
You are provided with a potentiometer, an ammeter, a voltmeter, a standard resistor, and other necessary apparatus. Using the circuit diagram above as a guide carry out the following instructions.
- Set up a circuit as illustrated in the diagram above.
- Close the key, K.
- Read and record the ammeter reading l\(_{o}\) and the voltmeter reading V\(_{o}\) when jockey J is not making contact with the potentiometer wire OQ.
- Using J, make a contact with the potentiometer wire OQ at a point P such that OP = 1Ocm.
- Read and record the current and the corresponding value of the voltage V.
- Repeat the procedure for other values of OP= 20cm, 30cm, 40cm, 50cm, and 60cm.
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with V on the vertical axis and I on the horizontal axis, starting both axes from the origin (0, 0).
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
- Determine the value of V when I = 0.
- State two precautions taken to obtain accurate results.
(b) i. State two advantages of a lead-acid accumulator over a dry Leclanche cell.
ii. A cell of emf 2V and internal resistance of 1\(\Omega\) passes current through an external load of 9\(\Omega\). Calculate the potential drop across the cell.

You are provided with a syringe, a petri-dish firmly attached to the base of the movable piston (plunger) of the syringe, a Set of weights, and other necessary apparatus.
- Pull the piston of the syringe upward until it can no longer move. Read and record this position of the piston on the graduated mark on the syringe as V\(_{o}\).
- Clamp the syringe and ensure that it is vertical.
- Place a mass M= 500g gently at the center of the petri-dish.
- Read and record the new position of the piston as V.
- Evaluate V\(^{1}\).
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of M= 1000g, 1500g, 2000g, and 2500g.
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with V\(^{-1}\) on the vertical axis and M on the horizontal axis, starting both axes from the origin (0,0).
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
- Evaluate k = s\(^{-1}\).
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. When a weight is placed on the petri-dish, which quantities of the gas in the syringe (\(\Omega\)) increases; (\(\beta\)) decrease?
ii. What is responsible for the pressure exerted by a gas in a closed vessel?

Study the diagrams above and use them as guides in carrying out the following instructions.
- Using the spring balance provided, determine the weight of the object of mass M= 50.0g in air. Record this weight as W\(_{1}\).
- Determine the weight of the object when it is completely immersed in water contained in a beaker as shown in the diagram above. Record the weight as W\(_{2}\).
- Determine the weight of the object when it is completely immersed in a liquid labeled L. Record the weight as W\(_{3}\).
- Evaluate U = (W\(_{1}\) – W\(_{2}\)) and V = (W\(_{1}\) -W\(_{3}\)).
- Repeat the procedure with the objects of masses M= 100g, 150g, 200g, and 250g
- In each case, evaluate U = (W\(_{1}\) – W\(_{2}\)) and V = (W\(_{1}\) -W\(_{3}\)).
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with V on the vertical axis and U on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the horizontal graph.
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. State Archimedes’ principle.
ii. A piece of brass of mass 20.0g is hung on a spring balance from a rigid support and completely immersed in kerosene from of density 8.0 x 10\(^{2}\)kgm\(^{-3}\). Determine the readings of the spring balance (g= 10ms\(^{-2}\), density of brass 8.0 x 10\(^{3}\)kgm\(^{-3}\))
A spiral spring with a metal extends by 10.5 cm in air. When the metal is fully submerged in water, the spring extends by 6.8 cm. Calculate the relative density of the metal. (Assume Hooke’s law is obeyed)
(a) (i) Explain why x-rays can be used to produce photographs of fractures in bones.
(ii) List four uses of x-rays other than in medicine.
(b) State the energy transformations which takes place during the operation of an x-ray tube.
(c) (i) Explain three named dangers to which human beings may be exposed when subjected to large doses of x-rays.
(ii) State two precautions that must be taken by persons working with x-rays.
(d) In an x-ray tube, an electron is accelerated from rest towards a tungsten target biased at a potential of 33 kV. Calculate, for the electron, the
(i) kinetic energy;
(ii) velocity. [h = 6.6 x 10\(^{-14}\) Js; Me = 9.1 x10\(^{-31}\) kg; c = 3.0 x 10\(^4\) ms\(^{-1}\); e = 1.6 x 10\(^{-19}\) C.]
(a) Define magnetic line of force.
(b) A wire of length 10 cm carrying a current of 4.0 A is placed between the poles of a powerful electromagnet of magnetic flux density 2.0 T. Calculate the:
(i) force on the wire when it is parallel to the field;
(ii) maximum force on the wire;
(iii) force on the wire when it makes an angle of 60° with the field.
(c) Describe how keepers can be used to preserve the magnetic strength of permanent bar magnets.
(d) A sailor observes that his mariners’ compass reads N 10° W at a place where the angle of declination is N15° W. Calculate the true bearing of the place.
(a) Explain the term critical angle.
(b) List two factors which determine the deviation of a ray of light by a triangular glass prism.
(c) The angle of refraction (r) of a ray of white light from air through a triangular glass prism of refractive index 1.5 is 29.0°. Calculate the angle through which the ray is least deviated.
(d) Study the ray diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
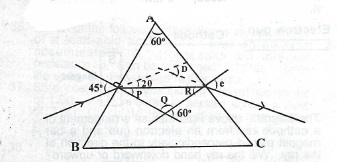
Calculate the:
(i) values of angles P,Q and R;
(ii) refractive index n of the glass prism;
(iii) value of e;
(iv) total deviation D.
(a) (i) What is a machine?
(ii) State two uses of gears.
(iii) Define the velocity ratio for a pair of gear wheels.
(iv) How can the mechanical advantage of a gear system be increased?
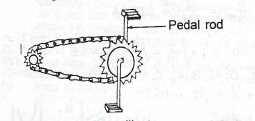
The diagram above illustrates the gears system of a bicycle.
(i) Determine its velocity ratio.
(ii) If the bicycle has an efficiency of 90%, calculate the effort required to overcome a load of 70N.
(iii) Why is the calculated effort less than the actual effort required?
(a) State the principle of conservation of linear momentum.
(b) Explain the mode of action of a propelled rocket.
(c) During a training session, two footballers pass a ball repeatedly between themselves. Give two reasons why the to and fro motion of the ball is not simple harmonic.
(d) A ball is dropped from a height, at the same time as another ball is projected horizontally from the same height.
(i) Would the balls hit the ground at the same time?
(ii) Explain your answer in (i).
(e) A ball of mass 0.10 kg is projected horizontally onto a vertical wall with a speed of 17 ms\(^{-1}\). The ball makes contact with the wall for 0.15 s and rebounds horizontally with a speed of 13 ms\(^{-1}\).
Calculate the:
(i) change in momentum of the ball;
(ii) average force exerted on the ball during its collision with the wall.
(a) Explain wave-particle duality of light.
(b) Illustrate your answer in (a) with observable phenomena.

