(a) Given that \(\sin \alpha = 0.3907\), use tables to find the value of : (i) \(\tan \alpha\) ; (ii) \(\cos \alpha\).
(b) A ladder of length 4.5m leans against a vertical wall making an angle of 50° with the horizontal ground. If the bottom of a window is 4m above the ground, what is the distance between the top of the ladder and the bottom of the window? (Answer correct to the nearest cm)
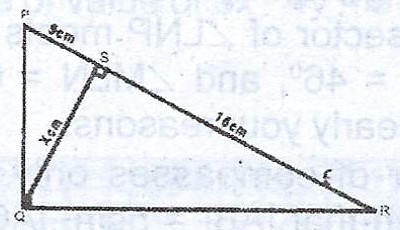
In the diagram, < PQR = < PSQ = 90°, |PS| = 9 cm, |SR| = 16 cm and |SQ| = x cm.
(a) Find the value of x using a trigonometric ratio.
(b) Calculate : (i) the size of < QRS to the nearest degree; (ii) |PQ|.
The number of items produced by a company over a five- year period is given below:
| Year | 1978 | 1979 | 1980 | 1981 | 1982 |
| No produced | 4100 | 2500 | 1500 | 1800 | 9200 |
(i) Plot a bar chart for this information; (ii) What is the average production for the five- year period.
(a) Derive the smallest equation whose coefficients are integers and which has roots of \(\frac{1}{2}\) and -7.
(b) Three years ago, a father was four times as old as his daughter is now. The product of their present ages is 430. Calculate the ages of the father and daughter.
(a) Triangle PQR is right-angled at Q. PQ = 3a cm and QR = 4a cm. Determine PR in terms of a.
(b) Ayo travels a distance of 24km from X on a bearing of 060° to Y. He then travels a distance of 18km to a point Z and Z is 30km from X.
(i) Draw the diagram to show the positions of X, Y and Z ; (ii) What is the bearing of Z from Y ; (iii) Calculate the bearing of X from Z.
(a) A pair of fair dice each numbered 1 to 6 is tossed. Find the probability of getting a sum of at least 9.
(b) If the probability that a civil servant owns a car is \(\frac{1}{6}\), find the probability that:
(i) two civil servants, A and B, selected at random each owns a car ; (ii) of two civil servants, C and D selected at random, only one owns a car ; (iii) of three civil servants, X, Y and Z, selected at random, only one owns a car.
(a) In an A.P, the difference between the 8th and 4th terms is 20 and the 8th term is \(1\frac{1}{2}\) times the 4th term. What is the:
(i) common difference ; (ii) first term of the sequence?
(b) The value of a machine depreciates each year by 5% of its value at the beginning of that year. If its value when new on 1st January 1980 was N10,250.00, what was its value in January 1989 when it was 9 years old? Give your answer correct to three significant figures.
(a) (i) Prove that the angle which an arc of a circle subtends at the centre is twice that which it subtends at any point on the remaining part of the circumference.
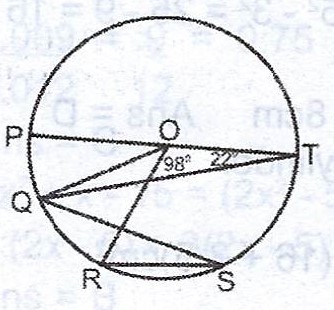
(ii) In the diagram above, O is the centre of the circle and PT is a diameter. If < PTQ = 22° and < TOR = 98°, calculate < QRS.
(b) ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral and the diagonals AC and BD intersect at H. If < DAC = 41° and < AHB = 70°, calculate < ABC.
When a stone is thrown vertically upwards, its distance d metres after t seconds is given by the formula \(d = 60t – 10t^{2}\). Draw the graph of \(d = 60t – 10t^{2}\) for values of t from 1 to 5 seconds using 2cm to 1 unit on the t- axis and 2cm to 20 units on the d- axis.
(a) Using your graph, (i) how long does it take to reach a height of 70 metres? (ii) determine the height of the stone after 5 seconds. (iii) after how many seconds does it reach its maximum height.
(b) Determine the slope of the graph when t = 4 seconds.
(a) 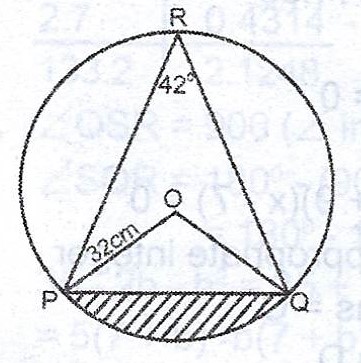
In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle radius 3.2cm. If < PRQ = 42°, calculate, correct to two decimal places, the area of the:
(i) minor sector POQ ; (ii) shaded part.
(b) If the sector POQ in (a) is used to form the curved surface of a cone with vertex O, calculate the base radius of the cone, correct to one decimal place.
