
You are provided with a constantan wire, a2 \(\Omega\)standard resistor, an accumulator E, an ammeter A, a key K, and other necessary apparatus.
- Measure and record the emf of the accumulator provided
- Connect a circuit as shown in the diagram above.
- Close the key, read and record the ammeter reading l\(_{o}\) when the crocodile clip is not in contact with the Constantan wire.
- Open the key with the clip making contact with the wire, when d=90cm, close the key. Read and record the ammeter reading l.
- Evaluate d\(^{_1}\)
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of d=80, 70, 60, and 50 cm
- In each case, read and record the ammeter reading and evaluatre d\(^{_1}\).
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with I on the vertical axis and d\(^{_1}\) on the horizontal aXIS.
- Determine the slope, S of the graph and its intercept, c, on the vertical axis.
- Evaluate k = \(\frac{c}{s}\)
- Using your graph, determine the current I when d=55cm.
- State two precautions taken to obtain accurate results.
(b)i. Explain what is meant by the potential difference between two points in an electric circuit.
ii. State two factors on which the resistance of a wire depends.

Using the diagram above as a guide, carry out the following instructions:
- Fix a plain sheet of paper on the Celotex board.
- Place the rectangular glass prism on the paper and trace its outline, ABCD. Remove the prism.
- Draw a normal NMP to meet AB and DC at M and P respectively such that |AM|=DP=2.0cm.
- Trace the ray PQ with two pins, P\(_{1}\) and P\(_{2}\) at P and Q respectively such that angle MPQ = i =50º
- Replace the prism on its outline. Trace the emergent ray with two other pins P\(_{3}\) and P\(_{4}\) such that they lie in a straight line with P\(_{2}\) and the image of P\(_{1}\) viewed through the glass prism.
- Measure and record \(\theta\), the angle between the emergent ray and face AB of the glass prism.
- Evaluate cos \(\theta\) and sin i.
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of i = 10°, 15°,20° and25°.
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with cos \(\theta\) on the vertical axis and sin i on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results. Attach your traces to your answer booklet
(b)i. State the laws of refraction of light
ii. Explain what is meant by the statement the refractive index of a material is 1.65

You are provided with a uniform metre rule of mass, M indicated on its reverse side, a knife-edge, a graduated measuring cylinder of known mass, M\(_{1}\) marked on it and other necessary apparatus.
- Read and record with values of M and m\(_{1}\).
- Balance the metre rule horizontally on the knife edge. Read and record the balance point as G.
- Tie a loop of thread around the neck of the measuring cylinder.
- Fill the cylinder with the sand provided to the 2cm\(^{3}\) mark. Record the volume, V, of the sand.
- Hang the cylinder at the 2 cm mark of the metre rule and adjust the position of the knife edge until the rule balances horizontally.
- Read and record the new balance position K.
- Determine the value of e and f.
- Determine the mass, m\(_{2}\), of the sand in the measuring cylinder. Hint: m\(_{2}\) = (\(\frac{\text {M x f}}{e}\)) – m\(_{1}\).
- Repeat the procedure by filling the measuring cylinder to the mark V = 4,6,8 and 10 cm\(^{3}\). In each case, ensure that the measuring cylinder is kept constant at the 2 cm mark on the metre rule.
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with m\(_{2}\) on the vertical axis and V on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
- State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. Determine the mass of 7.5 cm\(^{3}\) of the sand using your graph.
ii. A gold coin of mass 102.0 g has a uniform cross-sectional area of 10.0 cm\(^{2}\). Calculate its thickness. [Density of gold=19.3 g cm\(^{-3}\)]
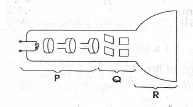
Name the three basic components P, Q and R that make up a cathode ray tube, as illustrated in the diagram above
(a) Define boiling point of a liquid.
(b) Describe how water in a round bottom flask could be made to boil without heating it. [diagram not necessary]
(c) State three applications of expansion of metals.
(d) A room with floor measurements 7m x 10 m contains air of mass 250 kg at a temperature of 34°C. The air is cooled until the temperature falls to 24°C. Calculate the: (i) height of the room;
(ii) quantity of energy extracted to cool the room;
(iii) which is higher: the calculated value or the actual energy needed to cool the room? Give a reason for your answer. [ Specific heat capacity of air = 1010 Jkg\(^{-1}\)K\(^{-1}\); density of air = 1.25 kg m\(^{-3}]
(a) Define ionization potential.
(b)(i) State the three types of emission spectra.
(ii) Name one source each which produces each of the spectra stated in (b)(i).
(c) In an x-ray tube, electrons are accelerated the target by a potential difference of 80 A Calculate the:
(i) speed of the electron;
ii) threshold wavelength of the electron. [h=6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\) Js; e = 1.6 x 10\(^{-19}\) C; Me = 9.1 x 10\(^{-31}\)
d) An x-ray photon of frequency 4.5 x 10\(^{-18}\) strikes an. electron, assumed to be at rest. If t electron absorbs all the photon energy, calculate the speed acquired by the electron. [ h = 6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\) Js; Me = 9.1 x 10\(^{-31}\) kg ]
(a) Explain briefly the purpose of earthing electrical appliance.
(b) Why does the light frorr bulb connected to a simple cell dim and eventually goes off after a while?
(c) A coil of incidence 0.007 H, a resistor of resistance 8 \(\Omega\) and a capacitor capacitance 0.001 F are connected in series an a.c. source of frequency \(\frac{500}{\pi}\)Hz. If the r.m.s voltages across the coil, the resistor and capacitor are 30v, 20v and 70v respectively;
(i) draw a vector diagram to illustrate the voltage across the components in the circuit.
(ii) Calculate the: (\(\alpha\)) r.m.s voltage of the source
(\(\beta\)) r.m.s current in the circuit;
(\(\gamma\)) power dissipated in the circuit.
iii) write down the sinusoidal equation for the r.m.s voltage, V, in terms of the time, t.
(a) On which day would sound wave travel faster: on a hot or cold day? Explain.
(b) Why are megaphones shaped like funnels?
(c) A ray of light is incident on a surface of a ectangular glass prism of refractive index 1.5 illustrated in the diagram below.
(i) Copy the diagram a label the angles of: (\(\alpha\)) Incidence (x); (\(\beta\)) Reflection (y); (\(\gamma\)) refraction (z); with t glass letters indicated.
(ii) Calculate the angle refraction to the nearest whole number.
(d) A sonomesr wire vibrates in simple harmoi motion with a maximum amplitude of 1.0 cm. Calculate the frequency of vibration of the wire, giv that the magnitade of the maximum acceleration of the wire is 980ms\(^{-2}\). [\(\pi \frac{22}{7}\)]
(a) State the triangle law of vector addition.
(b) Name the four physical quantities that are associated with the equationq of linear motion.
(c) Using the same set of axes, sketch and label two graphs to illustrate the variation of potential energy and kinetic energy with time for a body in simple harmonic motion.
(d)

