(a) State the role of each of the following substances in the treatment of river water for town supply (i) Sand bed. (ii) Alum (iii) Chlorine
(b)(i) Give three major uses of H\(_2\)SO\(_4\)
(ii) Explain the following observation: A strip of blue litmus paper dropped into concentrated H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) becomes charred whereas in dilute H\(_2\)SO\(_4\), it turns red and is not charred.
(iii) Write an equation to show how concentrated H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) reacts with zinc.
(c)(i) List two gaseous pollutants that can be generated by burning coal.
(ii) Explain why coal burns more easily when it is broken into pieces than when it is in lump form.
(ii) What gas is responsible for most of the explosions in coal mines?
(iv) Name: the non-volatile residue left behind after the destructive distlillation of coal
(d)(i) What is meant by allotropy?
(ii) Name two crystalline allotropes of carbon
(iii) Name two elements apart from carbon, which exhibit allotropy
(iv) It is now known that carbon has an allotropic form called fullerene, containing molecules of formula C\(_{60}\). Calculate the mass of one mole of these molecules [C = 12]
(a) Mention one oxide in each case, which
(i) used in bleaching
(ii) is a redish-brown gas
(iii) reacts with NaOH and also with HCI;
(iv) dissolves in water to give a solution with pH greater than 7;
(v) oxidizes hot, concentrated HCI to chlorine
(b)(i) State three methods that can be used to removo hardness in a sample of water that contains calcium hydrogentrioxocarbonate (IV).
(ii) Explain with the aid of appropriate equation, why it is not advisable to build a house with limestone in an environment polluted by sulphur (IV) oxide.
(c)(i) List two compounds of potassium which yield oxygen when heated strongly
(ii) Calculate the amount (in moles) of gas which occupies 250 cm\(^3\) at s.t.p. [1 mole of gas occupies 22.4 dm\(^3\) at s.t.p]
(iii) If 250 cm\(^3\) of a gas at s.t.p. is heated to 27°C at constant pressure, calculate its new volume.
(iv) Explain in terms of the collision theory what happens as a gas is heated at constant pressure.
(a)Give two reasons why aluminium is preferred to copper for making overhead electric cables.
(ii) Describe briefly the electrolytic extraction of aluminium from purified bauxite.
(b) The diagram below represents an electrolytic cell used for the purification of copper.
(i) Which of the electrodes I and II increases in mass during the electrolysis? Give reasons for your answers
(ii) State with reason the site of oxidation
(iii) Identify III and explain why its colour does not change in intensity during the electrolysis.
(c) Calculate the current in amperes that will deposit 8.00 g of calcium from used CaCl\(_2\) in 1 hour 15 minutes. [Ca = 40.0; 1 Faraday = 96500C]
(a) i) An organic compound X contains 40% carbon, 6.67% hydrogen, the rest being oxygen. If X has a relative molecular mass of 60, determine its
(i) empirical formula (ii) molecular formula. [H = 1 ; C = 12; O = 16]
(b) An alkanoic acid Y has a relative molecular mass of 74.
(i) State the functional group of Y
(ii) What t of reaction is involved when Y is converted to an alkanoate?
(iii) Determine the structural formula of Y.
(iv) Write an equation for the reaction between Y and sodium
(v) If X in (a) above boils at 118°C and belongs to the same homologous series as Y, state with reason, whether the boiling point of Y will be equal to, higher or lower than 118°C.
(c)(i) What is fermentation?
(ii) Write an equation for the fermentation of glucose.
(iii) What must be added to glucose solution to make it ferment?
(iv) Explain why a tightly corked grass bottle filled to the brim with fresh palm wine shatters on standing.
(a) (i) State three characteristic properties of transition metals.
(ii) What is the oxidation state of manganese In each of the following species? (1) MnCl\(_2\) (II) MnO\(_2\) (III) MnO\(_4^{-}\)
(iii) Explain why manganese conducts electricity in the solid state but manganese chloride conducts only when molten or in solution.
(b)(i) The collision theory suggests that for two particles to react, they must collide. What two factors determine whether or not the collision would lead to formation of products?
(ii) Use an energy profile diagram to illustrate what is meant by the enthalpy change (\(\Delta\)H) and the activation energy (E\(_A\)) of a reaction.
