mass of water that will boil away. Especific heat capacity of copper = 4.0 x 10\(^2\) J kg\(^{-1}\)K\(^{-1}\) specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 x 10\(^{3}\) J kg\(^{-1}\)K\(^{-1}\) specific latent heat of vaporization of steam = 2.26 x 10\(^6\)J kg\(^{-1}\)
(a) State the conditions of equilibrium for a number of coplanar parallel forces.
(b) A metre rule is found to balance horizontally at the 48 cm mark. When a body of mass 60 g is suspended at the 6 cm mark, the balance point is found to be at the 30 cm mark. Calculate the;
(i) mass of the metre rule;
(ii) distance of the balance point from the zero end, if the body were moved to the 13 cm mark.
(c) a man pulls up a box of mass 70 kg using an inclined plane of effective length 5 m unto a platform 2.5 m high at a uniform speed. If the frictional force between the box and the plane is 1000 N;
(i) draw a diagram to illustrate all the forces acting on the box while in motion;
(ii) calculate the I. minimum effort applied in pulling up the box; II. velocity ratio of the plane, if it is inclined at 30° to the horizontal; Ill. force ratio of the plane.
A stone projected horizontally from the top of a tower with a speed of 4 ms\(^{-1}\) lands on the level ground at a horizontal distance 25 m from the foot of the tower. Calculate the height of the tower. g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\)]
State two effects to show (a) the existence of matter waves;
(b) that radiation behaves like particles.
(a) List two factors that can affect the rate of diffusion
(b) State two examples to illustrate the effects of surface tension.
A wire of length 5.0 m and diameter 2.0 mm extends by 0.25 mm when a force of 50 N was used to stretch it from its end. Calculate the;
(a) stress on the wire;
(b) strain in, the wire. [\(\pi = 3.142\)]
(a) Explain thermiopic emission
(b) State two applications of electrical conduction through gases.
Copper of thickness d is plated on the cathode of a copper voltameter. If the total surface area of the cathode is 60 cm\(^2\) and a steady current of 5.0 A is maintained in the voltameter for 1 hour. calculate the value of d. [density of copper = 8.9 x 10\(^3\)kg m\(^{-3}\) electro chemical equivalent of copper = 3.3 x 10\(^{-7}\) kg C\(^{-1}\)
State;
(a) the difference between plane polarized light and ordinary light;
(b) two uses of polaroids.
A particle is projected at an angle of 30° to the horizontal with a speed of 250 ms\(^{-1}\). Calculate the;
(a) total time of flight of the particle;
(b) speed of the particle at its maximum height. [ g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\)]
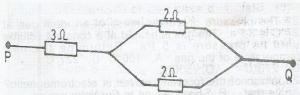
Calculate the effective resistance between P and Q in the diagram above
- A. 0.75\(\Omega\)
- B. 4.00\(\Omega\)
- C. 5.00\(\Omega\)
- D. 7.00\(\Omega\)
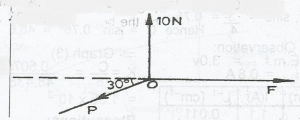
The diagram above illustrates three forces acting on an object at point O. If the object is in equilibrium, determine the magnitude of the force P.
- A. 10.5N
- B. 11.0N
- C. 17.3N
- D. 20.0N
There is always an uncertainty involved in any attempt to measure the position and momentum of an electron simultaneously. This statement is known as the
- A. de Broglie's law
- B. Heisenberg uncertainty principle
- C. Franck-Hertz experimental law
- D. wave-particle paradox


