(a) (i) Draw the structures of the isomers of the alkene with molecular formurat C\(_4\)H\(_8\)
(ii) State the class of alkanols to which each of the following compounds belongs:
I. CH\(_3\)C(CH\(_3\))\(_2\)OH;
II. CH\(_3\)CH(CH\(_3\))CH\(_2\)OH;
III. CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)CH(CH\(_3\))OH.
(b) (i) Write the formulae of the products formed in the following reactions:
I. CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)COOH \(\frac{K_{(s)}}{}\)
II. CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)COOH. \(\frac{C_4H_6OH, heat}{Conc.H_2SO_4}\)
III. CH\(_3\)CH\(_2\)CH\(_2\)CH\(_2\)OH \(\frac{H^+/KMnO_4}{(excess)}\)
(ii) Name the major product(s) of each of the reactions in (b)(i).
(c) A gaseous hydrocarbon R of mass 7.0 g occupies a volume of 2.24 dm\(^3\) at s. t.p. If the percentage composition by mass of hydrogen is 14.3, determine its:
(i) empirical formula;
(ii) molecular formula. [ H = 1.00, C = 12.0, Molar volume of gas at s.t.p, = 22.4 dm\(^3\) ]
(d) Define structural isomerism.
(a) Consider the following atoms: \(^R_T\)X; \(^S_T\)X.
(i) State the phenomenon exhibited by the two atoms.
(ii) What is the difference between the atoms?
(iii) Give two examples of elements that exhibit the phenomenon stated in (ai)
(iv) lf T is 17, write the electron configuration of the element
(b)(i) State two differences between metals and-non-metals with respect to their:
I. physical properties;
2. chemical properties.
(ii) Give one example of each for the following compounds:
I. an amphoteric oxide;
II. a hydride which evolves hydrogen when reacted with water;
Ill. a trioxocarbonate (IV) salt which is readily decomposed on heating;
IV. a chloride salt which is readily hydrolyzed in water.
(c)(i) State three characteristic properties of transition metals.
(ii) Write the electron configuration of \(_{30}Zn\)
(iii.) Explain briefly why zinc is not considered as a typical transition element.
(d) Consider the reaction represented by the following equation:- Na\(_2\)CO\(_{3(aq)}\) + MgCl\(_{2(aq)}\) —-> 2NaCl\(_{(aq)}\) + MgCO\(_{3(aq)}\). Calculate the mass of sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) needed to produce 3.36 of magnesium trioxocarbonate (IV). [C = 12.0, O = 16.0, Na = 23.0, Mg = 24:0 ]
(a) What are nucleons?
(b) State Graham’s law of diffusion.
(c) Explain briefly why aluminium does not corrode easily.
(d) State three examples of periodic properties.
(e) State two reasons why real gases deviate from ideal gas behaviour.
(f) List three uses of fractional distillation in industry.
(g) What factors determine the selective discharge of ions at the electrodes during electrolysis?
(h) State the type of reaction represented by each of the following equations:
(i) C\(_2\)H\(_6\) + Br\(_2\) —> C\(_2\)H\(_5\)Br + HBr;
(ii) C\(_2\)H\(_4\) + .Br\(_2\) —> CH\(_4\)Br\(_2\)
(i) Name the products formed when butane burns in limited supply of air.
(j) List three methods of separating a solid from a liquid.
(a)(i) Describe briefly how trioxonitrate (V) ions could be tested for in the laboratory.
(ii) State two uses of each of the following compounds: I. sodium chloride; II. sodium trioxocarbonate (IV).
(b) Write balanced equations for the reactions involved in the extraction of iron in the blast furnace.
(ii) State Faraday’s first law of electrolysis.
(iii) State two applications of electrolysis.
(c) Concentrated tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid is added to sugar crystals in a beaker. State what would be observed. Explain briefly your answer.
(d) Write an equation for the reaction of zinc powder with:
(i) dilute tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid;
(ii) concentrated tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid.
(e) What property of concentrated tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid is shown in (d)(ii)
(a)(i) Describe briefly the industrial preparation of ammonia.
(ii) Write a balanced equation for the reaction in (a)(i).
(iii) State one way of increasing the yield of ammonia in 4(a)(i).
(iv) State two uses of ammonia.
(b) Describe briefly, one chemical test for each of the following gases in the laboratory: (i) hydrogen; (ii) carbon (IV) oxide; (iii) oxygen.
(c)(i) State the composition of water gas.
(ii) List two uses of water gas.
(d) Describe briefly a simple experiment to determine the type of hardness in a sample of water.
