ANWSER
SECTION A
Question 1:
Answer: Ammeter
Question 2:
Answer:
14,400 seconds ÷ 3,600 seconds/hour = 4 hours
Question 3:
Answer: Hertz (Hz)
Question 4:
Answer: Brownian motion of particles in a gas or liquid
Question 5:
Answer: Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
Question 6:
Answer:
1. Kinetic energy
2. Potential energy
Question 7:
Answer: The current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, provided the temperature remains constant (V = IR).
Question 8:
Answer: Radio waves
Question 9:
Answer: \( v = u + at \)
Question 10:
Answer:
1. Force
2. Velocity
—
SECTION B
Question 1a:
Answer:
– Heat: A form of energy transferred due to temperature difference.
– Temperature: A measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance.
Question 1b:
Answer:
1. Expansion
2. Change of state (e.g., melting, boiling)
3. Increase in temperature
4. Thermal stress
5. Emission of thermal radiation
Question 1c:
Answer:
1. Conduction: Heat transfer through a material without bulk motion (e.g., metal rod).
2. Convection: Heat transfer through fluid motion (e.g., boiling water).
3. Radiation: Heat transfer via electromagnetic waves (e.g., sunlight).
—
Question 2i:
Answer:
– Electric stove: 2000W × 2h = 4000 Wh
– Electric fan: 250W × 8h = 2000 Wh
– Electric radio: 150W × 8h = 1200 Wh
– Light bulb: 15W × 12h = 180 Wh
Question 2ii:
Answer:
– Electric stove: 4000 Wh × 30 = 120,000 Wh
– Electric fan: 2000 Wh × 30 = 60,000 Wh
– Electric radio: 1200 Wh × 30 = 36,000 Wh
– Light bulb: 180 Wh × 30 = 5,400 Wh
Question 2iii:
Answer:
Total energy = 120,000 + 60,000 + 36,000 + 5,400 = 221,400 Wh
Question 2iv:
Answer:
221,400 Wh ÷ 1000 = 221.4 kWh
Cost = 221.4 × N15 = N3,321
Question 2v:
Answer:
a.
(i) Electromagnetic waves: Light, X-rays
