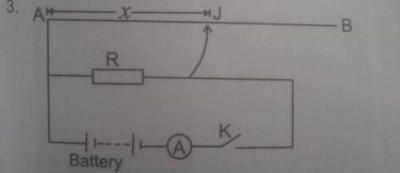
You are provided with a potentiometer AB, a 102\(\Omega\) standard resistor R, a battery of emf 4.5V, a jockey J, and other necessary materials.
- Connect a circuit as shown in the diagram above.
- Close key K. Without J making contact with AB, read and record the ammeter reading I. Open the key.
- Use the jockey to make contact with AB at the 20cm mark such that AJ = x = 20cm. Close the key, read and record the ammeter reading.
- Evaluate x\(^{-1}\).
- Repeat the procedure for values of x= 35cm, 45cm, 60cm, and 80cm respectively.
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with x\(^{-1}\) on the vertical axis and l\(_{i}\) on the horizontal axis, starting both axes from the origin (0, 0).
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
- From your graph, determine the value l\(_{o}\) of I\(_{1}\) for which x\(^{-1}\)= 0.
- Evaluate \(\frac{I_{o}}{I}\).
- State two precautions taken to obtain accurate results.
(b)i. Define the emf of a battery.
ii. A cell X of emf 1.018V is balanced by a length of 50.0cm on a potentiometer wire. Another cell Y is balanced by a length of 75.0cm on the same wire. Calculate the emf of Y.

You are provided with an illuminated object, converging lens, screen, metre rule, and other necessary materials.
- Measure and record the size a\(_{o}\) of the illuminated object.
- Place the object O and the screen S on Opposite sides of the converging lens L.
- Set the distance between the object and the lens U = 30cm.
- Adjust the screen until a sharp image of the illuminated object is obtained on the screen.
- Measure and record the size a of the image.
- Evaluate m = \(\frac{a}{a_{0}}\), and m\(^{-1}\)
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of U=35cm, 40cm, 45cm and 50cm respectively.
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with m\(^{-1}\) on the vertical axis and U on the horizontal axis.
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph and intercept, C, on the vertical axis.
- Determine the value of U for which m\(^{-1}\)=0.
- State two precautions taken to obtain accurate results.
(b)i. Using your graph, determine the value of m for which U= 37cm.
ii. Sketch a diagram to illustrate how a converging lens may be used to produce a real diminished image of an object.

You are provided with a grooved inclined plane, a solid sphere, a stopwatch, and other necessary apparatus.
- Place the pile of paper towels at the tail end of the inclined plane to stop the sphere from rolling off the table.
- Release the sphere from a point at distance D= 140cm from the tail end of the inclined plane.
- Determine the average time t taken by the sphere to cover this distance.
- Evaluate W = D/t.
- Calculate V= 2W.
- Repeat the procedure for four other values of D= 120cm 100cm, 80 cm and 60cm respectively.
- Tabulate your readings.
- Plot a graph with V on the vertical axis and t on the horizontal axis
- Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
- What is the significance of s?
- State two precautions taken to obtain accurate results.
(b)i. Write the equation for the velocity ratio of an inclined plane, giving the meaning of the symbols used.
ii. An object of mass 5kg is placed on a place inclined at an angle of 30° to the horizontal. Calculate the force on the object perpendicular to the plane when the object is at rest. (g =10ms\(^{-2}\)).
(a) Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation and identh: each component of the equation.
(b) For a photocell, star; one factor each that is responsible fo: the:
(i) emission (ii) rate of emission;
(iii) energy of photoelectrons.
(c)(i) Two nuclear equations are given below:
\(^{222}_{p}RN\) \(\to\) \(^{218}_{84}PO + ^q_2He\)……………….A
\(^{214}_{83}RN\) \(\to\) \(^{214}_{84}PO + ^m_nX\)……………….B
Determine the values of: (\(\alpha\)) p and q in equation A; (\(\beta\)) in and n in equation B and identify X.
(ii) Give a reason why it is important to dispose o radioactive waste safely.
(d)(i) A certain atom emits ultra violet photon of wavelength 2.4 x10\(^{-7}\)m. Calculate the energy of the photon:
—————– – 6.0 x 10\(^{-19}\)J
—————- – 8.2 x 10\(^{-19}\)J
—————- – 8.8 x 10\(^{-19}\)J
—————- – 16.7 x 10\(^{-19}\)J
(ii) The figure above illustrates the energy levels o the atom. Copy the figure in your answer booklet anc indicate on it, the energy level transitions which cause the emission of the photon in (d)(i) above. [h= 6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\) Js; c = 3.0 x 108 ms\(^{-1}\)].
(a) Define electromotive force.
(b) State:
(i) the principle of operation of a potentiometer,
(ii) two advantages that a potentiometer has over a voltmeter in measuring potential difference.
(c)(i) Sketch and label a diagram of a gold-leaf electroscope.
(ii) Give one use of a gold-leaf electroscope.
(d)(i) Explain the action of a magnetic relay.
(ii) List two factors which determine the magnitude of an induced emf in a coil.
(iii) A current of 5 A passes through a straight wire in a uniform magnetic field of flux density 2.0 x10\(^{-3}\) T. Calculate the force per unit length exerted on the wire when it is inclined at 30° to the field.
(a) State the three characteristics of sound and the factor on which each of them depends.
