(a)(i) List two physical properties used as criteria for purity of substances
(ii) describe how you would prepare a pure, dry sample of sodium chloride crystals by a neutralization reaction, using bench reagents.
(iii) Give two other general methods for preparing soluble salts.
(b) Explain the following observations:
(i) a sheet of iron placed in dilute copper (II) tetraoxosulphate (VI) solution reddish brown;
(ii) the white gelatinous precipitate formed when a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution are added to a solution of aluminium salt dissolves in excess alkali;
(iii) the pale green prepared iron(II) chloride solution changes to brown on bubbling chlorine gas through it.
(iv) Write a balanced equation for the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid with marble. List two industrial process in which limestone is used as a raw material.
Liquefied air is mainly a mixture of nitrogen and oxygen which can be separated into its components by fractional distillation (Boiling point of nitrogen is 196°C, Boiling point of oxygen is 174°C)
(a) Name the fraction which distills over first. Give the reason for your answer.
(b) Give another industrial application of fractional distillation as a separation technique.
(a) Name the type of solid structure possessed by:
(i) diamond;
(ii) iodine;
(iii) sodium chloride.
(b) Give:
(i) one alloy of tin:
(ii) a common reducing agent which is a compound of tin.
(a) Arrange the first three members of the halogen family in their increasing order of electronegativity. Give the reason for your answer.
(b) State and explain what happens when chlorine reacts with starch iodide paper.
Benzene contains six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms.
(a)(i) Draw two stable structures of benzene to show how these atoms are arranged.
(ii) What is the concept behind these structures?
(b) Give (i) two uses of benzene. (ii) one industrial source of benzene.
(a) Give the formula indicating the relationship between entropy, free energy and enthalpy changes of a system.
(b) For each of the following, state whether entropy change is positive, negative or zero.
(i) H\(_2\)O\(_{(g)}\) -> H\(_2\)O\(_{(g)}\)
(ii) Cl\(_{2(g)}\) —> 2CI\(_{(g)}\)
(iii) HCI\(_{(g)}\) -> HCl\(_{(g)}\)
(a) Give one reason why a collision between reactants may not produce new species.
(b) Explain, illustrating with appropriate equation(s), why an aqueous solution of aluminium chloride is acidic.
(a) Balance the nuclear equation below and hence identify Y.
\(^{238}_{94}U \to ^{234}_{92}Th + Y\)
(b) In a tabular form, state two of the observations in the cathode ray experiment and the corresponding deductions.
A hydrocarbon X which decolorizes bromine water but has no action on ammoniacal silver trioxonitrate (V) solution was found to have a molar mass of 58 g mol\(^{-1}\)
(a) Deduce the molecular formula of X. (H = 1, C = 12)
(b) Write the structures of two isomers of X.
(a) Give two reasons why carbon(IV) oxide is used for extinguishing fire
(b) Explain briefly the water softening action of cation exchane resins.
(a) Write the electronic configuration of an element with atomic number 15, indicating the distribution of electrons in the energy sub-levels
(b) Give the formula and the colour of the complex formed between ammonia and copper (II) ions
(a) State two factors which can affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
(b) 0.72g of magnesium was added to different volumes of 2 mol. per dm\(^3\) hydrochloric acid. The volume of liberated was as measured at room temperature and pressure. The result of the experiment was as tabulated
| vol. of 2 mol. per dm\(^3\) HCl used (cm\(^3\) | Vol. of H\(_2\) evolved in cm\(^3\) (to the nearest 10cm\(^3\)) |
|
5 15 25 35 45 |
120 360 550 600 600 |
Use the data in the table to plot a graph of the volume of hydrogen liberated against the volume of acid used.
(c) From the graph in (b) above, determine the volume of: (i) hydrogen that would be produced if 50 cm\(^3\) of the acid were added to 0.72g of magnesium.
(ii) the acid which must be added to 0.72 g of magnesium to produce 480 cm\(^3\) of hydrogen;
(iii) the acid needed exactly to dissolve 0.72 g of magnesium completely.
(d) Explain your answer to (c)(iii).