(a) If \(\cos \alpha = 0.6717\), use mathematical tables to find (i) \(\alpha\) ; (ii) \(\sin \alpha\)
(b) The angle of depression of a point P on the ground, from the top T of a building is 23.6°. If the distance of P from the foot of the building is 50m, calculate the height of the building, correct to the nearest metre.
Using a ruler and a pair of compasses only, construct a triangle ABC, given that |AB| = 8.4cm, |BC| = 6.5cm and < ABC = 30°. Construct the locus:
(a) \(l_{1}\) of points equidistant from AB and BC, and within the angle ABC;
(b) \(l_{2}\) of points equidistant from B and C. Locate the point of intersection P of \(l_{1}\) and \(l_{2}\). Measure |AP|.
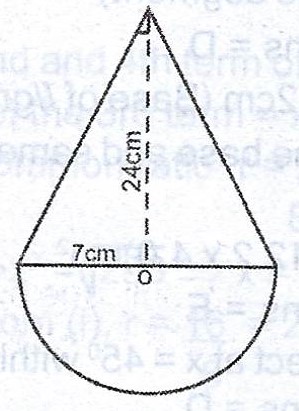
The diagram shows a wooden structure in the form of a cone, mounted on a hemispherical base. The vertical height of the cone is 24cm and the base height 7cm. Calculate, correct to three significant figures, the surface area of the structure. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
The table shows the weights, to the nearest kilogram, of twelve students in a Further Mathematics class
| Weight in kg | 55 | 57 | 59 | 61 | 63 |
| No of students | 2 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
(a) Draw a bar chart to illustrate the above information;
(b) What is (i) the mode; (ii) the median of the distribution?
(c) Calculate the mean weight correct to the nearest kilogram.
(a) Without using Mathematical tables, find x, given that \(6 \log (x + 4) = \log 64\)
(b) If \(U = {1, 2, 3,4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}, X = {1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9}, Y = {1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9}\) and \(Z = {2, 3, 4, 7, 9}\). What is \(X \cap Y \cap Z’ \)?
An aeroplane flies from a town P(lat. 40°N, 38°E) to another town Q(lat. 40°N, 22°W). It later flies to a third town T(28°N, 22°W). Calculate the :
(a) distance between P and Q along their parallel of latitude ;
(b) distance between Q and T along their line of longitudes;
(c) average speed at which the aeroplane will fly from P to T via Q, if the journey takes 12 hours, correct to 3 significant figures. [Take the radius of the earth = 6400km ; \(\pi = 3.142\)]
In a class of 40 students, 25 speak Hausa, 16 speak Igbo, 21 speak Yoruba and each of the students speak at least one of the these three languages. If 8 speak Hausa and Igbo, 11 speak Hausa and Yoruba and 6 speak Igbo and Yoruba.
(a) Draw a Venn diagram to illustrate the information, using x to represent the number of students that speak all three languages.
(b) calculate the value of x.
The following is an incomplete table for the relation \(y = 2x^{2} – 5x + 1\)
| x | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| y | 8 | 1 | -1 | 26 |
(a) Copy and complete the table.
(b) Using a scale of 2cm to 1 unit on the x- axis and 2cm to 10 units on the y- axis, draw the graph of the relation \(y = 2x^{2} – 5x + 1\) for \(-3 \leq x \leq 5\).
(c) Using the same scale and axes, draw the graph of \(y = x + 6\).
(d) Estimate from your graphs, correct to one decimal place : (i) the least value of y and the value of x for which it occurs ; (ii) the solution of the equation \(2x^{2} – 5x + 1 = x + 6\).
(a) If a number is chosen at random from the integers 5 to 25 inclusive, find the probability that the number is a multiple of 5 or 3.
(b) A bag contains 10 balls that differ only in colour; 4 are blue and 6 are red. Two balls are picked one after the other, with replacement. What is the probability that:
(i) both are red? (ii) both are the same colour?
(a) ABCD is a trapezium in which AB // DC, |AB| = 8cm, < ABC = 60°, |BC| = 5.5cm and |BD| = 8.3cm. Using a ruler and a pair of compasses only, construct:
(i) the trapezium ABCD ; (ii) a rectangle PQCD, where P, Q are two points AB;
(b) Measure |AB| and |QB|.
The weights to the nearest kilogram, of a group of 50 students in a College of Technology are given below:
65, 70, 60, 46, 51, 55, 59, 63, 68, 53, 47, 53, 72, 53, 67, 62, 64, 70, 57, 56, 73, 56, 48, 51, 58, 63, 65, 62, 49, 64, 53, 59, 63, 50, 48, 72, 67, 56, 61, 64, 66, 52, 49, 62, 71, 58, 53, 69, 63, 59.
(a) Prepare a grouped fraquency table with class intervals 45 – 49, 50 – 54, 55 – 59 etc.
(b) Using an assumed mean of 62 or otherwise, calculate the mean and standard deviation of the grouped data, correct to one decimal place.