(c) When few drops of aqueous KSCN are added to a solution of iron (III) salt the following equilibrium is set up:
Fe\(^{3}_{(aq)}\) + 3SCN\(^{-}_{(aq)}\) \(\rightleftharpoons\) Fe(SCN)\(_{3(aq)}\)
yellow colourless deep red
The equilibrium mixture has a pale red colour.
(i) Explain what would happen if more KSCN\(_{(aq)}\) were added to the equilibrium mixture.
(ii) Which of the ions in the equilibrium mixture forms an insoluble hydroxide with NaOH\(_{(aq)}\)? Write an equation for the reaction
(iii) State two changes observed on adding NaOH\(_{(aq)}\) to the equilibrium mixture.
(a) The electronic configuration of five elements represented by the letters P, Q, R, S and T are indicated below.
P – 1s\(_2\)2s\(_2\)2p\(_2\)
Q 1s\(_2\)2s\(_2\)2p\(_4\)
R 1s\(_2\)2s\(_2\)2p\(_6\)
S – 1s\(_2\)2s\(_2\)2p\(_6\)3s\(_2\)
T – 1s\(_2\)2s\(_2\)2p\(_6\)3s\(_2\)3p\(_5\)
without identifying the elements, state which of them
(i) belongs to group VI in the periodic table;
(ii) is strongly metallic in character;
(iii) readily ionizes by gaining one electron;
(iv) contains two unpaired electrons in the ground state atom
(v) readily loses two electrons during chemical bonding
(vi) Does not paricipates in chemical reactions?
(vii) is an s-block element.
(b)(i) Copy and complete the table below as appropriate
| Particle | Number of Protons | Number of Electrons | Number of Neutrons |
| \(^1_1H\) | 1 | 1 | |
| \(^{27}_{13}\)Al\(^{3+}\) | |||
| \(^{16}_{8}O^{2+}\) | 8 |
(ii) Give the reason why atomic radius increases down a group in the periodic table but decreases from left to right in a period.
(c)(i) What is meant by the half-life of a radioactive element?
(ii) The nuclide \(^{210}_{84}PO\) loses an alpha 4° particle to form lead. Write an equation for the reaction.
(d) State the type of chemical bonding which accounts for each of the following observations:
(i) Chlorine exists as discrete molecules
(ii) Sodium chloride dissolves readily in water;
(iii) CuSO\(_{4(aq)}\) forms a deep blue complex ion with excess NH\(_{3(aq)}\)
(a)(i) Give the reason why copper turnings dissolve in AgNO\(_3\) solution but remain insoluble in Pb(NO\(_3\) )\(_2\) solution.
(ii) Copper turnings of mass 1.06g were placed in 250 cm\(^3\) of 0.20 mol dm\(^{-3}\) AgNO\(_3\). Calculate the amourt of silver ions present. [Cu = 63.5]
(iii) Determine whether all the copper in (a)(ii) above will discolvo in the solution. The equation for the reaction is CU\(_{(S)}\) + 2Ag\(^+_{(aq)}\) –> Ag\(_{(aq)}\) + Cu\(^{2+}_{(aq)}\)
(b)(i) List cheicil properties of acids
(ii) Give two large scale uses of HNO\(_3\)
(iii) Write an equation for the action of heat on each of the following compounds: I. Pb(NO\(_3\))\(_2\)
Il. AgNO\(_3\).
(c)(i) State what would be observed if a piece of damp blue litmus paper is dropped into a glass jar of chlorine.
(ii) Name the type of reaction which occurs in (c)(i) above.
(iii) Give the property of chlorine which is exhibited in the reaction in (c)(i) above.
(i) Name two products obtained directly from the destructive distillation of coal.
(ii) Give one use of each product named in (d)(i) above.
(a)(i) State one physical method and one chemical method in each case by which the following can be removed:
I. Permanent hardness in water
II. A suspension of CaCO\(_3\) in water.
(ii) Give one disadvantage of hard water.
(b) Explain the following observations: (i) Crystals of washing soda become powdery on exposure to air for a long time
(ii) The concentration of chloride ions in 0.02 mol dm\(^{-3}\) calcium chloride solution is not the same s in 0.02 mol dm\(^{-3}\) sodium chloride solution.
(iii) Iron filings corrode faster than iron nails of the same mass.
