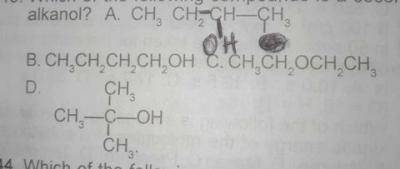
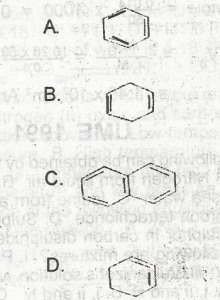
Which of the following compounds is a secondary alkanol?
- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. D
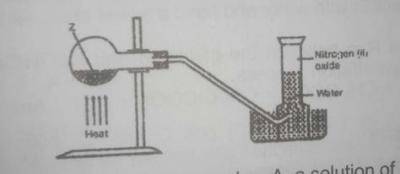
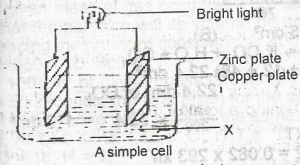
In the experiment above. Z can be
- A. a solution of sodium dioxonitrate (lll) and ammonium chloride
- B. a solution of lead trioxnitrate (V)
- C. a solution of sodium trioxonitrate (V) and ammonium chloride
- D. concentrated tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid and sodium trioxonitrate (V)
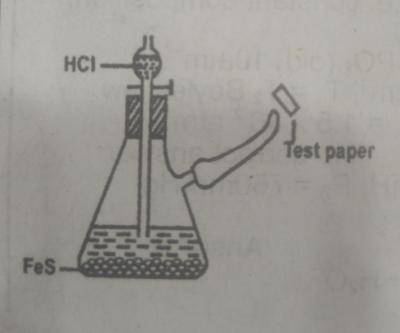
The appropriate test paper to use in the above experiment is moist
- A. litmus psper
- B. potassium heptaoxodichromate (IV) paper
- C. lead (ll) trioxonitrate (V) paper
- D. universal indicator paper
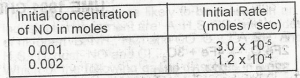
The data in the table above shows the rate of reaction of nitrogen (ll) oxide with chlorine at 25oC It can be concluded that doubling the initial concentration of NO increase the rate of reaction by a factor of
- A. two
- B. three
- C. four
- D. five
50 cm3 of sulphur (lV) oxide, 800 cm3 of carbon (IV) oxide will respectively saturate 1.0cm3 of water at 15oC. Which of the following is suitable for demonstrating the fountain experiment?
- A. Sulphur (IV) oxide and hydrogen chloride.
- B. Carbon (IV) oxide and ammonia
- C. Ammonia and hydrogen chloride
- D. Carbon (IV) oxide and Sulphur (IV) oxide
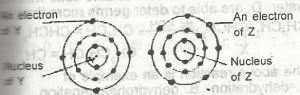
The electrons of two atoms Y and Z are arranged in shells as shown above. The bond formed between the atoms of Y and Z is
- A. ionic
- B. covalent
- C. dative
- D. metallic
Select the right answer from the structure above.Which of the following compounds represents the polymerization product of ethyne?
- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. D
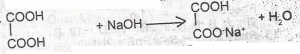
The above reaction is an example of
- A. a displacement reaction
- B. a neutralization reaction
- C. an elimination reaction
- D. saponification

Use the above graph above to answer this question . CH3-C = CH \(\frac{Na}{liq NH_3}\)> P, Compound P, in the above reaction, is
- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. D
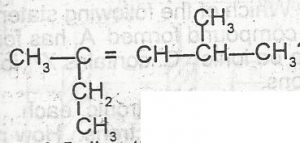
What is the IUPAC name for the hydrocarbon?
