Methane is obtained when a powdered mixture of anhydrous sodium ethanoate and soda-lime is heated in a hard glass test tube.
(a) Write an equation for the reaction.
b) Explain briefly why soda-lime is preferred to sodium hydroxide for the preparation.
A colourless and odourless gas X burns in oxygen with a pale blue flame.
(a) Suggest two gases which X could be.
(b) Give one chemical test that could be used to confirm which of the two gases X is.
(a)State three characteristics of a catalyst.
(b) Mention one manufacturing process in which each of the following metals is used as a catalyst:
(i) iron;
(ii) nickel;
(iii) platinum
(c) Give one example of an organic catalyst.
State the atoms represented as shown below:

(a) State the relationship between the two atoms.
(b) What is the difference between them?
(c) Give two examples of elements which exhibit the phenomenon illustrated above.
(a)(i) List two uses of aluminium and state how each use is related to the properties of the element.
(ii) State the reason why aluminium oxide is said to be amphoteric.
(b) Calcium is extracted by the electrolysis of fused calcium chloride containing about one-sixth of its mass of calcium fluoride.
(i) Sketch and label the cell used for the extraction.
(ii) Write equations for the reactions at the electrodes.
(iii) State the role of the calcium fluoride in the extraction.
(c) W, X, Y and Z represent four metals which have the following properties: W does not react with cold water but it liberates hydrogen from steam; X is one of the products formed when its trioxonitrate (V) decomposes on strong heating; Z forms the oxide when heated in air and it displaces W from an aqueous solutions of a salt of W; Y tarnishes rapidly exposure and reacts vigorously with cold water. Use the information provided to deduce the order of reactivity of the metals.
(a)(i) State Graham’s law of diffusion.
(ii) Consider the reaction represented by the following equation:
N\(_2\)O\(_{4(g)}\) 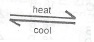 2NO\(_{2(g)}\)
2NO\(_{2(g)}\)
Night yellow dark brown
State what would happen to the vapour density of N\(_2\)O\(_4\) as the temperature of the system is increased. If the system is cooled, would the gases become lighter or darker in colour? Explain your answer in each case.
(b) Explain the following observations:
(i) an inflated balloon that was left in the sun. burst after some time;
(ii) a pure sample of a liquid did not have a constant boiling point at the top and at the base of a high mountain
(c)(i) List two gaseous reducing agents
(ii) Write one equation each to illustrate the reducing property of the gases you listed in (c)(i) above.
(a) Give the products of the following reactions:
(i) hydrolysis of simple proteins.
(ii) alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils.
(b) A combustion tube was packed with small pieces of broken clay pot and the tube maintained at a temperature of 750K. When the vapour of decane was passed into the tube, the main products included a gaseous hydrocarbon X.
(i) Name the process involved in the reaction. Give its industrial application.
(ii) State the function of the pieces of broken pot in the experiment.
(iii) Give one chemical test to distinguish between X and methane.
(iv) Draw a labelled diagram for the laboratory preparation of X.
(c)(i) State what would be observed if a piece of sodium was added to 10cm\(^3\) of propanol in a beaker. Write an equation for the reaction.
(ii) Give the main product formed when excess acidified potassium heptaoxodichromate (VI) reacts with each of the following: propan-1- ol: propan – 2 -of; State the type of process involved in the reactions.
(a)(i) State three differences between electrovalent compound and covalent compound.
(ii) Name the type of chemical bonding involved in the formation of ammonium ion from ammonia.
(b)(i) Name the quantum numbers which define an electron within an atom.
(ii) State the orbital in which the fifth electron of an atom is most likely to be found. Sketch the shape of the orbital.
(iii) State the period and the group to which the element boron belongs in the Periodic Table.
(c)(i) What is meant by the entropy of a chemical system?
(ii) Calculate the free energy change for a given reaction at 300 K using the following data obtained for the reaction: \(\Delta\) = -710KJ mol\(^{-1}\); \(\Delta\)S = 0.15 KJ mol\(^{-1}\)K\(^{-1}\)
(iii) From your evaluation in (c)(i) above, state whether the reaction is spontaneous or not at the given temperature. Give reason for your answer.
(a) Name: (i) one structural isomer of glucose.
(ii) the process by which starch is converted to glucose.
(b) The open-chain structure of glucose is shown below.