(e) From your answers to (c) above, deduce the: (i) volume of the acid which will dissolve 1 mole of magnesium completely. (Mg = 24)
(ii) volume of hydrogen that would be liberated if 1 mole of magnesium dissolves completely in the acid;
(iii) equation for the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid. Show clearly how you arrived at you answers
(a) Give three differences between electrovalent compounds and covalent compounds
(b) List two physical properties of metals which can be accounted for by their structure
(c) Thorium (Th) metal undergoes a reaction represented by the following equation:
\(^{234}_{90}Th \to X + ^{234}_{91}Pa\)
(i) State the type of process involved in the reaction
(ii) Balance the equation equation and hence identify X.
(iii) Name one equipment which can be used to detect X.
(iv) Sketch a curveto show the mass of given quantity of thorium will change over a long period of time.
(d) Y is a moderately reactive divalent found naturally in the combined state as the trioxocarbonate (IV) salt, YCO\(_3\) is decomposed by strong heat, state the steps you would use in extracting Y from the ore. Write equation to show the chemical processes involved.
(a) Name one gaseous hydrocarbon which is
(i) used for welding.
(ii) a major raw material for the plastic industry.
(b) Write the structural formula of the hydrocarbon in (a)(i) above. Name the process by which it can be converted to neoprene rubber.
(c) Potatoes contain a high proportion of carbohydrate.
(i) Give the main product formed when potatoes are dehydrated completely
(ii) Describe how you would convert potatoes to ethanol. State the reactions involved the process and write equation for the final stage of the conversion.
(iii) Draw a labelled diagram of the apparatus you would use to obtain a sample of fairly pure ethanol from the product formed in (c)(ii) above. What is the name given to the technique?
(a)(i) Give two uses of chlorine.
(ii) State the action of chlorine on moist blue litmus paper
(b) Draw a labelled diagram for the laboratory preparation of a dry sample of chlorine
(c) State the type of reaction involved between chlorine and (i) aqueous iron (II) chloride;
(ii) propane. Write an equation for each reaction and name the product formed in (c)(ii).
(d) Consider the reactions the following equations: Cl\(_{2(g)}\) + 2Br\(^-_{(aq)}\) \(\to\) 2Cl\(^-_{(aq)}\) + Br\(_{2(g)}\)
F\(_{2(g)}\) + 2Cl\(^-_{(aq)}\) —> 2F\(^-_{(aq)}\) + Cl\(_{2(g)}\)
From the equations, arrange bromine, chlorine and fluorine in increasing order of oxidizing ability. Give the reason for your answer.
The set-up shown in the diagram below was used to separate a drop of universal indicator into the constituent dyes using ethyl ethanoate as the solvent.
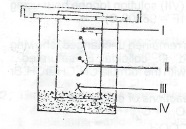
(a) What name is given to the separate strated in the diagram?
(b) State: (i) how many components are resolved in the separation;
(ii) the material normally used in laborary as the adsorbent medium;
(iii) which of the labels the point of application of the indicator.
Sketch a curve to show how the solubility of a gas varies with increasing temperature
Give one oxide in each case which;
(a) can act as a reducing agent
(b) can be used as a refrigerant
(c) is the anhydride of a strong acid;
(d) is yellow when hot and white then hot and white when cold;
(f) is usad as a pigment in paints.
(a) Name the industrial process by which ethene is obtained from petroleum fractions
(b) Give the I. U. P.A.C name of the isomer whose structure is shown below.
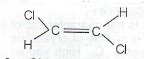
(c) Illustrate with an equation, one reaction in which benzene behaves as:
(i) unsaturated hydrocarbon
(ii) a saturated hydrocarbon
(a) Give two reasons why fused alumina is mixed with cryolite in the electrolytic extraction of aluminium.
(b) Write an equation for the reaction of sodium hydroxide with bauxite.
(a) Give the products of electrolysis of dilute copper (II) tetraoxosulphate(VI) solution using the following materials as electrodes:
(i) carbon rod;
(ii) copper rods
(b) For each of the process in (a) above;
(i) write the anodic half reaction;
(ii) state how electrolysis affects the pH of electrolyte