(c)(i) Classify each of the following oxides as acidic, basic, neutral or amphoteric. I. ZnO II. CO III. NO\(_2\)
(ii) Give the formula of the acid anhydride of each of the following: I. H\(_2\)CO\(_3\) II. H\(_2\)SO\(_4\)
(iii) Give the IUPAC name of the following salts: I. COCl\(_2\) II. Mg(NO\(_3\))\(_2\).
(d)(i) Mention one pollutant associated with depletion of ozone layer in the atmosphere
(ii) Calculate the volume occupied by 0.125 mole of oxygen at 27°C and a pressure of 2.02 x 105 Nm\(^{-2}\) [I mole of gas occupies 22.4 dm\(^3\) at s.t.p; standard pressure = 1.01 x 105 Nm\(^{-2}\)]
(iii) State one process used for the industrial preparation of oxygen.
(a) Methane reacts with chlorine under certain condition to produce tetrachloromethane.
(i) State the condition for the reaction
(ii) Name the type of reaction
(iii) Give two uses of methane
(iv) Name one major natural source of methane
(b)(i) Mention one similarity between the reaction of ethanol with sodium and that of sodium with water
(ii) Write the structure of two isomers of C\(_3\)H\(_8\)O
(iii) Differentiate between a fine chemical and a heavy chemical
(iv) Give one example of each in (b)(iii) above
(c) Two compounds X and Y have the same percentage composition by mass of 92.3% carbon and 7.7% hydrogen. Calculate the:
(i) empirical formula of X and Y;
(ii) molecular formula of each compound if molar mass of X is 26 g and Y is 78g.
(d) A protein is boiled for a long time with dilute HCI and a reaction occurred.
(i) State the type of reaction that occurred
(ii) Name the major product formed
(iii) Give the functional groups present in (d)(ii) above.
(a) Draw an energy profile diagram to illustrate a catalysed exothermic reaction and label parts of the curves representing the following:
(i) activated complex (without catalyst);
(ii) activated energy (with catalyst)
(iii) enthalpy change
(b) Give the reasons for the following observations:
(i) A balloon filled with liyilrogen becomes deflated faster than a balloon filled with air under the same conditions.
(ii) Hydrogen peroxide decomposes slowly at room temperature but when a pinch of MnO, is added, bubbles form rapidly.
(iii) A solution of hydrogen chloride as in methylbenzene has no effect on `litmus but a solution of the gas in water turns blue litmus paper red.
(c) Consider the reaction represented by the following equation: 2MnO\(^-_{4(aq)}\) + 5C\(_2\)O\(^{2-}_4\) + 16H\(^+\) \(\to\) 2Mn\(^{2+}_{(aq)}\) + 8H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) + 10C\(_{2(g)}\) .
Write down: (i) the species undergoing reduction giving reasons;
(ii) the reducing agent giving reasons;
(iii) the reduction half equation;
(iv) one observation made during the reaction.
(d)(i) What is an electrochemical cell?
(ii) State three differences between an electrochemical cell and an electrolytic cell.
(i) State Two assumptions of the kinetic theory of gases
(ii) When some solids are heated, they change directly into the gaseous state. What narne is given to this phenomenon?
(iii) List two substances which exhibit the phenomenon referred to in (a)(ii) above
(iv) Write an expression to show the mathematical relationship between the rate of diffusion of a gas and its vapour density.
(b) Consider the following equilibrium reaction:
3Fe\(_{(s)}\) + 4H\(_2\)O\(_{(g)}\) \(\rightleftharpoons\) FeO\(_3\)O\(_{4(s)}\) + 4H\(_{2(g)}\), \(\Delta\)H = – 150KJ mol\(^{-1}\)
Explain the effect of the following factors on the position of equilibrium: (i) tecrease in temperature; (ii) Increase in pressure; (iii) Removal of hydrogen.
(c) . Three beakers labelled P, Q and S each contained zinc metal of the same mass but in different forms. P contained a length of zinc rod, Q contained zinc dust while S contained zinc foil. 100cm\(^3\) of 5.0 mol dm\(^{-3}\) hydrochloric acid was added to each beaker to react with all the zinc.
(i) State the order in which the reaction came to completion in beakers P,Q and S starting with the fastest.
(ii) Give reason for your answer in (c)(i) above
(iii) Write an equation to represent the reaction between zinc rid the hydrochloric acid.
