(a) State two properties of alkalis
(b)(i) Why is tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid able to produce two types of salt?
(ii) Write an equation for the reactior involved on heating sodium trioxosulphate (IV) with hydrochloric acid.
(a) List two industrial uses of concentrated tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid
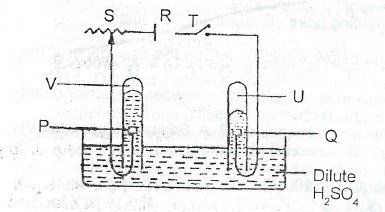
(b) The diagram below represents the set-up for the electrolysis of dilute tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid. Use it to answer Questions (i) to (iii).
(i) Which letter on the diagram represents the battery?
(ii) Write an equation for the reaction occurring at the cathode
(iii) What product does V represent?
(a)(i) State the two main processes involved in the manufacture of oxygen from air
(ii) Name the type of chemical bonding which exists between oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen
(b) What term is used to describe the relationship between oxygen and ozone (O\(_3\))?
(a) List two properties of alpha particles.
(b) X is an element which exists as an isotopic mixture containing 90% of \(^{39}_{19} X\) and 10% of \(^{41}_{19}X\).
(i) How many neutrons are present in the isotope \(^{41}_{19}X\)?
(ii) Calculate the mean relative atomic mass of X.
(a)(i) What is an electrolyte?
(ii) Classify each of the following as strong electrolyte/weak, electrolyte/non-electrolyte. Potassium chloride; sodium ethanoate, aqueous ammonia; cane sugar
(b)(i) Write half-cell equations for the reactions in the Daniel cell .
(ii) Why is the Daniel cell classified as an electrochemical cell?
(iii) Give two other examples of electrochemical cell.
(c) Explain the following observations.
(i) Graphite conducts electricity, unlike most non-metals
(ii) In the electrolysis of copper (II) tetraoxosulphate (VI) solution, the blue colour fades with platinum electrodes while the colour intensity is unaffected with copper electrodes (equations required)
(iii) A solution of dry hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene (toluene) does not conduct electricity whereas hydrochloric acid does.
(a)(i) Define heat of neutralization
(ii) Give the reason why copper (II) chloride can be prepared by neutralization, unlike lead (II) chloride.
(b)(i) Describe in outline, the manufacture of trioxonitrate (V) acid by the catalytic oxidation of ammonia, giving equations where appropriate.
(ii) What are the products obtained when sodium tioxonitrate (V) is heated strongly?
(c) When powdered magnesium is heated to redness in a stream of nitrogen, magnesium nitride (Mg\(_3\)N\(_2\)) is formed.
(i) Write an equation for the reaction
(ii) Hence, calculate the amount (in mole) of magnesium nitride that can be obtained from 3.0g of magnesium [Mg = 24].
(a)(i) What type of reaction is involved in each of the conversion processes indicated as I to V below?
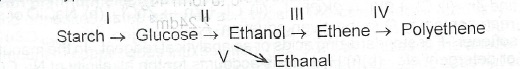
(ii) Name one isomer of glucose
(iii) Explain why palmwine becomes sour on prolonged exposure to air.
(b)(i) List the reagents and the reaction condition necessary for ethanoic acid to form an alkanoate.
(ii) Give two uses of alkanoates
(c)(i) What is the lUPAC name of the following compound?
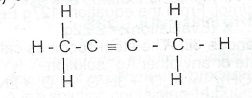
(ii) Outline one chemical test to distinguish between methane and the compound in (c)(i) above.
(iii) Write an equation for the combustion of ethene in excess oxygen.
(a)(i) List the quantum number that are assigned to an electron in an atom.
(ii) What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the 3d orbital?
(b) An element represented as P has the following electronic configuration: 1s\(^2\)2s\(^2\)2p\(^6\)2s\(^2\)
(i) Write the electronic configuration of the ion of P.
(ii) Without identifying P, write the likely formula of its chloride.
(iii) State with reason, whether P will be a good oxidizing or reducing agent.
(c)(i) What is electron affinity?
(ii) Explain briefly why ammonia can precipitate in dative bonding.
(d)(i) If an element in Group IV loses an alpha particle, to which group would the product belong?
(ii) Two equally toxic substances X and Y which decay to non-toxic products, were absorbed through the skin. If their half-lives are 8 minutes and 2 months respectively, which of them constitutes the greater health hazard? Explain your answer
(a) If a steel spoon were to be plated with silver, state what would be suitable for use as the;
(i) anode. (ii) cathode; (iii) electrolyte
(b)(i) Write an equation for one of the reactions involved in the purification of bauxite.
(ii) Give the reason why the carbon anodes are changed at intervals during the electrolysis of pure alumina solution in molten cryolite.
Xg of a pure sample of iron (II) sulphide reacted completely with excess dilute hydrochloric acid to give 3.20g of iron (II) chloride according to the following equation: FeS\(_{(s)}\) + 2HCI\(_{(aq)}\) —> FeCl\(_{2(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)S\(_{(g)}\).
(a) Mention one method apart from heating by which the reaction can be made to proceed faster
(b) Calculate the value of X. [CI = 35.5, Fe = 56; FeS = 88g mol\(^{-1}\)]
(a) List two uses of sodium trioxocarbonate (IV).
(b) Sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) solution is alkaline.
(i) What phenomenon is responsible for this observation?
(ii) Name the product obtained on passing carbon (IV) oxide into saturated sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) solution.
