
You are provided with a voltmeter V, a chemical cell/ battery E; two standard resistors R, and R a potentiometer a key K a jockey, and other necessary materials.
- Set up a circuit as shown in the diagram above.
- Close the key K.
- Make contact with the potentiometer wire AB using the jockey at a point C such that AC = x = 20cm
- Read and record the voltmeter reading
- Evaluate x\(^{-1}\) and v\(^{-1}\)
- Repeat the procedure for other values of x= 30, 40, 50, 60 and 80cm.
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with V\(^{-1}\) on the vertical axis and x\(^{-1}\) on the horizontal axis, starting both axes from the origin (0, 0).
- Determine the:
(a) slope, s, of the graph;
(b) intercept, c, on the vertical axis. - State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. State the two devices in which ohm’s law does not apply.
ii. A current of 1 A is supplied to two resistors of resistance 2\(\Omega\) and 3\(\Omega\) connected in parallel. Calculate the current in each resistor.

You are provided with a glass block, plane mirror, and optical pins.
- Place the glass block on a drawing sheet and trace its outline ABCD as shown in the diagram above.
- Remove the block, measure, and record the width W of the block.
- Draw a normal ON to DC at a point about one-quarter the length of DC.
- Draw a line making an angle i = 10° with the normal.
- Replace the block on its outline and mount the plane mirror vertically behind the block such that it makes good contact with the face AB.
- Stick two pins P\(_{1}\) and P\(_{2}\) on the line MO.
- Looking through the face CD, stick two other pins P\(_{3}\) and P\(_{4}\) such that they appear to be in a straight line with the images of pins P\(_{1}\) and P\(_{2}\) seen through the block.
- Join P\(_{3}\) and P\(_{4}\) with a straight line and extend it to touch the face CD at O.
- Draw a perpendicular line from the midpoint of OO to meet AB at QD.
- Draw lines OQ, O’Q, and normal O’N’ produced.
- Measure and record \(\theta\), e and d.
- Evaluate m = sin e and n = cos(\(\frac{\theta}{2}\))
- Repeat the procedure for i = 20°, 30°, 40° and 50°.
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with m on the vertical axis and n on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph and evaluate q = 2Ws.
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results. (Attach your traces to your answer booklet.)
(b)i. Explain the term refractive index and give a mathematical expression for it in terms of wavelength.
ii. State the conditions necessary for total internal reflection to occur for a given pair of media.

You are provided with three retort stands, a pendulum bob, a drawing board, a stopwatch, and other necessary apparatus. Using the diagram above as a guide, carry out the following instructions.
- Fix the drawing paper on the drawing board and hold the board with two clamps such that it is vertical.
- Suspend the pendulum bob such that it hangs freely in front of the drawing paper.
- Draw a line RP representing the rest position of the pendulum string and mark the position P of the centre of the pendulum bob at rest.
- Displace the pendulum bob to one side in a plane parallel to the drawing board.
- Mark the new position P\(^{1}\) of the centre of the bob.
- Measure and record the perpendicular distance, d of P\(^{1}\) from the line RP
- Evaluate and record d\(^{2}\).
- Measure and record the vertical height h of P\(^{1}\) above P.
- Evaluate G =\(\frac{d^{2}}{h}\)
- Repeat the procedure for four other positions of P\(^{1}\).
- Tabulate your readings.
- Remove the drawing board so that the pendulum bo can swing freely.
- Set the pendulum bob oscillating through a small bob amplitude and determine the time, t for 20 oscillations.
- Determine and record the period, T.
- Plot a graph with G on the vertical axis and h on the horizontal axis, starting both axes from the origin (0,0).
- Determine the intercept I on the horizontal axis.
- Evaluate A = \(\frac{1}{19.7T^{2}}\)
- State two precautions taken to obtain accuratee results. (Attach your drawing paper to your answer booklet.)
(b)i. Distinguish between the period and frequency of oscillation of a simple pendulum.
ii. Differentiate between oscillatory and rotational motions.
(a) State three conclusions that can be drawn from Rutherford’s experiment on the scattering of alpha particles by a thin metal foil in relation to the structure of the atom
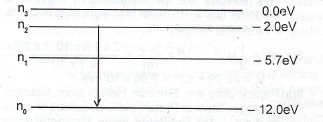
The diagram above illustrates th3 energy levels of an electron in an atom. If an excited electron moves from n\(_2\) to n\(_\theta\), calculate the:
(i) frequency;
(ii) wavelength of the emitted radiation. [ h = 6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\) Js; le V = .6 x 10\(^{-19}\) J; C = 3.0 x 10\(^8\) ms\(^{-1}\)]
(c) The following nuclear equations represent two types of radioactivity.
\(^{226}_{88}R_a \to ^{222}_{86}R_n + ^a_2a\) (Equation A)
\(^{14}_7N + ^4_2a \to ^{17}_8O + ^1_1p\) (Equation B)
Identify each type and explain briefly the difference between them
(a)
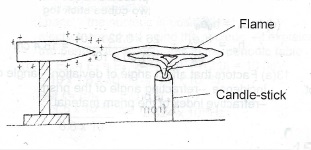
When a positively charged conductor is placed near a candle flame, the flame spreads out as shown in the diagram above. Explain this observation.
