50cm\(^{3}\) of sulphur (IV) oxide were produced at s.t.p. when some quantity of powdered sulphur were burnt in excess oxygen
(a) Write the equation for the reaction
(b) Calculate the volume of oxygen used up during the reaction
(c) Which of the gas laws is applicable? State the law.
(a) Arrange the following in their correct order of increasing energy: alpha particles, gamma rays and beta particles
(b) State one difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion
(a) Give one example of;
(i) heavy chemicals
(ii) fine chemicals
(b) Write the structural formulae and the names of compounds having the formula CH\(_4\)CI,
(a) Name two allotropes of carbon
(b) Name two products of the destructive distillation of coal and state one use of each.
(a) Explain the differences in the reactions of zinc with dilute trioxonitrate (V) acid and zinc with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(b) Write equations to illustrate how ammonia gas can be converted into trioxonitrate (V) acid.
(c) Calculate the mass of sodium trioxonitrate (V) produced when 30.0g of pure sodium hydroxide reacts with 100cm\(^3\) of 1.00 M trioxonitrate (V) acid. (H =1, N = 14, 0 = 16, Na = 23)
(d) Write the equations for the decomposition by heat of:
(i) sodium trioxonitrate(V);
(ii) copper (II) trioxonitrate (V);
(iii) mercury (II) trioxonitrate (V);
(a) Distinguish between a conductor and an electrolyte
(b)(i) State Faraday’s first law of electrolysis
(ii) Describe how you would investigate Faraday’s law of electrolysis, using copper (II) tetraoxosulphate (VI) solution and copper electrodes.
(c) 0.222g of a divalent metal is deposited when a current of 0.45 ampere is passed through a solution of its salt for 25 minutes using appropriate electrodes. Calculate the relative atomic mass of the metal. 1F = 96500C mol\(^{-1}\)
`(d) State two applications of electrolysis.
(a) List three characteristics of a homologous series
(b) Give one example of;
(i) alkanes; (ii) alkynes.
(c) A hydrocarbon contains 7.7% by mass of hydrogen and 92.3% by mass of carbon. The relative molar mass of the compound is 78.
(i) Derive the empirical formula of the compound and hence its molecular formula.
(ii) Name the hydrocarbon and write its structural formula. (H=1, C=12)
(d) Two hydrocarbons, X and Y were treated separated with acidified potassium tetraoxomanganate (VII) solution. X decolorized the solution and Y did not. Which of X and Y will undergo
(i) substitution reaction only,
(ii) both addition and substitution reactions.
(iii) polymerization?
(e) If ethanol is to be converted into ethanoic acid
(i) What are the conditions required?
(ii) name the type of reaction that will be involved and write the equation
(a) State Le Chatelier’s principle
(b) Use Le Chetelier’s principle to deduce the conditions that favour a high yield of ammonia in the Haber process
(c) Give the chemical test for ammonia.
(d) State what would be observed when aqueous ammonia solution is added to:
(i) zinc chloride solution, (ii) copper (II) tetraoxosulohate (V) solution
(e) Explain why the H — N — H bond angle in ammonia is less than that of H — C — H in methane
(f) Give two uses of ammonia.
(a) Name the components of
(i) producer gas; (ii) water gas;
(b) Give the reason why water is a better fuel than producer gas.
Consider the compounds represented as A and B below:
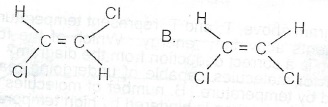
(a) What is the celationship between A and B? (
b) Name A and B.
(c) Will the chemical properties of A and B be the same? Give one reason for your answer.
(a) The half-life of 56/25 Mn is 9.3 x 10\(^3\)S. What does the statement mean?
(b) Give the three types of radiation that are usually emitted by radioactive substances.
(a) Name the gas evolved when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to each of the following solids and the mixture is warmed
(i) sodium trioxocarbonate (IV);
(ii) potassium trioxosulphate (IV);
(iii) iron (II) sulphide.