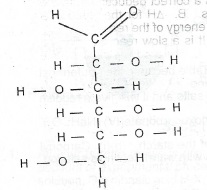
(a) State the functional groups present in the structure.
(ii) Which of the functional groups would react with warm Fehling’s solution?
(a) What is meant by the term acid salt? Give one example.
(b) State the reason why an all-glass apparatus must be used for the laboratory preparation of concentrated trioxonitrate (V) acid.
(a) Name one metal in each case Which:
(i) exists as a liquid at room temperature,
(ii) can be found in nature in the uncombined state
(b) X and Y are 0.5 mol. dm\(^{-3}\) freshly prepared aqueous solutions of two salts of iron
(II) With excess sodium hydroxide solution, X gave a dirty green precipitate which was not obtained in the case of Y.
(a) Three elements A, B and C have atomic numbers 8, 11 and 12 respectively.
(i) Write the formula of the compound formed by the chemical combination of A and B.
(ii) State which of the three elements belong(s) to the s-block of the Periodic Table. Give reason for your answer:
(b) List the component elements of bleaching powder.
(a) Give one example of naturally-occurring acids
(b) If 0.5 mole of a mono-alkanoic acid weighs 44g, determine the molecular formula and the name of the acid. (H = 1, C = 12, O = 16)
Magnesium ribbon reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid at room temperature.
(a) State three ways by which the reaction can be made to proceed faster
(b) Write an equation for the reaction.
(a) Give the electrolyte of a named secondary electrochemical cell.
(b) Consider the cell represented as shown below: \(Cu_{(s)}Cu^{2+}_{(aq)}/Zn^{2+}_{(aq)}/Zn{(s)}\)
(i) What does the vertical double stroke represent?
(ii) Which of the metals forms the cathode?
(iii) Name the electrode to which each half-cell should be coupled if the oxidation potential of the half-cells are to be determined.
(a) Name the crystalline allotrope of sulphur that is stable at room temperature.
(b)(i) Give one example of a fuel that contains significant amount of sulphur as an impurity.
(ii) State one environmental disadvantage of using a fuel that has high sulphur content
(a) State the main ore of tin.
(b) Write an equation for the reaction involved in the smelting of purified tin ore
(c) List two alloys of tin
(a) State the method of collecting gases which are denser than air.
(b) Name two gases that can be used to perform the fountain experiment in the laboratory. State the physical property which makes it suitable for the experiment.
(a)(i) List four characteristic properties of transition metals
(ii) Name two metals that can be extracted from their ore by electrolysis.
(b)(i) Determine the oxidation number of chromium in Cr\(_2\)O\(^{2-}_{7}\)
(ii) State the colour observed on adding a few drops of dilute tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid to the system representedby the following equation: Cr\(_2\)O\(^{2-}_{7(aq)}\) + H\(_2O_{(l)}\) \(\rightleftharpoons\) 2CrO\(^{2-}_{4(aq)}\) + 2H\(^+_{(aq)}\). Explain your answer.
(c)(i) State and explain what would be observed if hydrogen sulphide gas were bubbled into acidified K\(_2\)Cr\(_2\)O\(_7\). Write an equation for the reaction.
(ii) What precaution should be taken to avoid excessive exposure to hydrogen sulphide gas while it is being generated in the laboratory?
(a)(i) What is meant by the rate of a chemical reaction?
(ii) Explain in terms of the vision theory, the effect of temperature increase on reaction rate.
(b) When hydrogen peroxide is exposed to air, it decomposes
(i) Write an equation for the reaction.
(ii) Outline an experiment to illustrate that effect of a named catalyst on the rate of decomposition.
(iii) Sketch an energy profile diagram to show the effect of the catalyst on the reaction rate, given that the reaction is exothermic.
(c)(i) Explain why enthalpy data alone cannot be used to predict whether a reaction can occur spontaneously or not.
(a)(i) Define the term polymerization.
(ii) List the three conditions required for the polymerization on of ethene.
(iii) State the property which is common to compounds that can be easily polymerized
(b) Write appropriate equations to show how the following can be obtained from propan-1-ol in the labouratory
(i) propene;
(ii) propylmethanoate. State the type of reaction involved in each case.
(c)(i) A compound contains 40.0% carbon, 6.7% hydrogen and 53.3% oxygen. Determine its molecular formula if its molar mass is 180 (H = 1, C = 12, O = 16)
(ii) Explain why ethanoic acid boils at a much higher temperature than butane even though their molar masses almost equal.