(a) Write the molecular formula of X.
(i) What type of reaction is represented by the equation?
(ii) Consider the following reaction equation: C\(_{12}H_2\) \(\to\) X + C\(_8\)H\(_{18}\)
(iii) Draw the structure of two isomers of X.
(iv) Name the isomers drawn in (a)(iii).
(v) Write a balanced equation for the reaction between X and hydrogen.
(b) Describe one test for fats.
(c) Sulphur (IV) oxide is converted to tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid according to the following equation: 2SO\(_{2(g)}\) + O\(_{2(g)}\) + 2H\(_2\)O\(_{(l)}\) \(\to\) 2H\(_2\)OSO\(_{4(aq)}\). If 1.5 moles of oxgen reacts with sulphur (IV) oxide, calculate the mass of tetraoxosulphate (VI) acid produced. [H = 1.0; O = 16.0; S = 32.0].
(d) Consider the following neutralization reaction:
CH\(_3\)COOH + NaOH \(\to\) CH\(_3\)COONa + H\(_2\)O; \(\bigtriangleup\)H\(_1\)
CH\(_3\)COOH + NH\(_4\)OH \(\to\) CH\(_3\)COONH\(_4\) + H\(_2\)O; \(\bigtriangleup\)H\(_2\)
NaOH + HCl \(\to\) NaCl + H\(_2\)O \(\bigtriangleup\)H\(_3\)
(i) Arrange the enthalphy changes for the reactions in order of increasing magnitude.
(ii) Explain briefly your order in (d)(i).
(e) Consider the following substances. Cu\(_{(s)}\), BeCl\(_2\), NaH\(_{(s)}\), HF\(_{(s)}\)and CCl\(_{4(l)}\). State the substance(s) which;
(i) can conduct electricity;
(ii) is/are soluble in water.
(a)(i) 1. State the periodic law.
2. What is meant by the term periodic property of elements?
(ii) List three properties of an element which show periodicity.
(iii) Explain briefly how each of the properties listed in (a)(i) in varies across the period.
(b) Defulle relative atomic mass.
(c)(i) What phenomenon is exhibited by an element Z which exist as \(^{35}_{17}Z\) and \(^{37}_{17}X\)
(ii) What accounts for the difference in the mass numbers of the element Z?
(iii) Calculate the relative atomic mass of Z if the percentage abundance of \(^{37}_{17}Z\) is 75%
(d)(i) State the method used for collecting each of the following gases: I. CO II. HCI III. H\(_2\)
(ii) Give a reason for your answer stated in (d)(i) I and II
(a)(i) What is an acid-base indicator?
(ii) Give one example of an acid-base indicator.
(b) State the property exhibited by nitrogen(IV) oxide in each of the following equations:,
(i) 4Cu + 2NO\(_2\) -> 4CuO + N\(_2\) (ii) H\(_2\)O + 2NO\(_2\) –> HNO\(_3\) + HNO\(_2\)
(c)(i) Define enthalpy of combustion..
(ii) State why the enthalpy of combustion is always negative.
(d)(i) Distinguish between a primary cell and a secondary cell.
(ii) Give an example of each of the cells stated in I (d)(i).
(e) Define the term mole.
(f) Calculate the amount of hydrochloric acid in 40.0 cm\(^3\) of 0.40 moldm\(^{-3}\) dilute HCl.
(g) Name two substances which can be used as electrodes during the electroylsis of acidified water.
(h) List two forces of attraction that can exist between covalent molecules.
(i) Name the products formed when butane undergoes incomplete combustion.
(j) Write the electron configuration of \(_{26}\)Fe\(^{3+}\)
(a)(i) State two industrial uses of hdrogen.
(ii) Consider the equation below. Mg(HCO\(_3\))\(_{2(aq)}\) \(\to\) MgCO\(_{3(g)}\) + H\(_2\)0\(_{(l)}\) + CO\(_{2(g)}\)
1. State the type of hardness of water being removed as shown by the above equation.
2. Give two disadvantages of hardness of water.
(b)(i) In the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis, graphite electrodes are used. State the disadvantages of using this type of electrode.
(ii) Calcuim oxide reacts with water to form slaked line: I. Write a balanced equation for this reaction; II. State one use of slaked line.
(c)(i) What is meant by saponification?
(ii) List the raw materials needed for the manufacture of soap.
(iii) Name the main by-product obtained from the manufacture of soap.
