(a) Use logarithm tables to evaluate \(\frac{15.05 \times \sqrt{0.00695}}{6.95 \times 10^{2}}\).
(b) The first 5 students to arrive in a school on a Monday morning were 2 boys and 3 girls. Of these, two were chosen at random for an assignment. Find the probability that :
(i) both were boys ; (ii) the two were of different sexes.
(a) Given that \(\frac{5y – x}{8y + 3x} = \frac{1}{5}\), find the value of \(\frac{x}{y}\) to two decimal places.
(b) If 3 is a root of the quadratic equation \(x^{2} + bx – 15 = 0\), determine the value of b. Find the other root.
The table below shows how a company’s sales manager spent his 1995 annual salary.
| Food | 30% |
| Rent | 18% |
| Car Maintenance | 25% |
| Savings | 12% |
| Taxes | 5% |
| Others | 10% |
(a) Represent this information on a pie chart.
(b) Find his savings at the end of the year if his annual salary was N60,000.00.
(a) Given that \(\sin x = \frac{5}{13}, 0° \leq x \leq 90°\), find \(\frac{\cos x – 2 \sin x }{2\tan x}\).
(b) 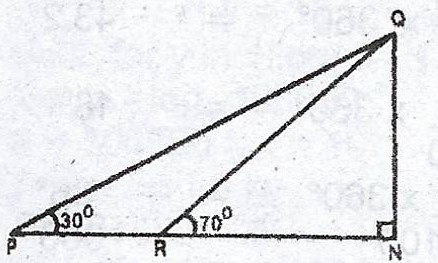
The diagram represents the vertical cross-section of a mountain with height NQ standing on a horizontal ground PRN. If the angles of elevation of the top of the mountain from P and R are 30° and 70° respectively and PR = 500m, calculate, correct to 3 significant figures :
(i) |QP| ; (ii) the height of the mountain.
(a) The 6th term of an A.P is 35 and the 13th term is 77. Find the 20th term.
(b) 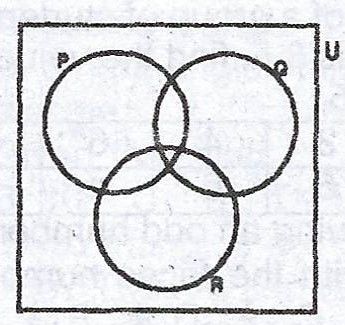
The Venn diagram represents three subsets P, Q and R of the universal set U. Copy the Venn diagram. Shade and indicate the regions represented by (i) \(P \cap Q’ \cap R\) ; (ii) \(P’ \cap Q \cap R’\).
(a) Copy and complete the binary multiplication table:
| x | 10 | 11 | 100 | 101 |
| 10 | 100 | 1000 | ||
| 11 | 110 | 1100 | ||
| 100 | 10000 | 10100 |
(b) Convert \(11.011_{two}\) to a number in base ten.
(c) Simplify \(\frac{9.6 \times 10^{18}}{0.24 \times 10^{5}}\) and express your answer in the form \(P \times 10^{m}\) where 1 < P < 10 and m is an integer.
The table below shows the number of eggs laid by the chickens in a man’s farm in a year.
| No of eggs per year | No of chickens |
| 45 – 49 | 10 |
| 50 – 54 | 36 |
| 55 – 59 | 64 |
| 60 – 64 | 52 |
| 65 – 69 | 28 |
| 70 – 74 | 10 |
(a) Draw a cumulative frequency curve for the distribution.
(b) Use your graph to find the interquartile range.
(c) If a woman buys a chicken from the farm, what is the probability that the chicken lays at least 60 eggs in a year?
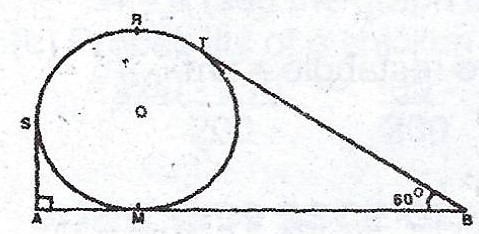
In the diagram, ASRTB represents a piece of string passing over a pulley of radius 10cm in a vertical plane. O is the centre of the pulley and AMB is a horizontal straight line touching the pulley at M. Angle SAB = 90° and angle TBA = 60°.
