(a) Give one example each of a naturally occurring substance that;
(i) conforms to the general formula C(_x\)(H\(_2\)O)\(_y\);
(ii) contains the carboxyl group as its functional group.
(b) Name the process for obtaining: (i) paraffin oil from crude oil; (ii) benzene from ethyne.
A shortened form of the Periodic Table is shown below. Use it to answer questions (a) and (b)
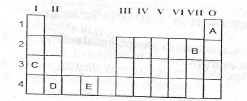
(a) Which of the elements represented as A to E in the table, above is:
(i) transition metal;
(ii) an alkaline earth meta
(iii) the least reactive;
(iv) the most electronegative?
(b)(i) What type of bond would exist in a compound formed when element D reacts with oxygen?
(ii) Write the formula of the compound formed in (b)(i) above.
(1)(a) State Avogadro’s law
(b) Which of the state of matter contains particles that are: (i) readily used
(ii) held firmly together by some forces of cohesion;
(iii) involved in rapid random motion?
(a) State two differences in the chemical properties of metals and non-metals.
(b) List two general methods of extract metals from their ores.
(a)(i) Explain what is meant by saturated solution
(ii) Describe in outline, a suitable procedure for preparing a saturated solution of sodium trioxonitrate(V) at 30°C.
(ii) State two techniques that can be used to recover crystals of sodium trioxonitrate(V) from its saturated solution.
(b) 1.0dm\(^3\) of an aqueous solution at 90°C contains 404g of potassium trioxonitrate(V) and 245g of potassium trioxochlorate (V).
(i) Determine which of the two salts will separate out when the solution is cooled to 60°C. N = 14. O = 16, CI = 35.5, K = 39; Solubility of KNO\(_3\) in water at 60\(^o\)C = 5.14 mol.dm\(^{-3}\), Solubility of KCIO\(_3\) in water at 60°C = 1.61 mol.dm\(^{-3}\)
(ii) Calculate the mass of salt that will separate out at 60°C
(c)(i) List two salts which cause hardness of water.
(ii) Explain why temporary hardness of water result in the furring of kettle.
(a) List three properties of a system that is in a state of chemical equilibrium.
(b) Consider reaction represented by the following equation: 3H\(_{2(g)}\) + N\(_{2(g)}\) \(\rightleftharpoons\) 2NH\(_{3(g)}\); H = 92KJ
(i) Explain the effect of increasing the temperature of the reaction on the yield of ammonia
(ii) Uses of energy profile diagram to illustrate the effect of a positive catalyst on the rate of either the forward reaction or the reverse reaction.
(c) In the extraction of aluminium from bauxite:
(i) outline the procedure used for purifying the ore;
(ii) write equation for the reaction at each electrode, during the electrolysis of the pure alumina;
(iii) state the function of molten cryolite in the electrolytic cell for the extraction.
(a)(i) What is isomerism?
(ii) Name the alkanol that is isomeric with methoxymethane (CH\(_3\)OCH\(_3\)).
(b)(i) Outline the laboratory:preparation of ethylethanoate. (Diagrams not required)
(ii) Write the structural formula of ethylethancqte
(iii) State two physical properties of ethylethanoate.
(c) When gas oil which consists of larger hydrocarbons was subjected to high temperature and pressure, the following reaction occurred.
C\(_{17}\)H\(_{36(l)}\) \(\to\) 3C\(_2\)H\(_{4(g)}\) + C\(_3\)H\(_{6(g)}\) + Q\(_{(l)}\)
(i) What name is given to the process indicated above?
(ii) State the importance of the process to the petroleum industry.
(iii) Find the formula of the product which Q represents in the equation above.
(iv) Mention one type of chemical industry that utilizes ethene as raw material.
(d) Consider the following compounds: CH\(_3\) — (CH\(_2\))\(_2\) —CH\(_3\); C\(_6\)H\(_5\) —CH = CH\(_2\); CH=C — CH\(_3\). State which of them:
(i) is used as a domestic fuel;
(ii) is an aromatic compound,
(iii) participates in such situation but not addition reactions;
(iv) would react with two moles of hydrogen per mole.
(a)(i) List the three types of particles present in atoms.
(ii) name the element which does not contain all the three particles in its atom. Mention the particle that is not present.
(b) Give the reason why:
(i) the relative atomic masses of some elements are not whole number;
(ii) relative atomic masses are used instead of the actual masses of atoms in grams;
(iii) metals are good conductors of electricity.
(c)(i) Name the type of bond present in the oxonium ion,
(ii) State one effect of the existence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding on the physical properties of ethanol.
(d)(i) Explain what is meant by water of crystallization.
(ii) When 5.0g of a compound Y was heated to constant mass, 1.8g of water vapour was given off. Determine the number of molecules of water of crystallization in one molecule of Y, given that the molar mass of its anhydrous form is 160g. [H = 1, 0 = 16]
(a) List two differences between solids and liquids.
(b) The graph below is the heating curve for a solid X. Use the graph to answer Questions (i) — (iii) below.
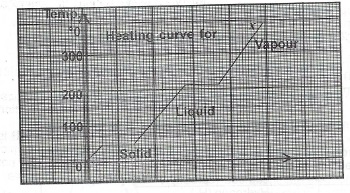
(i) What is the melting point of X?
