
You are provided with cells, a potentiometer, an ammeter, a voltmeter, a bulb, a key, a jockey, and other necessary materials.
- Measure and record the emf E of the battery.
- Set up a circuit as shown in the diagram above.
- Close the key K and use the jockey to make a firm contact at J on the potentiometer wire such that PJ = x = 10cm.
- Take the record of the voltmeter reading V and the corresponding ammeter reading I.
- Evaluate log V and log I.
- Repeat the procedure for other values of x =20, 30. 40, 50, and 60cm.
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with the log I on the vertical axis and log V on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
- Determine the intercept, c, on the vertical axis.
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. How is the brightness of the bulb affected as x increases? Give a reason for your answer.
ii. List two electrical devices whose actions do not obey ohm’s law
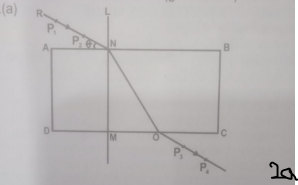
Use the diagram above as a guide to carry out the following experiment.
- Trace the outline ABCD of the rectangular glass prism on the drawing paper provided.
- Remove the prism. Select a point N on AB such that AN is about one-quarter of AB.
- Draw the normal LNM. Also, draw a line RN to make an angle \(\theta\) = 75° with AB at N.
- Fix two pins at P\(_{1}\) and P\(_{2}\) on line RN. Replace the prism on its outline.
- Fix two other pins at P\(_{3}\) and P\(_{4}\) such that they appear to be in a straight line with the images of the pins at P\(_{1}\) and P\(_{2}\) when viewed through the prism from DC.
- (vi) Remove the prism and the pins at P\(_{3}\) and P\(_{4}\). Draw a line to join P\(_{3}\) and P\(_{4}\)
- Produce line P\(_{4}\) P\(_{3}\) to meet the line DC at O. Draw a line to join NO.
- Measure and record the values of MO and NO.
- Evaluate \(\theta\) = \(\frac{MO}{NO}\) and cos \(\theta\).
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of \(\theta\) = 65° 55°, 45°, and 35°. In each case, evaluate \(\theta\) and cos \(\theta\).
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with cos \(\theta\) on the vertical axis and \(\theta\) on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results
(b)i. State Snell’s law of refraction.
ii. Calculate the critical angle for the glass prism used in the experiment above if its refractive index is 1.5.

You are provided with a wooden block to which a hook is fixed, a set of masses, spring balance, and other necessary materials. Using the diagram above as a guide, carry out the following instructions.
- Record the mass m\(_{0}\), indicated on the wooden block.
- Place the block on the table.
- Attach the spring balance to the hook.
- Pull the spring balance horizontally with a gradual increase in force until the block just starts to move Record the spring balance reading F.
- Repeat the procedure by placing in turn mass m=200, 400, 600, and 800g on top of the block. In each case, read and record the corresponding value of F.
- Evaluate M = m\(_{0}\) + m and R = \(\frac{m}{100}\) in each case
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with F on the vertical axis and R on the horizontal axis
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. Define coefficient of static friction.
ii. A block of wood of mass 0.5 kg is pulled horizontally on a table by a force of 2.5 N. Calculate the coefficient of static friction between the two surfaces.(g = 10ms\(^{-2}\))
State three properties of cathode rays which suggest the particle nature of matter
(a) Explain the terms:
(i) transmutation as it relates to radioactivity; (ii) stopping potential.
(b) \(^{23}_{11}A + ^2_1B\) —> \(^p_qC\) + proton
\(^p_qC\) —> \(^r_sE\) + beta
A nucleus C, formed artificially from A and B radioactive and quickly decays to another nucli E as indicated in the nuclear equations abc Datermine the values of p, q, r and s.
(c) A certain metal of work function 1.6 eV is irradiated with ultra-violet light of wavelength 3.6 x 10\(^{-7}\) Calculate the maximum
(i) kinetic energy of ejected electron in joules;
(ii) speed of an emitted electron. (1eV = 1.6 x 10\(^{-18}\) J; C = 3.0 x 10\(^{8}\) ms\(^{-1}\); m, = 9.1 x 10\(^{-31}\) kg; h = 6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\) Js)
(d) If source of the ultra-violet light in (c) above is mo away from the surface of the metal, state the of on the maximum speed of the ejected electron
(a) Explain mutual induction
(b) State four use of electromagnets
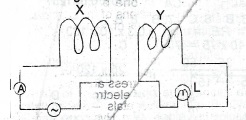
The diagram above illustrates two coils X an arranged so that their axes are collinear. X is connected to an a.c. supply and has an amme in series with it while Y is connected to a lamp Explain the following observations. The (i) lamp is lit when the a.c. supply is switched on;
(ii) brightness of the light from the lamp increases when distance between X. and Y is decreased;
(iii) filament of the lamp glows brighter whet bundle of insulatttriron wires is placed along ccmmon axis of the coils.
(d) Two cells, one have an emf of 2.0 V and an internal resistance of 0.4 and the other having an emf of 2.0 V and an internal resistance of 0.1 \(\Omega\), are connected in parallel. The combination is then connected in series with a resistor.
(i) Draw a circuit diagram of the arrangement.
(ii) Calculate the current through 5\(\Omega\) resistor.