(ii) Mechanical waves: Sound waves, water waves
b.
(i) Wind instrument: Flute
(ii) String instrument: Guitar
(iii) Percussion instrument: Drum
c.
(i) Series: \( 5Ω + 2Ω = 7Ω \)
(ii) Parallel: \( \frac{1}{5} + \frac{1}{2} = \frac{7}{10} \) → \( R = \frac{10}{7} ≈ 1.43Ω \)
—
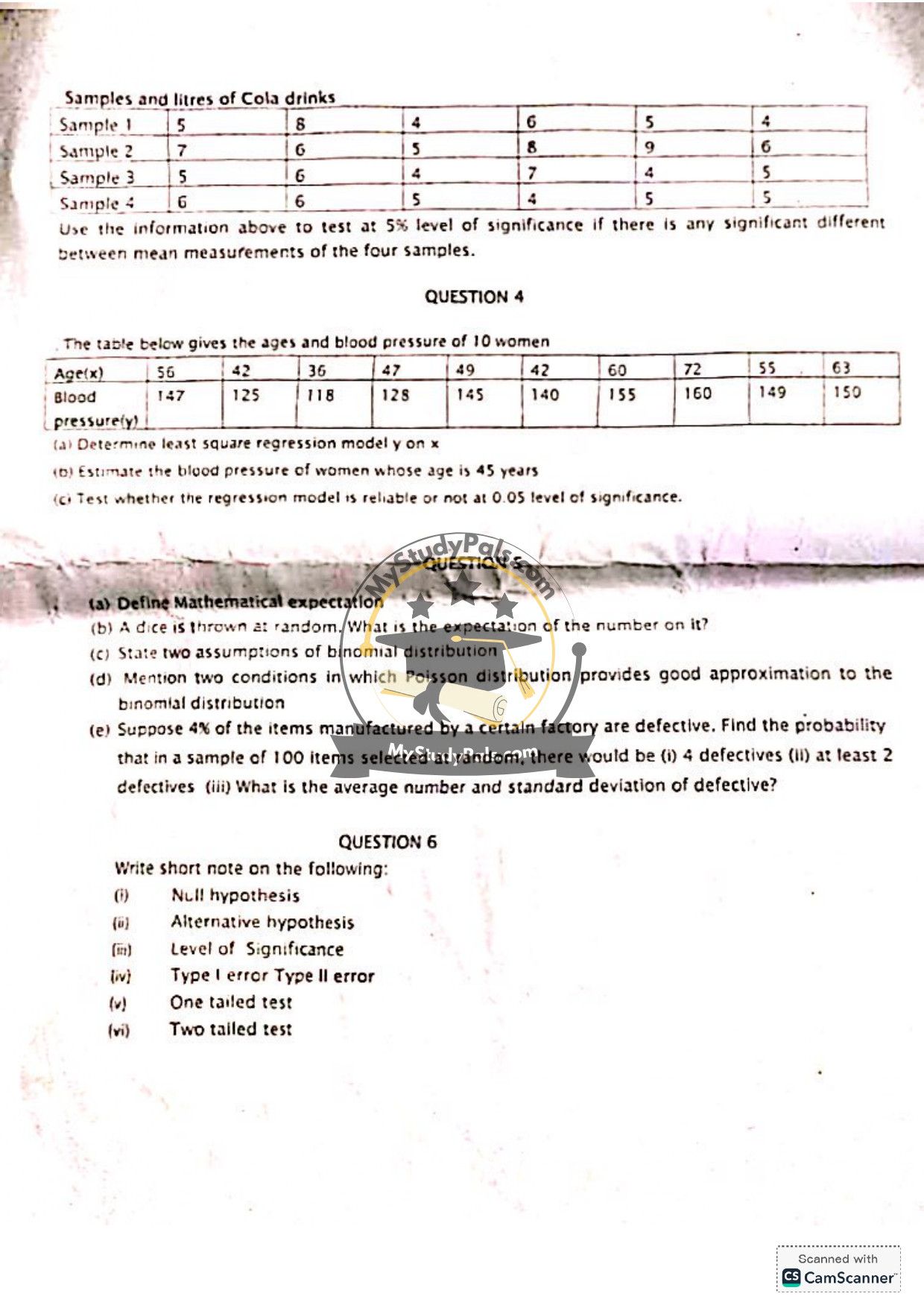
Question 4a:
Answer:
The least square regression model is \( y = a + bx \), where calculations yield:
\( y ≈ 90.27 + 0.97x \)
Question 4b:
Answer:
For \( x = 45 \):
\( y ≈ 90.27 + 0.97(45) ≈ 133.92 \) (estimated blood pressure)
Question 4c:
Answer:
Perform a t-test or F-test for regression significance. If p-value < 0.05, the model is reliable.
—
Question 5a:
Answer:
Mathematical expectation is the average value of a random variable over many trials.
Question 5b:
Answer:
Expectation = \( \frac{1+2+3+4+5+6}{6} = 3.5 \)
Question 5c:
Answer:
1. Fixed number of trials (n).
2. Independent trials with constant success probability (p).
Question 5d:
Answer:
1. Large \( n \) and small \( p \).
2. \( np \) is moderate (e.g., \( np ≤ 5 \)).
Question 5e:
Answer:
(i) \( P(X=4) ≈ \frac{e^{-4}(4)^4}{4!} ≈ 0.1954 \)
(ii) \( P(X≥2) = 1 – P(X=0) – P(X=1) ≈ 1 – e^{-4} – 4e^{-4} ≈ 0.9084 \)
(iii) Average = \( np = 4 \); Standard deviation = \( \sqrt{np(1-p)} ≈ 1.96 \)
—
Question 6:
Answer:
(i) Null hypothesis (\( H_0 \)): Default assumption of no effect/difference.
(ii) Alternative hypothesis (\( H_1 \)): Claim to test against \( H_0 \).
(iii) Level of Significance (\( \alpha \)): Probability threshold for rejecting \( H_0 \) (e.g., 0.05).
(iv) Type I error: Rejecting \( H_0 \) when true; Type II error: Failing to reject \( H_0 \) when false.
(v) One-tailed test: Tests effect in one direction.
(vi) Two-tailed test: Tests effect in both directions.