
You are provided with an ammeter, resistor, key, metre bridge, and other necessary apparatus.
i. Connect a circuit as shown in the diagram above.
ii. Close the key and use the jockey to make contact with AB at N such that AN = d = 25cm
iii. Read and record the ammeter reading.
iv. Evaluate 1\(^{-1}\).
v. Repeat the procedures for values of d = 35cmm, 50cm, 65cm and 80cm. In each case, record I and determine 1\(^{-1}\)
vi. Tabulate your results.
vii. Plot a graph with log on the vertical axis and d on the horizontal axis.
viii. Determine the slope, s of the graph.
ix. State two precautions taken to obtain accurate results.
(b)i. Use your graph to determine the value of d = l = 1.5A.
ii. State two factors that affect the resistance of a wire.
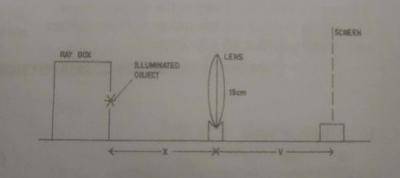
You are provided with a metre rule, lens, screen, ray box, and other necessary apparatus.
i. Set up the experiment as shown in the diagram above. Measure and record the diameter a\(_{0}\), of the illuminated object.
ii. Place the object at a distance x= 25cm from the lens. Adjust the screen until a sharp image is obtained on the screen.
iii. Measure and record the diameter, a, of the image.
iv. Measure and record the distance v between the lens and the screen.
v. Evaluate y = P = \(\frac{1+y^{2}}{y}\) and T= x+v.
vi. Repeat the procedure for x = 30cm, 35cm, 40cm and 45cm. In each case, determine the corresponding values of a,v,y, P and T.
vii. Tabulate your results.
viii. Plot a graph of P on the vertical axis against T on the horizontal axis starting both axes from the origin (0,0).
ix. Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
x. Determine the intercept, c, on the horizontal axis.
xi Evaluate K = \(\frac{c}{2}\)
xii. State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. Explain the statement, the focal length of a converging lens is 20cm.
ii. An object is placed at a distance x from a converging lens of focal length 20cm. If the magnification of the real image is 5, calculate the value of x.
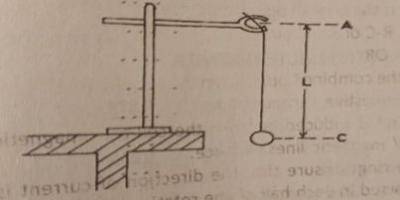
You are provided with a pendulum bob, a metre rule, a stopwatch, a retort stand with clamp, and other necessary apparatus.
i. Suspend the pendulum bob from the clamp as illustrated in the diagram.
ii. Adjust the pendulum such that AC=L= 90 cm
iii. Displace the pendulum bob slightly such that it oscillates in a vertical plane.
iv. Measure and record the time t for 20 complete oscillations.
v. Evaluate T and \(\sqrt L\)
vi.Repeat the procedure for four others values of L= 80 cm,70 cm, 60 cm, and 50cm.
vii. Tabulate your readings
viii. Plot a graph with T on the vertical axis and \(\sqrt L\) on the horizontal axis.
ix. Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
x. Evaluate g= \(\frac{4\pi^{2}}{5^{2}}\)
xi. State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b) i. Determine from your graph, the period of the pendulum for L= 75 cm.
ii. A simple pendulum bob is set into simple harmonic motion. Sketch a diagram of the setup and indicate on it; the positions of:
(a) maximum velocity.
(b) maximum acceleration of the bob
(a) Define binding energy in an atom.
(b) List three evidence to support the claim that X-rays are electromagnetic waves.
(c) List three peaceful uses of nuclear energy.
(d) Light of wavelength 4.5 x 10\(^{-7}\) in is incident on a metal resulting in the emission of photo electrons. If the work function of the metal is 3.0 x 10\(^{-9}\) J, calculate the:
(i) frequency of the incident light;
(ii) energy of the incident light;
(iii) energy of the photoelectrons. [Speed of light = 3.0 x 10\(^8\) ms\(^{-1}\), h = 6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\) Js]
(a) Define:
(i) reactance;
(ii) impedance in an a.c.
The diagram here illustrates an a.c. generator. When the coil is rotated, an e.m.f is induced in the coil.
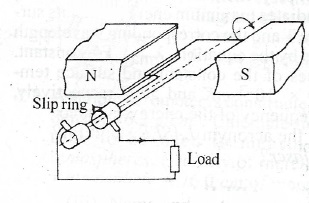
(i) Explain why an e.m.f. is induced.
(ii) State the purpose of the slip-rings.
(iii) Name and state the law used to determine the direction of the induced current.