(d) With the aid of chemical equations explain briefly how iron is extracted in the blast furnace using iron ore, coke and limestone as raw materials at the:
(i) bottom of the furnace; (ii) middle of the furnace (iii) top of the furnace.
(a)(i) Draw and label a diagram for the laboratory preparation of a dry sample of sulphur(IV)oxide.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in (a)(i).
(iii) State the precaution that must be taken in the preparation of the gas stated in (a)(i).
(iv) Give a reason why the precaution stated in (a)(ii) must be taken.
(b)(i) State Dalton’s law of partial pressures.
(ii) The volume of a sample of methane collected over-water at a temperature of 12°C and a pressure of 700 mmHg was 30cm\(^3\). Calculate the volume of the dry gas at s.t.p. [Saturated vapour pressure of water at 12°C is 10 mmHg] •
(c)(i) Write an equation for the reaction between chlorine and water.
(ii) Why does litmus paper turn red when put in the resulting solution in (c)(i)?
(d)(i) State the trend in the boiling points of chlorine, bromine and iodine.
(ii) Explain briefly why water has a higher boiling point than ammonia.
(a)(i) Draw the structure of the sixth member of the alkenes.
(ii) Calculate the relative molecular mass of the sixth member of the alkene.
(iii) State one difference between cracking and reforming in the petroleum industry. [H = 1, C = 12]
(b)(i) Define the term enthalpy of neutralization.
(ii) Describe briefly how the enthalpy of neutralization of the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous potassium hydroxide could be determined.
(c) An electrochemical cell is constructed with copper and silver electrodes.
(i) State which of the electrodes will be the: 1. anode; II. cathode.
(ii) Give the reason for your answer in 3(c)(i).
(iii) State the type of reaction occurring at each electrode.
(iv) Write a balanced equation for the overall cell reaction.
(d)(i) Name the compound formed when iron is exposed to moist air for a long time.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in 3(d)(i).
(iii) Name one ore of iron.
(a)(i) Sketch a graphical representation of Charles’ law.
(ii) Calculate the volume of oxygen that would be required for the complete combustion of 2.5 moles of ethanol at s.t.p. [molar volume at s.t.p. = 22.4 dm\(^3\)]
(b)(i) State the collision theory of reaction rates.
(ii) Using the collision theory, explain briefly how temperature can affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
(c)(i) Define esterification.
(ii) Give two uses of alkanoates.
(iii) Give the products of the alkaline hydrolysis of ethyl ethanoate.
(d) A tin coated plate and a galvanized plate were exposed for the same length of time.
(i) Which of the two plates corrodes faster
(ii) Explain briefly your answer in 2(d)(i)
Petroleum is a non-renewable source of energy because it
- A. is formed naturally
- B. is cheap
- C. can be recycled after use
- D. cannot be regenerated once used up
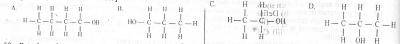
A primary alkanol has a molecular mass of 60. What is the structural formula of the compound? [C= 12.0, H= 1.0, O= 16.0)
- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. D
The real harmful effect of the release of chlorofluorocarbons into the atmosphere is that it eventually causes
- A. excessive ultraviolet light from the sun to reach the earth surface
- B. excessive release of infrared light from the sun to the earth surface
- C. corrosive effect of the chemicals on humans and animals
- D. acidic effect of chemicals on humans
The IUPAC name for the compound \(ClCH_{2}CH_{2}OH\) is
- A. 1- chloropropanol
- B. 2-chloropropanol
- C. 1-chloroethanol
- D. 2-chloroethanol
The condensation of two units of glucose will produce a dissacharide with the formula \(C_{12}H_{22}O_{11}\) which is
- A. sucrose
- B. maltose
- C. galactose
- D. mannose
Fats and oils can be obtained from any of the following sources except
- A. paraffin oil
- B. animals
- C. groundnuts
- D. palm kernel
Which of the following pairs of gases are pollutants from car exhaust?
- A. Nitrogen(II) oxide and Carbon(IV) oxide
- B. Carbon(IV) oxide and Nitrogen
- C. Carbon(II) oxide and Sulphur(IV) oxide
- D. Carbon(II) oxide and oxygen
The name of the compound \(C_{4}H_{9}COOC_{3}H_{7}\) is
- A. propyl pentanoate
- B. pentyl propanoate
- C. butyl propanoate
- D. propyl butanoate
Classification of alkanols is based on the
- A. number of carbon atoms present in the compound
- B. molecular mass of the compound
- C. molecular formula of the compound
- D. number of alkyl groups bonded to the carbon having the hydroxyl group