(d) (i) What is meant by pH of a solution?
(ii)(I) State with reason in each case whether the pH would increase, decrease or remain constant if the following experiments were carried out Neutralizing bench HNO\(_3\);
II. Diluting 25.0 cm\(^3\) of a given NaOH solution to 100.0cm\(^3\) Concentrating a solution of NaCI.
(a)(i) Mention two types of bond present in the ammonium ion
(ii) Give three characteristic properties of electrovalent compounds
(iii) State. two differences between chemical reactions and nuclear reactions
(b) Two elements represented by the letters and Y have atomic numbers 9 and 12 respectively.
(i) Write the electronic configuration of X using the s,p,d, notation
(ii) To what group does Y belong in the periodic table?
(iii) Write the formula of the compound formed when X copibines with Y
(iv) Explain wily X is a good oxidizing agent
(v) State with reason, whether Y would be expected to form acidic or basic oxide
(c) Balance the following nuclear equations and identify the particles represented by X and Y.
(i) \(^{14}_6C\) \(\to\) X + \(^{14}_7N\)
(ii) \(^{14}_7C\)
Y \(\to\) \(^1_1H\) + \(^{17}_8O\)
(d) Consider the following list of substances: Carbon (IV) oxide, hydrogen, zinc, sulphier, methane, potassium and mercury. From the list above, state the:
(i) elements that are metals
(ii) compounds that are gases at room temperature
(iii) non-metals that are solids at room temperature
(i) Name two amorphous forms of carbon
(ii) State the reason why graphite is a lubricant but diamond is not.
(iii) Draw and label a diagram for the laboratory preparation of a dry sample of carbon (IV) oxide.
(b)(i) Give one example of the following: I. Soil pollutant; II. Water pollutant; III. Air pollutant.
(ii) State the major use of sulphur (IV) oxide in a chemical industry.
(c)(i) Explain in terms of the kinetic theory why petrol is volatile
(ii) State two criteria for determining the purity of a substance.
(iii) Mention one use of each of the following gases: I. Krypton; II. Argon
(d)(i) When zinc metal was added to aqueous copper (I) tetraoxosulphate (VI), the solution turned colourless. I. Name the compound in the colourless solution. II. Write the ionic equation for the reaction. Ill. State what would be observed when a few drops of sodium hydroxide solution is added to a portion of the colourless solution.
(ii) Calculate the volume of CO\(_2\) produced when 5.3g of Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) reacted with excess HNO\(_{3(aq)}\) + Na\(_2\)CO\(_3\) + 2HNO\(_{3(aq)}\) \(\to\) 2NaNO\(_{3(aq)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) [H = 1, C = 12, N = 14, O = 16, Na = 23, 1 mole of a gas occupies 22.4 dm\(^3\) at s.t.p.]
(a)(i) State the two types of hardness in water.
(ii) Name a salt that causes each type of hardness.
(ii) Write a balanced equation for the removal of each type of hardness.
(iv) State one effect of hard water on soap.
(b)(i) State whether the pH of each of the following is less than, equal to, or greater than 7.
I. Glucose solution II. Chlroine water III. Lime water IV. Sour milk
(ii) Give the difference between the following compounds: I. an acidic oxide and an amphoteric oxide; II. concentrated acid and a dilute acid; Ill. a normal salt and an acid salt
(c)(i) Iron reacts with H\(_2\)SO\(_4\) according to the equation: Fe\(_{(s)}\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) —> FeSO\(_{4(aq)}\) + H\(_{2(g)}\)
Calculate the mass of FeSO\(_4\) that would be produced by 0.5 mole of Fe. [H = 1, S = 32, Fe = 56]
(ii) List two allotropes of sulphur
(d)(i) State what would La observed when a damp starch-iodide paper is dropped into a gas jar of chloride
(ii) Explain your ansv.er in (d)(i) above.
(iii) State the products formed when ammonia reacts with excess chlorine.
(a)(i) List three observable changes that take place when a dilute solution of copper (II) chloride is electrolysed using platinum electrodes. Stage III
(ii) Calculate the quantity of electricity used during electrolysis when a current of 0.21 ampere flows for 2 hours.
(iii) State what is meant by the term preferential discharge of ions in electrolysis
(iv) Give one factor which influences the preferentia! discharge of ions during electrolysis.
(v) State one Q difference between-a conductor and an electrolyte.
