(a) State two uses of specimen D in animal production (b) Mention four activities which requires the use of specimen E in animal production. (c)(i) State three precautions which should bee taken by the farmer when using specimen F for the purpose of catration in pigs. (d) Name three tools which could be used in place of specimen F for carrying out castration in famr animals.
(a)(i) Mention the major nutrients supplied by specimen A (Fish meal) in animal diet. (ii) State four functions of the nutrients mentioned in 1(a)(i). (iii) Name three feed stuffs that could be used in place of specimen A.
(b)Give four reasons for keeping specimen B on a farm (Chicken)
(c) Mention three management practices which are carried out during the rearing of specimen B.
(a) Explain each of the following terms as used in animal production: (i) flushing: (i) dystocia: (iii) parturition.
(b) State five ways in which fencing is important in livestock production.
(c) Mention five ways in which rearing of rabbits is important.
(d) List four disadvantages of deep litter system in poultry production.
(a) Explain the following terms as used in pasture and range management. (i) fodder; (ii) paddocking: (iii) reseeding; (iv) stocking rate; (v) natural pasture.
(b) State five factors which could affect the establishment of pasture in West Africa.
(c) State five ways in which weeds are of economic importance in livestock production.
(a) Mention two organs each in each of the following parts of rabbit: (i) head; (ii) thorax; (i) abdomen.
(b) State one function of each of the following organs in farm animals: (i) caecum; (1) gizzard; (1) crop: (iv) rumen; (v) lung
(C) State six practical ways of checking malnutrition in livestock production.
(d) Mention three examples of non-traditional farm animals.
a)(i) Explain the term monogastric.
(ii) Give two examples of monogastric animals.
(b) Explain each of the following terms as used in animal nutrition: (i) concentrate: (ii) additive.
(c) State four ways in which roughage is important in the diet of farm animals.
(d) List four materials which could be used in milking cow.
(e) Mention two animals each which could be fed on each of the following forms of prepared feed: (i) pellets: (ii) mash.
(a) Explain each of the following terms as used in animal husbandry:
(i) coprophagy: (ii) rumination (iii) candling (iv) tethering.
(b) List four local materials which could be used for constructing a goat house.
(c)(i) Name the three members of the honey bee colony. (ii) State five ways in which honey beekeeping is important.
(a) Explain each of the following mating methods in farm animals: (i) hand mating (ii) pen mating (iii) pasture mating.
(b)(i) Mention two advantages of each of the mating methods explained in (a).
(ii) Mention two disadvantages of each of the mating methods explained in (a).
(c) Mention two methods of collecting semen from a bull.
The botanical name of Guinea grass is_________.
- A. Pennisetum pupureum
- B. Inmperata cylindrica
- C. Panicum maximum
- D. Axonopus compressus
An organism that habours another organism is referred to as________
- A. host
- B. parasite
- C. pest
- D. predator
A record which shows all the assets on a poultry farm is called_________
- A. Inputs record
- B. Inventory record
- C. Labour record
- D. Production record
Which of the following vitamins is water-soluble?
- A. Vitamin A
- B. Vitamin B
- C. Vitamin D
- D. Vitamin E
An ewe which is not lactating after lambing should be given_________
- A. antibiotics
- B. oxytocin
- C. iron dextran
- D. progesterone
Which of the following terms is a technique used in processing farm animals?
- A. Fattening
- B. Flushing
- C. Slaughtering
- D. Steaming up
The function of an electro-ejaculator during artificial insemination is to___________
- A. collect semen
- B. service the female
- C. induce semen release
- D. induce heat in the animal
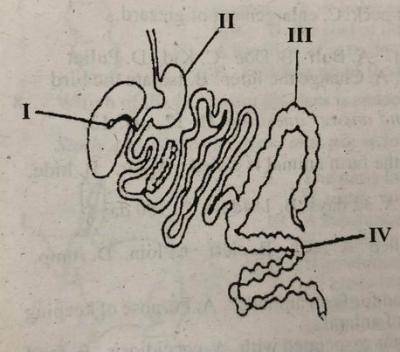
The parts labelled I and II are known respectively as________
- A. stomach and caecum
- B. liver and stomach
- C. gall bladder and caecum
- D. gall bladder and stomach
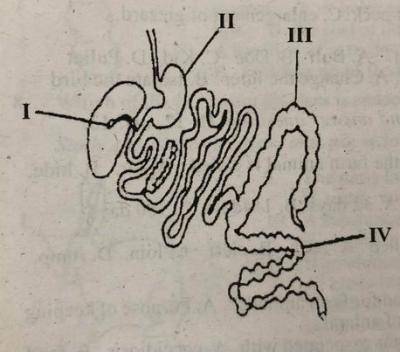
Which of the following farm animals has the digestive system shown in the diagram?
- A. Chicken
- B. Pig
- C. Rabbit
- D. Sheep
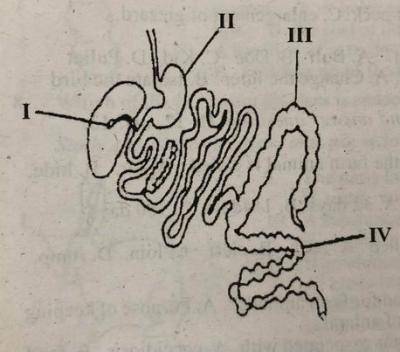
Cellulose digestion by micro-organisms takes place in the part labelled _______
- A. I only
- B. II only
- C. III only
- D. IV only
Which of the following practices is most vital during introduction of a farm animal?
- A. Medication
- B. Quarantine
- C. Sanitation
- D. Vaccination
Forage crops could be ploughed in the soil to serve as_______
- A. compost manure
- B. farmyard manure
- C. green manure
- D. cover crops
Chronic Respiratory Disease is prevalent in________
- A. cattle
- B. poultry
- C. rabbit
- D. swine