(a)(i) What is an eclipse?
(ii) List the three types of eclipse.
(b) A student in a lecture theatre can read from the board clearly but requires a pair of spectacles to read from a book.
(i) What eye defect has this student?
(ii) What type of lens is needed to correct the eye defect?
(iii) The focal length of the lens used to correct this defect is 10cm. Calculate the power of the lens.
(c) A car B moves towards a stationary car A. If B produces an ultrasonic sound at a point and it takes 5.6 x 10\(^{-3}\)s for a beep to be heard in B, calculate the distance between the two cars at that instant. (Speed. sound in air = 340 ms\(^-\))
(d) The image of an object is located 9 cm behind a convex mirror. If magnification produced is 0.6, calculate the focal length of the mirror.
(a)(i) State two advantages of alcohol over mercury as a thermometric liquid.
(ii) When the bulb of a thermometer is placed in a beaker of hot water, the level of the mercury first falls and then rises gradually. Explain this observation.
(b) List two factors, other than temperature, that affect the rate of evaporation of a liquid.
(b) A block of lead of mass 100 kg in a crucible and at a temperature of 40 °C was placed in an electric furnace rated 10 kW. If the melting point of lead is 320 °C, calculate the:
(i) quantity of heat required to heat the lead to its melting point;
(ii) additional heat energy required to melt the lead;
(iii) time taken to supply this additional energy. (Specific heat capacity of lead = 120 Jkg\(^{-1}\) K\(^{-1}\) (Specific Idtent heat of fusion lead = 2.5 x 10\(^{4} JK^{-1}\))
(d) State two precautions necessary in an experiment to determine the specific latent heat of vaporization of water.
(a) What is a vector quantity?
(b) Three vectors 3 ms\(^{-1}\) N 45° W, 12 ms\(^{-1}\)W and 5 ms\(^{-1}\)S act at a point.
(i) Sketch a vector diagram to illustrate the given information.
(ii) Calculate the resultant of the vectors.
(c) In a laboratory experiment to determine the force constant of a spiral spring, the mass or, the spring was varied and the corresponding extensions were measured and recorded as shown in the table below.
| Mass M/g | Weight W/N | Extension e/cm |
|
50 100 150 200 250 |
6.5 11.0 15.0 20.0 25.0 |
(i) Copy and complete the table. (Take g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\))
(ii) Plot a graph with weight, W, on the vertical axis and extension, e, on the horizontal axis.
(iii) Using the graph, determine the force constant of the spring.
(iv) Determine the natural length of the spring if its length was 38.0 cm when loaded with 250 g mass.
The uncertainty in determining the duration during which an electron remains in a particular energy level before returning to the ground state is 2.0 x 10\(^{-9}\)s. Calculate the uncertainty in determining its energy at that level. (\(\frac{h}{2 \pi}\) = h = 1.054 x 10\(^{-34}\)Js)
An electron of charge 1.60 x 10\(^{-19}\) C is accelerated under a potential difference of 1.0 x 10\(^5\) V. Calculate the energy of the electron in joules.
Explain why water in a narrow glass tube has a concave meniscus while mercury, in the same tube, has a convex meniscus.
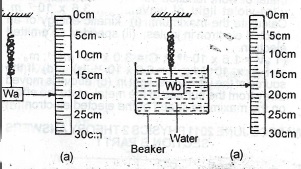
In fig. la and fig.1 b above, Ida and Wb represent the respective loads on a spring placedtiear a 30 cm rule, when in air and when in water:
(a) Identify the force causing a shrink in the spring in fig.(b).
(b) Given that the force constant of the spring is 2.0 x 10\(^{11}\) Nm\(^{-1}\), calculate the work done by the force in causing the shrink.
(a). State: (a) two applications of electrolysis in an industry
(b) one application of electrolysis in a school laboratory.
State: (a) the difference between plane polarized light and ordinary light;
(b) two uses of polaroids.
(a) Explain diffusion.
(b) Give one reason why the rate of diffusion is higher in gases than in liquids at the same temperature.
A stone projected horizontally from the top of a tower with a speed of 4 ms\(^{-1}\) lands on the level ground at a horizontal distance of 25 m from the foot of the tower. Calculate the height of the tower. = 10 ms\(^{-2}\)]
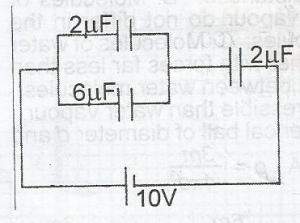
Using the circuit diagram above. Calculate the potential difference across the capacitors in parallel
- A. 10.0V
- B. 8.0V
- C. 6.7V
- D. 2.0V
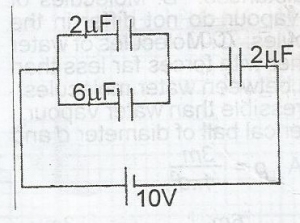
Using the circuit diagram above. Calculate the total charge in the circuit
- A. 80\(\mu C\)
- B. 35\(\mu C\)
- C. 20\(\mu C\)
- D. 16\(\mu C\)
Nuclear fusion is not used as a source of enegy because
- A. very high temperature is needed for the reaction
- B. the fuel for the reaction is not easy to obtain
- C. less energy is released
- D. the reaction is too slow


