
You are provided with a battery of e.m.f. E, a key K, a voltmeter, a standard resistor R\(_{0}\) = 2\(\Omega\), a resistance box R, and some connecting wires.
i. Measure and record the e.m.f. E of the battery.
i. Set up a circuit as shown in the diagram above with the key open.
iii. Set the resistance on the resistance box to R 22.
iv. Close the key, read and record the potential difference V on the voltmeter.
v. Evaluate V\(^{-1}\)
vi. Repeat the procedures for five other values of R = 5\(\Omega\) 10\(\Omega\),12\(\Omega\),15\(\Omega\) and 20\(\Omega\). In each case, record V and evaluate V\(^{-1}\)
vii. Tabulate the results.
viii. Plot a graph with R on the vertical axis and V\(^{-1}\) l on the horizontal axis, starting both axes from the origin (0,0).
ix. Determine the slope, s, of the graph and the intercept c on the vertical axis.
x. Calculate \(\propto\) and \(\beta\) from the equations s = R\(_{0}\) \(\propto\) and c= – (R\(_{0}\)+B).
xi. State two precautions taken to obtain accurate results.

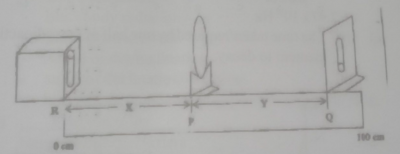
You are provided with a converging lens and holder, a screen, a ray box containing an illuminated object pin, and a meter rule.(See illustration above)
i. Place the lens in its holder such that it is facing a distant object seen through a well-lit laboratory window. Move the screen to and fro until a sharp image of the distant object is formed on it. Measure the distance, f\(_{0}\), between the screen and the lens.
ii. Clamp the meter rule securely to the table. Place the illuminated object pin at the end R of the meter rule.
iii. Place the lens at a position P such that X = RP = 20cm.
iv. Move the screen to a position Q to receive a sharp image of the object. Measure the distance Y = PQ.
v. Evaluate Z = (X+Y)
vi. Repeat the procedure for five other values of x = 25cm. 3Ocm, 35cm, 40cm and 45cm. In each case, record X,Y and evaluate Z.
vii. Tabulate the results.
viii. Plot a graph with Z on the vertical axis and X on the horizontal axis. Draw a smooth curve through the points.
ix. Determine from your graph the minimum value of Z=Z\(_{0}\) and its corresponding distance
x. Evaluate W = ½ (\(\frac{Z_0}{4} + \frac{X_0}{2}\))
xi. State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b) i. Draw a ray diagram to show how a Convex lens forms an image of magnification less than one.
ii. Name two pairs of features in the human eye and a lens camera that performs similar functions.
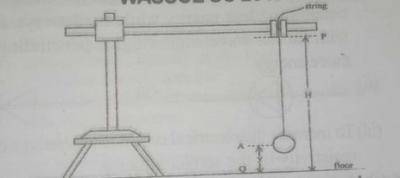
You are provided with a stopwatch, a meter rule, a split cork, retort stand and clamp, a pendulum bob, a piece of thread, and other necessary apparatus.
i. Place the retort stand on a laboratory stool. Clamp the split cork.
ii. Suspend the pendulum bob from the split cork such that the point of support P of the bob is at height H = 100cm above the floor Q. The bob should not touch the floor and H should be kept constant throughout the experiment.
iii. Adjust the length of the thread such that the center A of the bob is at a height y= AQ= 20cm from the floor.
iv. Displace the bob such that it oscillates in a horizontal plane.
v. Take the time t for 20 complete oscillations.
vi. Determine the period T of oscillation and evaluate T
vii. Repeat the procedure for four other values of y = 30cm, 40cm, 50cm, and 60cm. In each case, determine T and T.
viii. Tabulate the results.
ix. Plot a graph of T on the vertical axis and y on the horizontal axis, starting both axes from the origin (0,0).
x. Determine the slope, s, of the graph and the intercept c on the vertical axis.
xi. If in this experiment SR= c, calculate R.
x. State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b) i. The bob of a simple pendulum is displaced a small distance from the equilibrium position and then released to perform simple harmonic motion Identify where its:
(\(\propto\)) kinetic energy is maximum
(\(\beta\)) acceleration is maximum
ii. An object of weight 120N vibrates with a period of 4.0s when hung from a spring. Calculate the force per unit length of the spring. [g= 10ms\(^{-2}\), \(\pi\)=3.142]
(a) (i) Define atomic spectra.
(ii) Differentiate between emission spectra and absorption spectra.
(b)

