The process by which an animal re-ingests its soft faeces to recover unused nutrients is called______
- A. coprophagy
- B. digestion
- C. regurgitation
- D. rumination
Which of the following members of the bee colony produces honey?
- A. Brood
- B. Drone
- C. Worker
- D. Queen
Fresh forage cut and served to farm animals in their shed is referred to as_______
- A. haulm
- B. hay
- C. silage
- D. soilage
Which of the following parasites Is controlled by dipping?
- A. Liver Fluke
- B. Louse
- C. Tapeworm
- D. Tsetse Fly
Cellulose is broken down in the rumen mainly with the help of _____
- A. Bacteria
- B. Fungi
- C. Protozoa
- D. Viruses
Docking is the process of removing an animal’s__________
- A. Horn
- B. Ovary
- C. Tail
- D. Testes
(a) Mention FIVE advantages and THREE Disadvantages of castration in Livestock production
(b) (i) Draw and label FIVE parts of the digestive system of a domestic fowl
(ii) State ONE function of each of the parts labelled in (b) (i)
Which of the following organisms is an ectoparasite?
- A. Flea
- B. Liver Fluke
- C. Roundworm
- D. Cattle egret
An area of land on which forage grass and legumes naturally grow is called________
- A. forest
- B. grassland
- C. rangeland
- D. artificial pasture
Mad cow disease can easily spread on a farm through___________
- A. overgrazing
- B. overcrowding
- C. poor feeding
- D. poor ventilation

The tool illustrated in the diagram above is_________
- A. Hand fork
- B. Digging fork
- C. Garden fork
- D. Hay fork
The egg yolk in the diluents used in artificial insemination_________
- A. protect the semen from mixing with the glycine
- B. prevents the semen from being contaminated
- C. protect the semen from sunlight
- D. provide food for the spermatozoa
In order to prevent overgrazing of pasture, a farmer should adopt___________
- A. regular weeding
- B. controlled stocking
- C. fertilizer application
- D. pest and disease control
The keeping of honey bees is known as_________
- A. apiary
- B. apiculture
- C. aviculture
- D. silviculture
Which of the following characteristics are associated with protein concentrates?
I. High in energy
II Low in fibre
III. Highly digestible
- A. I and II only
- B. I and III only
- C. II and III only
- D. I, II and III
Which of the following plants is a source of coagulant in local cheese making?
- A. Mangifera indica
- B. Panicum maximum
- C. Azonopus compressus
- D. Calotropics procera
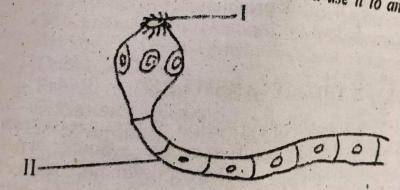
The secondary host of the organism is_______
- A. Chicken
- B. Human
- C. Pig
- D. Water Snail
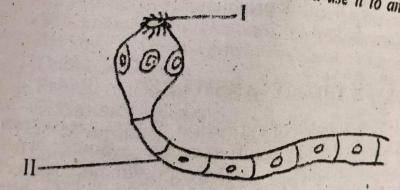
The part labelled II is the ________
- A. hook
- B. mouth
- C. proglottid
- D. sucker
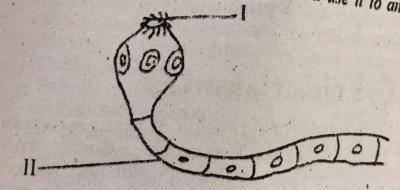
The part labelled I is called________
- A. hook
- B. mouth
- C. proglottid
- D. sucker
One of the aims of animal improvement is to _________
- A. transfer desirable qualities from exotic breeds to local breeds
- B. produce animals susceptible to local pests and diseases
- C. produce animals with high rate of infantile mortality
- D. produce animals whose parents perform better than the offspring
Which of the following activities are involved in the process of rumination?
I. Re-chewing
II Regurgitation
III, Vomiting
- A. I and II only
- B. I and III only
- C. II and III only
- D. I, II and IIl