The diagram above illustrates an arrangement of a cathode ray from an electron gun and a bar magnet placed perpendicularly to the direction of the ray. Will the ray bend downward or upward? Explain.
(a) On what principle does lighting in a fluorescent tube operate?
(b) State two factors which determine the colour of light produced in a fluorescent tube.
Explain why it is desirable to install an air conditioner near the ceiling of a room and not close to the floor.
a) Define surface tension.
(b) State two methods by which the surface tension of a liquid can be reduced.
(a) Explain the term electrodes in electric cells.
b) An electric current passing through an electrolyte for 2 minutes deposited 200 g of a substance. If the electrochemical equivalent of the substance is 8.33 x 10\(^{-4}\)g C\(^{-1}\), calculate the current passed.
(a)
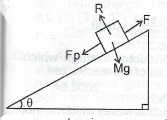
In the diagram illustrated, a body of mass m slides on an inclined plane. Show that the coefficient Mg of friction between the surfaces in contact is tan \(\theta\).
A spiral spring with a metal extends by 10.5 cm in air. When the metal is fully submerged in water, the spring extends by 6.8 cm. Calculate the relative density of the metal. (Assume Hooke’s law is obeyed)
A ray of light is incident on an air-glass boundary at an angle \(\theta\). If the angle between the partially reflected ray and the refracted ray is 90°, calculate \(\theta\), given that the refractive index of glass is 1.50.
Which of the following radiations emitted in radioactive decay has momentum, a fairly high penetrating power and is deflected by a magnet?
- A. alpha particles
- B. beta particle
- C. gamma radiation `
- D. X-radiation
Which of the following arrangements of radiations is in the order of decreasing penetrating power?
- A. \(\alpha, \beta, \gamma\)
- B. \(\alpha, \gamma, \beta\)
- C. \(\gamma, \beta, \alpha\)
- D. \(\beta, \gamma, \alpha\)
Which of the following statements about X-rays is correct? X-rays
- A. are produced when a metal surface is irradiated with ultraviolet light
- B. are produced when a metal target is used to block fast miving electrons
- C. have long wavelengths and are therefoer very penetrating
- D. are not part of the electromagnetic spectrum