- A. 2-ethyl-4-methylpent-2-ene
- B. 3,5-dimethylhex-3-ene
- C. 2,4-dimethylhex 3-ene
- D. 2-methyl-4-ethylpent-3-ene
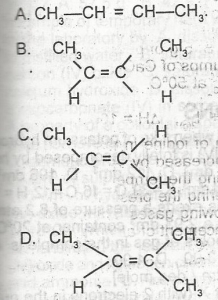
Use the graph above to answer this question. The structure of cis-2-butene is
- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. D
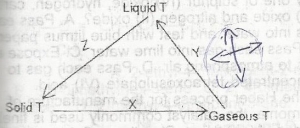
Changes in the physical in the scheme above.The letter X,Y and Z respectively represent
- A. sublimation, condensation and freezing
- B. sublimation, vapourization and solidification
- C. freezing, condensation and sublimation
- D. evaporation, liquefaction and solidification
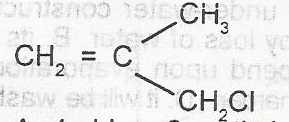
What is the IUPAC name for the compound
- A. 1-chloro-2-methylprop-2,3-ene
- B. 1-chloro-2-methylprop-2-ene
- C. 3-chloro-2-methylprop-1-ene
- D. 3-chloro-2methylprop-1,2-ene
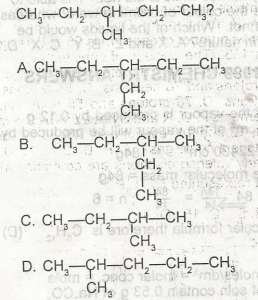
Use the figure above to answer this question. Which of the following is NOT a monomer?
- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. D
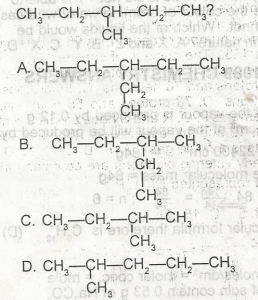
Use the figure above to answer this question. Which of the following compounds is an isomer of the compound
- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. D
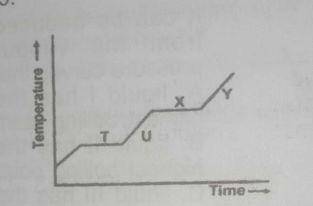
The above graph shows a typical heating curve from the solid phase through the liquid phase to the gaseous phase of a substance. Which part of the curve shows solid and liquid in equilibrium?
- A. T
- B. U
- C. X
- D. Y
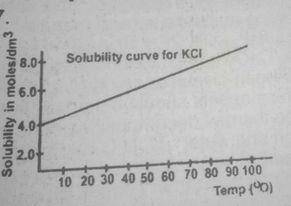
If in the graph above 1 dm 3 of a saturated solution of KCL is cooled from 80°C, the mass of crystals deposited will be
[K = 39, Cl = 35.5]
- A. 7.45 g
- B. 14.90 g
- C. 74.50 g
- D. 149.00 g
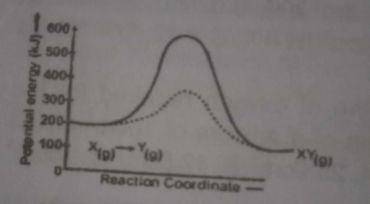
The above diagram gives the potential energy profile of the catalyst and uncatalysed reactions of X(g) + Y(g) → XY(g). Deduce the respective activation energies in KJ of the catalysed and uncatalysed reverse reactions: XY(g) → X(g) + Y(g)
- A. 300, 500
- B. 500, 300
- C. -300, -500
- D. -500, -300
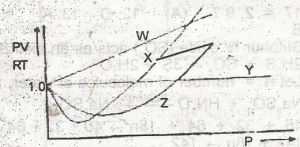
Which of the curves in the above graph illustrates the behaviour of an ideal gas?
- A. W
- B. X
- C. Y
- D. Z

In the above set up substances X and Y are respectively
- A. lime water copper (ll) tetraoxosulphate (lV)
- B. potassium trioxocarbonate and alkaline pyrogallol
- C. potassium hydroxide and alkaline pyrogallol
- D. potassium trioxocarbonate (lV) and concentrated tetraoxosulphate (IV) acid
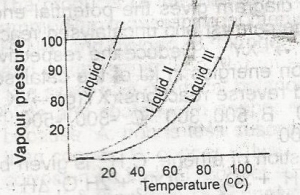
It can be deduced from the vapour pressure curves above that
- A. liqiud 1 has the highest boiling point
- B. liquid ll has the highest boiling point
- C. liquid lll has the highest boiling point
- D. liquid lll has the lowest boiling point


