ANWSER
Question 1:
What are KOMS structures?
Answer: KOMS structures are functional components that make a road operational.
—
### Question 2:
What is the calibration of Colter + Appyster?
Answer: The calibration of Colter + Appyster is Asphalt or Tramicayam.
—
### Question 3:
What is the role of an estimator in construction?
Answer:
– The estimator evaluates standard measurements.
– They ensure the quality of work by adhering to standard material specifications.
– They provide a common language for measurement and define the nature of the work to be done.
—
### Question 4:
Describe the construction method for piles.
Answer:
– Displacement Pile: Driven into the ground, displacing soil.
– Replacement Pile (Bored Pile): A hole is drilled, and concrete is cast in place.
– Economical Choice: Depends on depth; replacement piles are used for deeper foundations.
– Obstruction Handling: Delays due to obstructions must be accounted for in project timelines.
—
### Question 5:
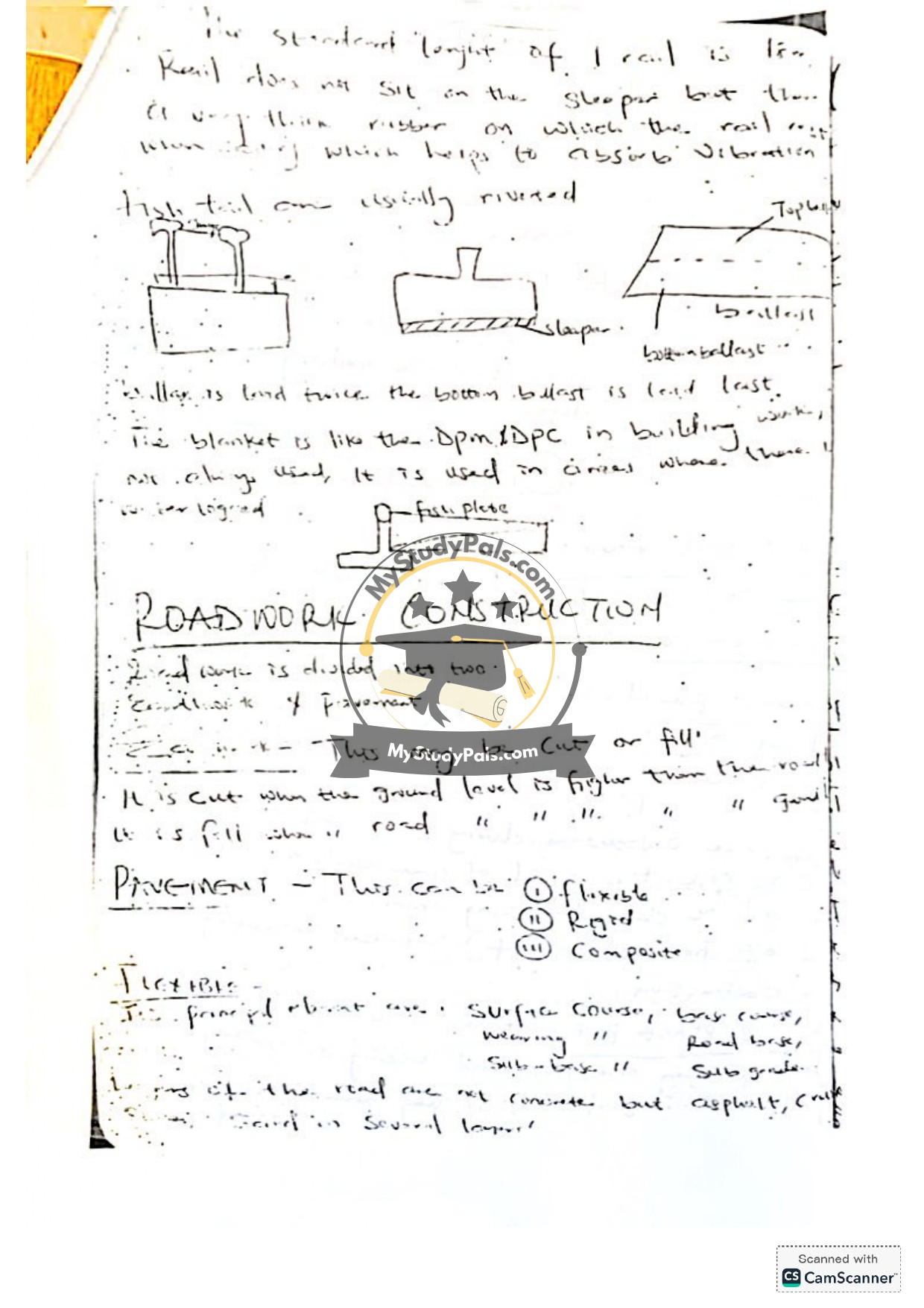
What are the components of railway track laying?
Answer:
– Ballast: Initial and top layers for stability.
– Sleepers: Made of steel, timber, or concrete (pre-stressed).
– Track Gauge: Standard distance between rails (not more than 2ft).
– Slope & Speed: Adjustments for hills and transitions.
– Materials: Rails must not have smooth/low interior steps.
—
### Question 6:
What is the role of a council in railway construction?
Answer:
– Ensures compliance with railway laws and standards.
– Manages land use and track alignment (e.g., Young Earl & Top Erlish).
– Oversees material selection (e.g., sleepers: steel, timber, or concrete).
—
### Question 7:
What is composite pavement?
Answer:
– A combination of Concrete Slab (rigid) and Continuous Surfaces (flexible).
– Provides rigidity and durability, suitable for high-traffic areas (e.g., TARMA).
– Layers include: Subgrade, Sub-base, Concrete, Bituminous spray, and Surface finish.
—
### Question 8:
What are the key elements of specification writing?
Answer:
1. Clarity: Avoid ambiguity; use common terms.
2. Material Details: Include manufacturer references, quality standards, and required tests.
3. Compliance: Adhere to codes (e.g., British Standards).
4. Scope: Define work methods, timelines, and site conditions.
—
### Question 9:
Differentiate between “Close Specification” and “Open Specification.”
Answer:
– Close Specification:
– Restricted to a single supplier/material (e.g., “300mm×300mm×3mm Asphalt by XYZ Corp”).
– Used for exact replication or proprietary products.
– Open Specification:
– Allows flexibility in material/method selection (e.g., “galvanized steel shaft”).
– Contractor chooses suitable options within broad limits.
—
### Question 10:
What is the principal element of rigid pavement?
Answer:
– Concrete Slab (rigid layer) formed by consolidating all road layers.
– Provides durability and load distribution.
—