(b) Explain resonance as applied to sound.
(c) What role does echo play in the construction of a concert hall?
(d) The surface of an ear drum (assumed circular) has a radius 2.1 mm. It resonates with an amplitude of 0.8 x 10\(^{-7}\) in as a result of impulses received from an external body vibrating at 2400 Hz. If the resulting pressure change on the ear drum is 3.6 x 10\(^{-5}\) NM\(^{-2}\), calculate the:
(i) period of oscillation;
(ii) velocity;
(iii) acceleration;
(iv) force. [\(\pi\) = 3.14 ].
a) Define heat capacity and state its unit.
(b) List two effects of heat on a substance.
(c) Explain how a tightly fitted glass stopper could be removed from a reagent bottle.
(d) A quantity of pepper soup of mass 800 g poured into a plastic container with a tight-fitting lid has a temperature of 30°C. The container is then placed in a microwave oven, rated 1200 W and operated for 3 minutes.
(i) Calculate the final temperature attained by the soup. (Assuming no heat losses).
(ii) Explain why containers with tight-fitting lids are not suitable for use in microwave cooking.
(iii) When the soup is brought out and allowed to cool, a dent is observed on the container. Explain. [Take specific heat capacity of the soup = 4000 Jkg\(^{-1}\) K\(^{-1}\)]
(a) Give two examples each of:
(i) rotational motion;
(ii) linear motion.
(b) Describe a laboratory experiment to determine the density of an irregularly shaped solid.
(c) State Newton’s second law of motion
(d) Explain the term inertia.
(e)
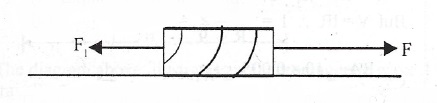
The diagram above illustrates a body of mass 5.0 kg being pulled by a horizontal force F. If the body accelerates at 2.0 ms\(^{-2}\) and experiences a frictional force of 5 N, calculate the:
(i) net force on it;
(ii) magnitude of F;
(iii) coefficient of kinetic friction. [ g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\)]
(a) State two conditions under which photo-electrons can be emitted from the surface of a metal.
(b) List two particle characteristics of electromagnetic waves.
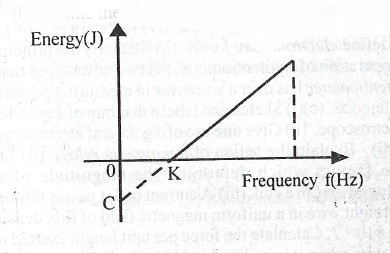
The diagram above represents the graph of electron energy against the frequency of the radiation incident on a metal surface. Interpret the: (a) slope of the graph; (b) intercept, OC; (c) intercept, OK.
(a) Explain how a gas can be made to conduct electricity.
(b) Name the electric charge carriers in gases.
A metallic bar 50 cm long has a uniform cross-sectional area of 4.0 cm\(^2\). If a tensile force of 35 kN produces an extension of 0.25 mm, calculate the value of Young’s modulus
An electron moves with a speed of 2.00 x 10\(^7\) ms\(^{-1}\) in an orbit in a uniform magnetic field of 1.20 x 10\(^{-3}\) T. Calculate the radius of the orbit. [Mass of an electron = 9.11 x 10\(^{-3}\) kg; charge on an electron = 1.61 x 10\(^{-19}\)C]
A tennis ball projected at an angle 0 attains a range R = 78. If the velocity imparted to the ball by the racket is 30 ms\(^{-1}\), calculate O. [ g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\)]
A particle is projected horizontally at 10 ms\(^{-2}\) from the top of a tower 20 M high. Calculate the horizontal distance travelled by the particle when it hits the level ground. [g= 10 ms\(^{-2}\)
An element of nucleon number P and atomic number Q emits an alpha particle from its nucleus. The resultant numbers of the new element formed are respectively
- A. P - 4 and Q + 2
- B. P - 4 and Q - 2
- C. P + 2 and Q + 2
- D. P + 2 and Q - 2
An aluminum foil is placed across a beam of radiation from a radioactive source. Which of the following types of radiation will be stopped by it?
- A. alpha and beta particles
- B. alpha and gamma particles
- C. beta and gamma particles
- D. gamma particles only
Which of the following statements is the major advantage of nuclear fusion over nuclear fission?
- A. nuclear fusion releases more energy
- B. more neutrons are released in fusion than in fission
- C. fussion does not release as much dangerous radiation as fission
- D. fusion reactions occur more readily than fission
The energy required to separate the nucleus in an atom completely is known as
- A. mass defect of the atom
- B. electron binding energy
- C. excitation energy
- D. nuclear binding energy
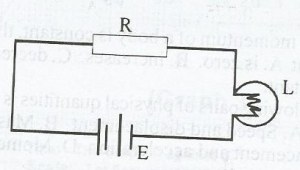
The circuit above illustrates a standard resistor R, voltage source E and a lamp L connected in series. If the temperature of R is increased, the brightness of the lamp will
- A. increase sharply
- B. decrease slightly
- C. remains the same
- D. increase gradually
A transformer has 400 turns of wire in the primary coil and 40 turns in the secondary col. If the input voltage is 150 volts. Calculate the magnitude of the output voltage
- A. 150V
- B. 55V
- C. 36V
- D. 15V