(b) Consider the reaction represented by the equation below: Na\(_2\)S\(_2\)O\(_{3(aq)}\) + 2HCI\(_{(aq)}\) \(\to\) 2NaCI\(_{(aq)}\) + H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) + SO\(_{2(g)}\) + S\(_{(s)}\)
(i) List two factors that can affect the rate of this reaction.
(i) Which of the products can be readily used to measure the rate of the reaction. Give a reason for your answer.
(iii) Name two instruments that can be used to measure factors in (b)(i) above.
(c)(i) State the reasons for regarding rusting and burning as oxidation processes.
(ii) I. Write the balanced half equations for the following redox reaction: Mg\(_{(s)}\) + Fe\(^{2+}_{(aq)}\) —-> Mg\(^{2+}_{(aq)}\) + Fe\(_{(s)}\)
II. Which of the reactants is the oxidizing agent?
Ill. State the change in the oxidation number of the oxidizing agent.
(d)(i) State one ore from which each of the following metals can be extracted. I. Tin II. Iron (ii) List two uses of copper (iii) Name one alloy of tin.
(i) Write the structure of 2—chloro-2—methylpropane.
(ii) Consider the compound X represented by the structure below:
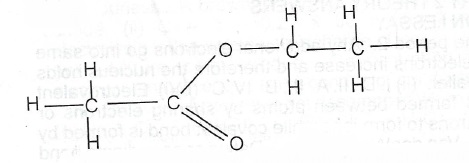
I. State the functional group in X; II. Give the IUPAC name of X; Ill. State the homologous series to which X belongs. IV. Give the names of two compounds from which X is formed. V. State one physical characteristt of X.
(b)(i) List two products obtained from fractional distillation of petroleum;
(ii) State one use of each product in (b)(i) above,
(iii) Mention one disadvantage of crude oil production
(c)(i) Mention the monomer of protein (ii) A compound has an empirical formula of CHO\(_2\) and its molar mass is 90. Deduce the molecular formula of the compound. [H = 1, C = 12, O = 16].
(d) Use the reaction scheme below to answer questions (i).— (iv).

(i) State the reagents needed for stages II and V;
(ii) Nanie the product Q of reaction in stage IV;
(iii) State the conditions required for stage III;
(iv) Give the names of the processes in stages I, II, Ill and V respectively.
(a)(i) State Graham’s law of diffusion
(ii) If 100 cm\(^3\) of oxygen diffused in 4 seconds and 50cm\(^3\) of gas Y diffused in 3 seconds, calculate the relative molecular mass of gas Y. (0 = 16)
(b) Consider the following equilibrium reaction: X + 2Y\(_{(g)}\) \(\rightleftharpoons\) XY\(_{2(9)}\) \(\Delta\)H = -52KJ mol\(^{-1}\)
(i) State what happens to the yield of XY\(_2\) when the temperature is increased
(ii) Explain the effect of decrease in pressure on the equilibrium position.
(iii) State the effect of a catalyst on the I. position of equilibrium II. activation energy
(c)(i) State the differences between the solubilities of solids and gases in liquids.
(ii) Name the physical-properties used it choosing separation techniques for the following mixtures:
I. kerosene and petrol II. calcium trioxocarbonate (IV) and potassium chloride. III. ammonium chloride and sodium chloride.
(d)(i) State a method of preparing each of the following salts:
| Acid | Basicity |
| H\(_3\)PO\(_4\) | |
| CH\(_3\)COOH | |
| HNO\(_2\) |
(iii) State the difference between anhydrous and hydrated salts.
(a) The electronic configurations of atoms of elements A, B, C and D are given as follows: A. Is\(^2\)2s\(^2\)2p\(^2\); B. 1s\(^2\)2s\(^2\)2sp\(^1\) ; C. 1s\(^2\)2s\(^2\) 2p\(^1\) ; D. 1s\(^2\) 2s\(^2\)
(I) Arrange the elements in order of increasing atomic size, giving reasons
(ii) State which of the elements I. is divalent II. contains atoms with two unpaired electrons in the grouped state. Ill, readily loses one electron from its atom during chemical bonding IV. belongs to group Ill in the Periodic Table.
(b)(i) State one difference between electrovalent and covalent bonds.
(ii) Name two other bonds apart from the ones in (b)(i) above which bind atoms and molecules together.