(iv) State two ways to increase the induced e.m.f.
(c) A lamp is rated 12 V. 6 W. Calculate the amount of energy transformed by the lamp in 5 minutes.
(a) Define dffraction.
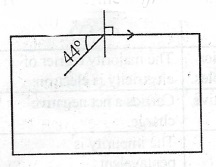
(b)(i) Explain critical angle. The diagram here illustrates a ray of light passing through a rectangular transparent plastic block \(\alpha\) Determine the value of the critical angle. \(\beta\) Calculate the refractive index of the block.
(c) A pipe closed at one end has fundamental frequency of 200Hz. The frequency of the first overtone of the closed pipe is equal to the frequency of the first overtone of an open pipe. Calculate the:
(i) fundamental frequency of the open pipe;
(ii) length of the closed pipe;
(iii) length of the open pipe. [Speed of sound in air = 330 ms\(^{-1}\)]
(a) List two factors each that affect heat loss by:
(i) radiation;
(ii) convection.
(b) State two factors that determine the quantity of heat in a body.
(c) Explain the statement: The vecilic latent heat of vaporization of mercury is 2.72 x 10\(^5\) Jkg\(^{-1}\).
(d)A jug of heat capacity 250 Jkg\(^{-1}\) contains water at 28°C. An electric heater of resistance 35\(\Omega\) connected to a 220 V source is used to raise the temperature of the water until it boils at 100°C in 4 minutes. After. another 5 minutes, 300 g of water has evaporated. Assuming no heat is lost to the surroundings, calculate the:
(i) mass of water in the jug before heating;
(ii) specific latent heat of vaporization of steam. [Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 kg\(^{-1}\)K\(^{-1}\)]
(a) Define uniform acceleration.
(b) Forces act on a car in motion. List the
(i) horizontal forces and their directions;
(ii) vertical forces and their directions
(c) A car starts from rest and accelerate uniformly for 20s to attain a speed of 25 ms\(^{-1}\). It maintains this speed for 30s before decelerating uniformly to rest. The total time for the journey is 60s.
(i) Sketch a velocity-tune graph for the motion.
(ii) Use the graph to determine the (\(\alpha\)) total distance travelled by the car (\(\beta\)) deceleration of the car.
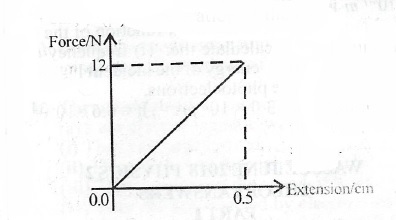
The figure here illustrates force-extension graph for a stretched spiral spring. Determine the work done on the spring.
A black body radiates maximum energy when its surface temperature T and the corresponding wavelength \(\lambda\)max are related by the equation \(\lambda\)max T = constant. Given the values of the constant and surface temperature as 2.9 x 10\(^{-3}\) mK and 57°C respectively; Calculate the frequency of the energy radiated.
A missile is projected so as to attain its maximum range. Calculate the maximum height attained if the initial velocity of projection is 200 ms\(^{-1}\). [g = 10ms\(^{-2}\)]
(a) What is an intrinsic semiconductor?
(b) Distinguish between the p-type and n-type semi-conductors.
(a) Define strain.
(b) A rubber band is stretched to twice its original length. Calculate the strain on the rubber band.
A nuclide is represented by \(_{32}^{70}B\). Determine its neutron-proton ratio
- A. 0.5
- B. 0.8
- C. 1.2
- D. 1.5
In which of the following fields is radioisotopes not used?
- A. Medicine
- B. Oil industry
- C. Agriculture
- D. Weather forecast
Which of the following radiations has the longest wavelength?
- A. Gamma ray
- B. Radio wave
- C. Infrared ray
- D. X-ray
In which of the following situations is photoelectric effect employed?
I. Automatic devices for switching on light at dusk
II. Automatic doors in departmental stores
III. Automatic devices for switching on air conditioners
IV. Automatic voltage stabilizers
- A. I, II and IV only
- B. I, III and IV only
- C. III and IV only
- D. I and II only
Which of the following is emitted in a process of natural radioactivity?
- A. \(\alpha\)- particles and \(\beta\)- particles
- B. \(\alpha\)- particles and X-rays
- C. \(\beta\)- particles and X-rays
- D. \(\lambda\)- rays and X-rays
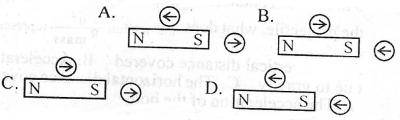
A student uses two compass needles to investigate the magnetic field around a bar magnet. Which of the following diagrams show the correct directions of the needles?
- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. D


