(a) Find the volume of a right solid cone of base radius 4cm and perpendicular height 6cm. [\(\pi = 3.142\)]
(b) A hemispherical tank of diameter which is 10m is filled by water issuing from a pipe of radius 20cm at 2m per second. Calculate, correct to three significant figures, the time, in minutes, it takes to fill the tank.
The feet of two vertical poles of height 3m and 7m are in line with a point P on the ground, the smaller pole being between the taller pole and P and at a distance of 20m from P. The angle of elevation of the top (T) of the taller pole from the top (R) of the smaller pole is 30°. Calculate the :
(i) distance RT ; (ii) distance of the foot of the taller pole from P, correct to three significant figures ; (iii) angle of elevation of T from P, correct to one decimal place.
A carpenter was told to make a rectangular desk with top of dimension 50cm by 40cm. The carpenter actually made the desk 60cm by 35cm.
(a) Calculate the percentage error in the (i) length and the breadth ; (ii) area of the table top.
(b) Find the product of the two errors in a(i).
(a) Prove that the sum of the angles in a triangle is 2 right angles.
(b) The side AB of a triangle ABC is produced to a point D. The bisector of ACB cuts AB at E. Prove that < CAE + < CBD = 2 < CEB.
Show on a graph, the area which gives the solution set of the inequalities: \(y – 2x \leq 4 ; 3y + x \geq 6 ; y \geq 7x – 9\).
(a) Simplify \(\frac{0.016 \times 0.084}{0.48}\) [Leave your answer in standard form].
(b) Eight wooden poles are to be used for pillars and the lengths of the poles form an Arithmetic Progression (A.P). If the second pole is 2m and the sixth is 5m, give the lengths of the poles, in order.
From a horizontal distance of 8.5 km, a pilot observes that the angles of depression of the top and the base of a control tower are 30° and 33° respectively. Calculate, correct to three significant figures :
(a) the shortest distance between the pilot and the base of the control tower;
(b) the height of the control tower.
(a) Using a ruler and a pair of compasses only, construct a parallelogram PQRS with diagonals |PR| = 9cm and |QS| = 6cm, intersecting at K and < QKR = 60°.
(b) Construct a rectangle PABS which is equal in area to PQRS in (a) above and on the same side of PS as PQRS. Measure |PA|.
The table below shows the distribution of the waiting times for some customers in a certain petrol station.
| Waiting time (in mins) | No of customers |
| 1.5 – 1.9 | 3 |
| 2.0 – 2.4 | 10 |
| 2.5 – 2.9 | 18 |
| 3.0 – 3.4 | 10 |
| 3.5 – 3.9 | 7 |
| 4.0 – 4.4 | 2 |
(a) Write down the class boundaries of the distribution.
(b) Construct a cumulative frequency curve for the data;
(c) Using your graph, estimate: (i) the interquartile range of the distribution ; (ii) the proportion of customers who could have waited for more than 3 minutes.
(a) Prove that the angle which an arc of a circle subtends at the centre is twice that which it subtends at any point on the remaining part of the circumference.
(b) 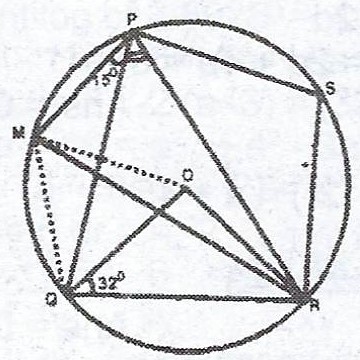
In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle, < OQR = 32° and < MPQ = 15°. Calculate (i) < QPR ; (ii) < MQO.
Using a scale of 2cm to 1 unit on the x- axis and 1cm to 1 unit on the y- axis, draw on the same axes the graphs of \(y = 3 + 2x – x^{2}; y = 2x – 3\) for \(-3 \leq x \leq 4\). Using your graph:
(i) solve the equation \(6 – x^{2} = 0\);
(ii) find the maximum value of \(3 + 2x – x^{2}\);
(iii) find the range of x for which \(3 + 2x – x^{2} \leq 1\), expressing all your answers correct to one decimal place.
A man bought 5 reams of duplicating paper, each of which are supposed to contain 480 sheets. The actual number of sheets in the packets were : 435, 420, 405, 415 and 440.
(a) Calculate, correct to the nearest whole number, the percentage error for the packets of paper;
(b) If the agreed price for a full ream was N35.00, find, correct to the nearest naira, the amount by which the buyer was cheated.
(a) Solve the equation, correct to two decimal places \(2x^{2} + 7x – 11 = 0\)
(b) Using the substitution \(P = \frac{1}{x}; Q = \frac{1}{y}\), solve the simultaneous equations : \(\frac{2}{x} + \frac{1}{y} = 3 ; \frac{1}{x} – \frac{5}{y} = 7\)
ABCDE is a regular pentagon and a rectangle AXYE is drawn on the side AE such that the vertices X and Y lie on the sides BC and CD respectively. Calculate the size of
(i) an interior angle of the pentagon ;
(ii) < BXA.
A man has 9 identical balls in a bag. Out of these, 3 are black, 2 are blue and the remaining are red.
(a) If a ball is drawn at random, what is the probability that it is (i) not blue? (ii) not red?
(b) If 2 balls are drawn at random, one after the other, what is the probability that both of them will be (i) black, if there is no replacement? (ii) blue, if there is a replacement?
In a certain class, 22 pupils take one or more of Chemistry, Economics and Government. 12 take Economics (E), 8 take Government (G) and 7 take Chemistry (C). Nobody takes Economics and Chemistry and 4 pupils take Economics and Government.
(a)(i) Using set notation and the letters indicated above, write down the two statements in the last sentence; (ii) Draw a Venn diagram to illustrate the information.
(b) How many pupils take (i) both Chemistry and Government ? (ii) Government only?
(a) Using logarithm table, evaluate \(\frac{\sqrt[3]{1.376}}{\sqrt[4]{0.007}}\) correct to three significant figure.
(b) Without using Mathematical tables, find the value of \(\frac{\log 81}{\log \frac{1}{3}}\).
Simplify :
(i) \(2\frac{2}{3} – (2\frac{1}{2} – 1\frac{4}{5})\)
(ii) \(\frac{3.25 – 1.64}{2.47 – 2.01}\)
The table below shows the weekly profit in naira from a mini-market.
| Weekly profit (N) | 1-10 | 11-20 | 21-30 | 31-40 | 41-50 | 51-60 |
| Freq | 6 | 6 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 5 |
(a) Draw the cumulative frequency curve of the data;
(b) From your graph, estimate the : (i) median ; (ii) 80th percentile
(c) What is the modal weekly profit?
Three towns P, Q and R are such that the distance between P and Q is 50km and the distance between P and R is 90km. If the bearing of Q from P is 075° and the bearing of R from P is 310°, find the :
(a) distance between Q and R ;
(b) baering of R from Q.
(a) The distribution of junior workers in an institution is as follows: Clerks – 78, Drivers – 36, Typists – 44, Messengers – 52, Others – 30. Represent the above information by a pie chart.
(b) The table below shows the frequency distribution of marks scored by 30 candidates in an aptitude test.
| Marks | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| No of candidates | 5 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
Find the mean score to the nearest whole number.