The diagram above illustrates an electron transition from energy level n = 3 to n = 1. Calculate the:
(i) energy of the photon
(ii) frequency of the photon
(ii) wavelength of the photon [h = 6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\)J s, c = 3.0 x 10\(^8\) ms\(^{-1}\); 1 ev = 1.6 x 10\(^{-19}\) J]
c)(i)Differentiate between soft x-rays and hard x-rays
(ii) Draw the circuit symbol for a p-n junction diode.
(iiii) Give the reason for doping a semiconductor material
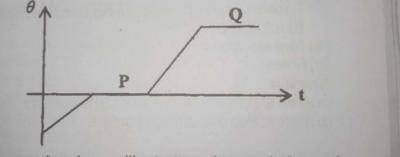

The graph above illustrates the variation of temperature \(\theta\) with time (t) for a solid that is being heated. Which processes take place at segments P and Q respectively?
- A. Freezing and vaporization
- B. Evaporation and solidification
- C. Melting and boiling
- D. Condensation and evaporation
When ultraviolet light is incident on certain metallic p articles are emitted. These particles are called
- A. positrons
- B. protons
- C. photoelectrons
- D. photons
Which of the following properties is not exhibited by sound waves?
- A. Diffraction
- B. Polarization
- C. Interference
- D. Reflection
Which of the following statements about a neutral atom is correct? The
- A. core is composed of electrons and protons
- B. number of electrons is equal to that of neutron
- C. number of neutrons is equal to that of protons
- D. number of protons is equal to that of electrons.
The area under a velocity-time graph represents
- A. speed
- B. acceleration
- C. moment
- D. distance
An instrument used to measure relative humidity is the?
- A. hygrometer
- B. hydrometer
- C. pyrometer
- D. manometer
The nucleon and proton numbers of a neutral atom of an element are 238 and 92 respectively. Determine the number of neutrons in the atom.
- A. 119
- B. 330
- C. 165
- D. 146
Which of the following liquids has the highest surface tension?
- A. Soapy water
- B. Cold water
- C. Hot water
- D. oily water
Which of the following materials does not serve as a safety device in electrical circuits?
- A. Connecting wires
- B. Earth wire
- C. Fuse
- D. Switch
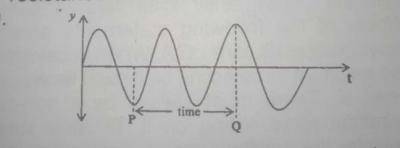

In the diagram above, the time taken to trace a wave between P and Q is?
- A. 2 periods
- B. 1 period
- C. 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) periods
- D. 1\(\frac{1}{4}\) periods
Which of the following thermometers is used to measure the temperature of the human body?
- A. Thermocouple
- B. Alcohol-in-glass thermometer
- C. Gas thermometer
- D. Platinum resistance thermometer
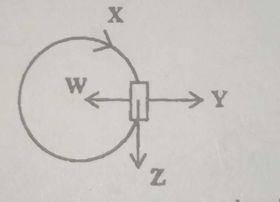

The diagram above illustrates an object moving in a circular path at a constant speed. Which of the arrows indicates the direction of linear velocity?
- A. z
- B. X
- C. Y
- D. W
Two bodies of masses 3.0 kg and 2.0 kg are separated by a distance of 50 cm. Calculate the force of attraction between them. [G = 6.67 x 10\(^{-11}\) Nm\(^2\) kg\(^2\)]
- A. 1.6 x 10\(^{-9}\)N
- B. 1.3 x 10\(^{3}\)N
- C. 2.3 x 10\(^{3}\)N
- D. 5.0x 10\(^{3}\)N
A rectangular piece of iron measuring 4 cm by 3 cm at 20\(^o\)C is heated until its temperature increases by 100 C. Calculate the new area of the metal. [Linear expansivity of iron is 1.2x 10\(^{-5}\) K\(^{-1}\)]
- A. 12.0144 cm\(^3\)
- B. 12.0346 cm\(^3\)
- C. 12.0288 cm\(^3\)
- D. 12.0173 cm\(^3\)
A ray of light traveling from a rectangular glass block of refractive index 1.5 into air strikes the block at an angle of incidence of 30. Calculate its angle of refraction.
- A. 48.6°
- B. 19.5°
- C. 20.0
- D. 45.0
The anomalous expansion of water occurs in the range
- A. 0 °C to 100 °C
- B. 0 °C to 4 °C
- C. 4 °C to 100 C
- D. -4 °C to 0 °C
Which property of a wave remains constant when the wave travels from one medium into another?
- A. Amplitude
- B. Wavelength
- C. Velocity
- D. Frequency