(ii) If the vapour of X is cooled, at what temperature will it start to condense?
(iii) (I) As X is heated, state what happens to the: I. frequency of collision of molecules of X;
(II) value of the entropy of the system.
(a) Mention one process apart from respiration, which increases the amount of carbon (IV) oxide in the atmosphere.
(b)(i) State one use of sodium hydrogentrioxocarbonate (IV).
(ii) Write an equation to show the action of heat on sodium hydrogentrioxocarbonate(IV).
(a) What is the change in oxidation state of chromium in the reaction represented by the following equation?
3SO\(_2\) + Cr\(_2\)O\(^2_{-7}\) + 2H\(^+\) -> 3SO\(_4^{2-}\) + 2Cr\(^{3+}\) + H\(_2\)O
(b) Use the half equations given below to deduce the equation for the reaction between iron(II) ions and heptaoxodichromate (VI) ions in acidic solution.
Fe\(^{2+}\) –> Fe\(^{3+}\) + e\(^-\)
Cr\(_2\)O\(^{2-}_7\) + 14H\(^+\) + 6e\(^-\) —-> 2Cr\(^{3+}\) + 7H\(_2\)O.
(a) Mention the chemical substance manufactured starting from each of the foirownc sets of materials:
(i) sugar and yeast;
(ii) ammonia, air and water;
(iii) vegetable oil and caustic alkali.
(b) State one air pollutant generated during the manufacture of fertilizers.
(a) Name the device used for producing an electric current from a chemical
(b) Copy and complete the table below.
|
Electrolyte |
Product at the anode (carbon) |
Product at the cathode (carbon) |
|
Dilute NaCl\(_{(aq)}\) Concentrated NaCI\(_{(aq)}\) |
(a) State the type of reaction involved in the conversion of:
(i) proteins.to amino acids:
(ii) ethanol to ethene;
(iii) benzene to bromobenzene
(b) Write an equation to show that ethene reasts with hydrogen in the presence of finely divided nickel.
(a)(i) Sketch a graph to illustrate Charles’ law.
(ii) A gas occupies 500 cm\(^{ 3}\) at 2TC. calculate its volume at 40°C constant pressure.
(b) List two gases that are used as refrigerant
(a)(i) Explain the term pH
(ii) If sodium hydroxide solution were added to a solution of a strong acid, what would happen to the pH of the solution?
(b) Give one example of each of the following:
(i) acidic oxide
(ii) acid salt.
What name is given to each of the following? The
(a) irregular random movement of smoke particles in air.
(b) existence of an element in various forms in the same physical-state
(c) disintegration of atomic nuclei, accompanied with radiation emission.
(d) conversion of a solid difitrunto vapour without melting.
(a) State three reasons why air is classified as a mixture.
(b) List two methods that can be used to separate a mixture of iodine crystals and iron filings.
(a)(i) List three factors which affect the discharge of ions during electrolysis
(ii) Describe in outline, the purification of copper by electrolysis.
(b) the following data were collected in an experiment on electrolysis:
| Current flowing(amps) | Time of current flow (secs) | Quantity of electricity (coulombs) | Mass of metal M deposited (gram) |
|
0.20 0.20 0.20 0.20 |
900 1800 2700 3600 |
0.06 0.12 0.18 0.24 |
(i) Copy and complete the table above calculating the quantity of electricity passed in each case
(ii) Plot a graph of the mass of M deposited against the quantity of electricity passed.
(iii) From the graph, determine the mass of M that was deposited by the same current passing for 20 minutes.
(iv) From the shape of the graph, which of the laws of electrolysis does the experiment verify?
(a)(i) What is an acid?
(ii) List three chemical properties of tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid
(iii) Give two uses of tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid.
(b)(i) Describe a suitable laboratory procedure for preparing a sample of zinc tetraoxosulphate (VI) crystals, starting from zinc oxide.
(ii) Write two equations to show why zinc oxide is classified as an amphoteric oxide.
(c) Zinc reacts with copper (II) tetraoxosulphate (VI) according to the following equation: Zn + CuSO\(_4\) -> ZnSO\(_4\) + Cu
(i) State the type of reaction involved
(ii) Determine the mass of zinc that would react completely with 8.0g of copper (II) tetraoxosulphate (VI). [CuSO\(_4\) = 160; Zn = 65]
(a)(i) Give one major use of alkenes.
(ii) Name the simplest alkane that exhibits structural isomerism
(iii) Determine the molar mass of an alkane that is represented as C\(_x\)F\(_{22}\). [H = 1, C = 12]
(iv) List two types of chemical reactions which the alkenes and alkynes undergo.
(b)(i) State the type of reaction involved in the conversion of palm oil to margarine.
(ii) Give the reason why the palm oil for manufacturing margarine is first treated activated charcoal
(iii) What is commonly used to catalyse the conversion of vegetable oils to margarine?
(c)(i) Name the class of organic compounds to which oils belong.
(ii) Describe briefly procedure for the manufacture of soap from vegetable oils
(iii) Explain why the presence of calcium ions in domestic water supply wastes soap.