(iii) State two characteristics of a covalent compound.
(c)(i) What is isotopy?
(ii) Illustrate with suitable example
(iii) Two isotopes of Z with mass numbers 18 and 20 are in the ratio 1:2 Determine the relative atomic mass of Z.
(d)(i) Which of the following elements: calcium, fluorine, iodine neon, magnesium and helium are I. halogens II. noble gases Ill. alkaline earth metals.
(ii) Write a balanced equation for the bombardment of \(^7_3Li\) with protons to produce \(^8_4\beta\) and \(\gamma\)-rays
(iii) State one use of radioactive isotopes.
(a)(i) Draw the energy profile diagram for the reaction
H\(_{2(g)}\) + I\(_{2(g)}\) —> 2HI\(_{(g)}\) \(\Delta\) = —13 kJmol\(^3\)
(ii) If the concentration of HI increases from 0 to 0.001 mol dm\(^3}\) in 50 seconds, what is the rate of the reaction?
(b) State the type of salt represented by each of the following compounds:
(i) K\(_4\)Fe(CN)\(_6\) (ii) (NH\(_4\))\(_2\)Fe(SO\(_4\))\(_2\)6H\(_2\)O (iii) Mg(OH)NO\(_3\) (iv) NaH\(_2\)PO\(_4\).
(c) Explain, giving equations, the following observation: When carbon (IV) oxide is passed into lime water, it turns milky initially but turns clear with excess carbon (IV) oxide.
(d)(i) Give one use for each of the following compounds: CaCO\(_3\), CaSO\(_4\), NaHCO\(_3\).
(ii) State a drying agent for each of the following gases: i. NH\(_3\), II. HCI Ill. SO\(_4\).
(iii) Write an equation to illustrate the reaction of ammonia as a reducing agent.
(e) An industrial raw material has the following composition by mass:
Iron = 28.1%
Chlorine = 35.7%
Water of crystallization = 36.2%
Calculate the formula for the material. [ H = 1, 0 = 16, Cl = 35.5, Fe = 56 ].
(a)(i) Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the preparation and collection of dry chlorine gas in the laboratory.
(ii) List two uses of chlorine.
(b)(i) Explain why river water flowing through an industrial town may be unsafe for drinking.
(ii) State the use of each of the following substances in water treatment: I. Sand, II. Chlorine, III. Calcium oxide, IV. Alum
(c)Consider the reaction represented by the following equation:
2Na\(_2\)CI\(_{(s)}\) + H\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) \(\to\) Na\(_2\)SO\(_{4(aq)}\) + 2HCI\(_{(g)}\)
Calculate the volume of HCI gas that can be obtained at s.t.p. from 5.85 g of sodium chloride. [H = 1, Na = 23, CI = 35.5, Molar volume a 22.4 dm\(^3\) at s.t.p]
(d) Give one example in each case of a (i) metal that is a liquid at room temperature. (ii) non-metal that is a iiquid at room temperature, (iii) gas at room temperature that is monatomic.
(e) State two differences between metals and nom metals with respect to their: (i) physical properties; (ii) chemical properties.
(a) A solution of CuSO\(_4\) was electrolyzed between pure copper electrodes and the following results were obtained:
Mass of copper anode before experiment = 7.20 g
Mass of copper anode after experiment = 4.00 g
Mass of copper cathode before experiment = 5.75 g
From the information provided,
(i) calculate the mass of the cathode, after the experiment.
(ii) write an equation for the reaction at the I. anode, II. cathode.
(iii) state whether the colour of the solution would change during the electrolysis. Give a reason for your answer.
(iv) if the electrolysis was carried out for 1 hour 20 minutes with a current of 2.0 amperes, determine the value of the Faraday.
(b) Consider the reaction represented by the following equation:
MnO\(^-_4\) + I\(^-\) + H\(^+\) \(\to\) I\(_2\) + H\(_2\)O + Mn\(^{2+}\)
Write balanced half equation for the (i) oxidation reaction, (ii) reduction reaction.
(c)(i) Describe briefly how tin can be extracted from its ore.
(ii) State one use of tin.
(iii) Mention one property that makes tin suitable for the use stated in (c)(ii)
(d)(i) What is meant by the term pollution?
(ii) Explain why it is dangerous to run a generator in a closed room.