(b) Name the reagent(s) that you would use to identify the gas in (a)(ii) above.
Name the type of chemical process involved in the production of
(a) polythene from ethene
(b) ethene from kerosene fraction of petroleum.
(c) soap from vegetable oils
(d) margarine from vegetable oils
(a) Write the formula of the oxide of nitrogen in which nitrogen has oxidation number of (i) +1;
(ii) +2;
(iii) +3;
(iv) +4;
(b) State which of the oxides in (a) above is/are: (i) acidic (ii) neutral.
(a) Give two characteristic features of boiling
(b) What will be the effect of the following on the boiling point of water:
(i) addition of crystals of sodium chloride,
(ii) reduction of the atmospheric pressure?
(c) State two ways in which boiling differs from evaporation.
(a) Give one physical property of
(i) diamond;
(ii) graphite
(b) Give two uses of diamond
(c) evidence that shows that both graphite and diamond are allotropes of carbon.
(a) When is a sample of water said to be hard?
(b) State one difference between temporary and permanent hardness of water
(c) Give one method of removing hardness completely from water
(d) Name two local is used for the production of soap.
(a) Write the chemical equation for the formation of named alkanoate.
(b)(i) What are the monomers of protein called?
(ii) Write the two functional groups present in the monomers named in (b)(i) above
(iii) State the type of reaction that leads to the formation of proteins from their monomers.
(a)(i) Define oxidation in terms of electron transfer.
(ii) Write balanced equations for the half reactions for the following changes in acidic solution: Mn0\(^-_4\) + Fe\(^{2+}\) —> Mn\(^{2+}\) + Fe\(^{3+}\)
(b)(i) Distinguish between an electrolytic celI and an electrochemical cell.
(ii) Sketch a cell for the electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride. Lable the anode and the cathode and indicate the direction of electron flow. Give the electrode reactions.
(iii) Give one reason why a platinum anode is not suitable for the eloctrolysis in (b)(i) above.
(c) Calculate the mass of lead that would be deposited from a solution of lead (II) trioxonitrate by the same quantity of electrically depositing 1.35g of copper. (Cu = 63.5, Pb = 207)
(a)(i) Define the term addition polymerization
(ii) What type of organic compounds undergo addition polymerization
(iii) List two factors which affect the strength of polymers
(b) The diagram below shows some reaction pathways involving ethanol

(i) Write the name and structural of the organic product X
(ii) State the reagent for the conversation indicated as step A.
(iii) What type of reaction will ethanol undergo CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)COOH during the process of conversation indicated as step B?
(c)(i) Write three balanced equation for the complete combustion of ethanol in :date the volume of oxygen required at s.t.p for the complete combustion of ethanol. (H = 1, C = 12, O = 16, molar volume of gases at s.t.p. = 22.4 dm\(^3\))
(d)( i} State two substances produced when coal is heated in the absence of air
(ii) What name is given to the process in (d)(i) above?
(iii) State the importance of the non-volatile residue of the process named in (d)(iii) to the iron and steel industry.
Consider the reaction represented by the equation: 2SO\(_{2(g)}\) + O\(_{2(g)}\) 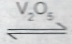 2SO\(_{3(g)}\). \(\Delta\)H = 188KJ.
2SO\(_{3(g)}\). \(\Delta\)H = 188KJ.
(a) Write an expression for the equilibrium constant
(b) Sketch an energy diagram for the forward reaction, showing the profile for the catalyzed and non-catalyzed systems.
(c) state the reason, the effect of the following on the position of equilibrium of the system:
(i) increase in temperature
(ii) increase in pressure;
(iii) removal of some of the SO\(_3\) produced;
(iv) presence of V\(_2\)O\(_5\)
(d)(i) Write equations to show how the sulphur(VI) oxide is converted to tetraoxosulphate(VI) acid in the contact process
(ii) Give two uses of tetraoxosulphate(VI) acid.