(b) A proton moving with a speed of 5.0 x 10\(^{5}\) ms\(^{-1}\) enters a magnetic field of flux density 0.2 T at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic fcrce exerted on the proton. [Proton charge = 1.6 x 10\(^{-19}\) C]
(c)
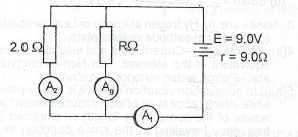
The diagram above illustrates a 9.0 V battery of internal resistance 0.5 \(\Omega\) connected to two resistors of values 2.0 \(\Omega\) and R \(\Omega\). A\(_1\) A\(_2\) and A\(_3\) are ammeters of negligible internal resistances. If Al reads 4.0 A, calculate the:
(i) equivalent resistance of the combined resistors 2.0 \(\Omega\) and R \(\Omega\);
(ii) currents through A\(_1\) and A\(_3\) ; (iii) value of R.
(a) State two factors which affect the angle of deviation of a ray of light through a triangular glass prism.
(b) Seven virtual images of an object are formed when two plane mirrors are inclined at an angle 0 to each other. Calculate the value of 0.
(c) By means of a ripple tank, a student was able to generate series of transverse waves by varying the frequency of the dipper and all the waves so generated covered a distance of 0.80 m in 0.2s.
(i) Determine the speed, v, of the waves.
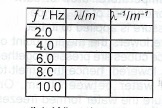
Copy and complete the table given in your answer booklet.
(iii) Plot a graph with f on the vertical axis and \(\lambda ^{-1}\) on the horizontal axis.
(iv) What does the slope of the graph represent?
(a) Explain the terms: (i) inertia; (ii) inertial mass.
(b) List three factors which affect the rate of evaporation of water in a pond.
(c) Two ice cubes pressed together for some time were found to stick together when the pressure was removed. Explain this observation.
(d) Two vertical capillary tubes of the same diameter are lowered into beakers situated at the same level, containing liquids A and B of densities 9.2 x 10\(^2\) kgm\(^{-3}\) and 1.30 x 10\(^3\) kgm\(^{-3}\) respectively. A suction pump is used to withdraw air from the top of the liquid columns in the tubes by means of a T-piece arrangement until the liquid in A rises to a height of 26.0 cm. Calculate the height of the liquid in tube B.
(a) Distinguish between perfectly elastic collision and perfectly inelastic collision.
(b) Sketch a distance — time graph for a particle moving in a straight line with:
(i) uniform speed;
(ii) variable speed.
(c) A body starts from rest and travels distances of 120, 300 and 180m in successive equal time intervals of 12 s. During each interval the body is uniformly accelerated. (i) Calculate the velocity of the body at the end of each successive time interval.
(ii) Sketch a velocity-time graph for the motion.
(s) State the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle.
(b) The product of the uncertainties in Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle is equal to or greater than a constant. State the mathematical expression for this constant.
(a) Write down the names of two particles used in explaining the wave nature of matter.
(b) State the wave characteristics which are exhibited by the particles named in (a) above.
An X-ray tube operates at a potential of 2500 V. If the power of the tube is 750 W, calculate the speed of the electron striking the target. [e = 1.6 x 10\(^{-19}\) C; mass of electron = 9.1 x 10\(^{-3}\) kg]
State one reason each why cathode rays:
(a) are not electromagnetic waves;
(b) cast sharp shadows of objects in their path;
(c) can rotate a light paddle wheel inside a discharge tube.
(a) List two examples each of substances with:
(i) low viscosity;
(ii) high viscosity.
(b) When is a liquid said to be viscostatic?
(a) Differentiate between plane polarization and interference as applied to waves.
(b) List two uses of polaroids.
(a) State two factors which affect the mass of elements deposited during electrolysis.
(b) List two non-electrolysis.
When a lead-acid accumulator is fully charged, evolution of gases occurs at the electrodes. Name these gases and the respective electrodes at which thcy are given off.
A force of 40 N is applied at the free end of a wire fixed at one end to produce an extension of 0.24 mm. If the original length and diameter of the wire art., 3 m and 2.0 mm respectively, calculate the: (a) stress on the wire; (b) strain in the wire.
A stone is projected vertically upward with a speed of 30ms\(^{1}\) from the top of a tower of height 50 m. Neglecting air resistance, determine the maximum height it reached from the ground. [g = 10 ms\(^-2\)]
Neutrons are used to induce artificial radioactivity because they
- A. are energetic
- B. have no charge
- C. have no mass
- D. are ionizing
A nuclide represented as \(^{70}_{32}X\) has a neutron-proton ratio of
- A. 0.5
- B. 0.8
- C. 1.2
- D. 1.5
In a cathode ray tube, the function of the x-plates is to
- A. deflect the electron beam horizontally
- B. deflect the electron beam vertically
- C. reflect the electron beam
- D. generate sinusoid waves