A light spiral spring of force constant K lies on a horizontal frictionless surface and has one end fixed to a vertical wall. A block P of mass 2.0 kg placed against the free end of the spring is pushed a distance 5 cm towards the wall with 10J of energy as illustrated in the diagram above. The block is released and after 0.25s, it collides inelastically with a stationary block Q of mass 4.0 kg. Calculate the:
(i) value of k;
(ii) force used to compress the spring;
(iii) acceleration of the block p after release;
(iv) common speed after collision of the blocks.
(a) what is Brownian motion?
(b) State the two inferences that can be drawn from Brownian motion experiment.
Write down the name of:
(a) two particles used in explaining the wave nature of matter;
(b) one device whose invention is based on the wave nature of matter.
The accelerating potential in a cathode ray oscilloscope is 2.5 kV. Calculate the maximum speed of the accelerated electrons. [ e = 1.6 x 10\(^{-19}\) C; Me = 9.1 x 10\(^{-31}\) kg]
Name one use of ‘LASER’ in each of the following areas:
(a) communication;
(b) medicine;
(c) security
(a) What is a polarizer?
(b) With the aid of a diagram, explain how a polarizer can be used to polarize a beam of unpolarized light.
A mass of 11.0 kg is suspended from a rigid support by an aluminum wire of length 2.0 m, diameter 2.0 mm and Young’s modulus 7.0 x 10\(^{11}\) Nm\(^{-2}\). Determine the extension produced. [g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\); \(\pi\) = 3.142]
In an electrolysis experiment, the ammeter records a steady current of 1 A. The mass of copper deposited in 30 minutes is 0.66 g. Calculate the error in the ammeter reading. [Electrochemical equivalent of copper = 0.00033 g C\(^{-1}\)]
The horizontal component of the initial speed of a particle projected at 30° to the horizontal is 50 ms\(^{-1}\). If the acceleration cf free fall due to gravity is 10ms\(^{-2}\), determine its: (a) initial speed; (b) speed at maximum height reached.
A projectile is released with a speed u at an angle \(\theta\) to the horizontal. With the aid of a diagram, show that the time of flight is equal to \(\frac{2uSin\theta}{g}\), where g is the acceleration of free fall.

An electric circuit is connected as illustrated above. Determine the equivalent e.m.f and current flowing through the circuit respectively, neglecting the internal resistance of the cells
- A. 2V, 1.0A
- B. 2V, 4.0A
- C. 6V, 0.3a
- D. 6V, 3.0a
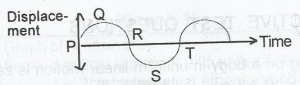
The diagram above illustrates a waveform. Which of the point on the waveform are in phase?
- A. P and R
- B. R and T
- C. P and T
- D. Q and S

The outlet of a bicycle pump is used to inflate a football as illustrated in the diagram above. Why does the pressure of the air inside the pump increases as the pump handle is slowly pushed downward at constant temperature?
- A. momentum of the air molecules are increased
- B. volume occupied by the molecules are increased
- C. frequency of collision of the air molecules with the walls of the pump is increased
- D. more air molecules are collidin with one another in the system