(a) Write an equation for the reaction of chlorine with
(i) potassium iodide solution;
(ii) zinc on heating
(b) Identify the product Q in the following reaction: Cl\(_2\) + 2NaOH \(\to\) NaCl + H\(_2\)O + Q.
(a)(i) What is meant by the activation energy of a reaction?
(ii) State the effect of a catalyst on activation energy.
(b) What substance serves as a catalyst in each of the following?
(I) Hydrogenation of oils
(ii) Biochemical reactions.
(a)(i) What is the general formula for alkanoic acids?
(ii) State two chemical properties of ethanoic acid.
(b) Which of propene, butane and pentane
(i) will decolorize acidified KMnO\(_4\) solution?
(ii) can be easily polymerized?
(iii) is an isomer of methylpropane?
(iv) can be obtained from an alkanol by dehydration?
(a) What is the IUPAC name of Fe\(_2\)(SO\(_4\))\(_3\)?
(b)(i) Write an equation to represent the reaction of hydrogen sulphide with iron (III) chloride solution.
(ii) Mention one change observed during the reaction in (b)(i) above.
(a)(i) Arrange the following elements in the order of increasing reactivity. Iron, Lead, Magnessium, Aluminium.
(ii) Which of the following elements in (a)(i) above reacts with sodium hydroxide to give hydrogen?
(b) What property of tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid does each of the following reactions illustrate?
(I) S + 2H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) —> 3SO\(_4\) + 2H\(_2\)O
(ii) MgO + H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) —> MgSO\(_4\) + H\(_2\)O
(iii) C\(_{12}\)H\(_{22}\)C\(_{11}\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) —> 12C + H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) + 11H\(_2\)O
(a) State two postulates of the kinetic theory of gases.
(b) Write two chemical properties that are common to both carbon (IV) oxide and sulphur (IV) oxide.
Copy and complete the following table
| Element | Number of Neutrons | Electronic Configuration | Group in the periodic Table |
| \(^{23}_{11}Na\) | — | 1s\(^{2}\)2s\(^{2}\)2p\(^{6}\)3s\(^{1}\) | 1 |
| \(^4_2He\) | 2 | —- | — |
| —- | 7 | 1s\(^{2}\)2s\(^{2}\)2p\(^{2}\) |
—- |
(a)(i) List two elements which react with steam at red heat to produce hydrogen.
(ii) Explain why an aqueous solution of potassium bromide turned reddish brown on bubbling chlorine through it.
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction in (a)(ii).
(b)(i) Name two types of chemical industry that use limestone as raw material.
(ii) Give one example of hygroscopic substances.
(iii) Copy and complete the table below.
|
Salt to be prepared |
Starting material |
Method of preparation |
| PbSO\(4\) | Pb(NO\(_3)_{2(ag)}\) | – |
| KNO\(_3\) | KOH | Neutralization |
| CaCl\(_2\) | CaCO\(_3\) | – |
| FeCl\(_3\) | Fe\(_(s)}\) | – |
| CuSO\(_4\) | CuO | – |
(c) In the contact process for the manufacture of tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid;
(i) State how sulphur (IV) oxide is obtained;
(ii) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the catalyst chamber;
(iii) Give the steps required to convert sulphur (VI) oxide to acid.
(d)(i) List two disadvantages of hard water.
(ii) Mention three methods which can be used to remove both permanent and temporary hardness in water at the same time.
(iii) State the role of alum and chlorine respectively in the purification of water for town supply.
(a)(i) Define allotropy.
(ii) Name the allotrope of carbon used in gas masks.
(iii) Mention two other elements which exhibit allotropy apart from carbon.
(b) List the products of each of the following reactions:
(i) Heating coal in the absence of air.
(ii) Burning of candle wax in plentiful supply of air
(c)(i) State the two properties of carbon (IV) oxide which make it useful in extinguishing fire.
(ii) Write an equation for the reaction of carbon (IV) oxide with lime water
(iii) Calculate the volume of oxygen that was in excess if 150cm\(^3\) of carbon (II) oxide was burnt in 80cm\(^3\) of oxygen according to the following equation: 2CO\(_{(g)}\) + O\(_{2(g)}\) \(\to\) 2CO\(_{2(g)}\).
(d)(i) State how nitrogen can be obtained from ammonia gas.
(ii) Name the gaseous fuels obtained when steam and air are passed over red hot coke.
(iii) Which of the fuels in (d)(ii) has the lower heating ability? Give reason for your answer.
(a)(i) Give two differences between a conductor and an electrolyte.
(ii) State three applications of electrolysis.
(iii) Write equation for the reaction at each electrode when a dilute solution of sodium chloride is electrolysed using carbon electrodes.
(b)(i) What is an electrochemical cell?
(ii) Give two examples of primary cells.
(iii) Split the following equation into two balanced hall cell equations. Mte + Fe\(^{2+} \to Mg^{2+} + Fe\).
(c)(i) A current of 0.72 amperes was passed through dilute tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid for 3 hours 20 minutes. Calculate the quantity of electricity that was passed
(ii) If 1 dm\(^3\) of gas evolved at the cathode during the electrolysis of acidified water, what was the volume of gas evolved at the anode?
(d)(i) 20g of copper(II) oxide was warmed with 0.05 mole of tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid. Calculate the mass of copper (II) oxide that was in excess. The equation for the reaction: CuO\(_{(s)}\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) —> CuSO\(_{4(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_l\) [0 = 16 ; Cu = 64]
(ii) What type of reaction was involved in (d)(i)?