(a) Calculate (i) the obtuse angle SOT ; (ii) arc SRT ; (iii) |BT|
(b) Find, correct to the nearest cm, the length of the string. (Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)).
A surveyor standing at a point X sights a pole Y due east of him and a tower Z of a building on a bearing of 046°. After walking to a point W, a distance of 180m in the South- East direction, he observes the bearing of Z and Y to be 337° and 050° respectively.
(a) Calculate, correct to the nearest metre : (i) |XY| ; (ii) |ZW|
(b) If N is on XY such that XZ = ZN, find the bearing of Z from N.
Using a ruler and a pair of compasses only, construct (a) triangle QRT with |QR| = 8cm, |RT| = 6cm and |QT| = 4.5cm.
(b) a quadrilateral QRSP which has a common base QR with \(\Delta\)QRT such that QTP is a straight line, PQ || SR, |QP| = 9cm and |RS| = 4.5cm.
(i) Measure |PS| ; (ii) Find the perpendicular distance between RS and PQ ; (iii) What is QRSP?
(a) Copy and complete the table of values for the relation \(y = 5 – 7x – 6x^{2}\) for \(-3 \leq x \leq 2\).
| x | -3 | -2 | -1 | -0.5 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| y | -28 | 6 | 5 |
(b) Using a scale of 2cm to 1 unit on the x- axis and 2cm to 5 units on the y- axis, draw the :
(i) graph of \(y = 5 – 7x – 6x^{2}\) ; (ii) line \(y = 3\) on the same axis.
(c) Use your graph to find the : (i) roots of the equation \(2 – 7x – 6x^{2} = 0\) ; (ii) maximum value of \(y = 5 – 7x – 6x^{2}\).
(a) A radio which a dealer bought for N6,000.00 and marked to give a profit of 30% was reduced in a sales by 10%. Find : (i) the final sales price ; (ii) the percentage profit.
(b) Solve the equation : \(2^{(2x + 1)} – 9(2^{x}) + 4 = 0\).
The third term of a Geometric Progression (G.P) is 360 and the sixth term is 1215. Find the
(a) common ratio;
(b) first term ;
(c) sum of the first four terms.
(a) A number is selected at random from each of the sets {2, 3, 4} and {1, 3, 5}. What is the probability that the sum of the two numbers will be less than 7 but greater than 3?
(b) 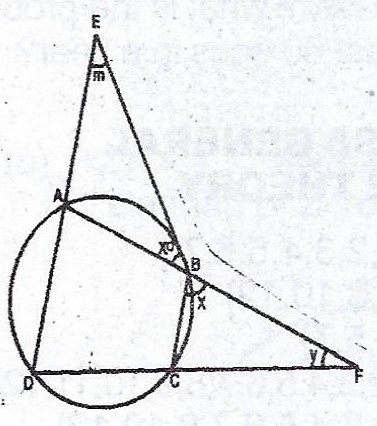
In the diagram, ABCD is a circle. DAE, CBE, ABF and DCF are straight lines. If y + m = 90°, find the value of x.
The area of a rectangular floor is 13.5m\(^{2}\). One side is 1.5m longer than the other.
(a) Calculate the dimensions of the floor ;
(b) If it costs N250.00 per square metre to carpet the floor and only N2,000.00 is available, what area of the floor can be covered with carpet?
(a) The value of the expression \(2Ax – Kx^{2}\) is 7 when x = 1 and 4 when x = 2. Find the values of the constants A and K.
(b) Solve the equation \(x^{2} – 3x – 1 = 0\), giving your answers correct to 1 decimal place.
(a) Given that \(\log_{10} 2 = 0.3010, \log_{10} 7 = 0.8451\) and \(\log_{10} 5 = 0.6990\), evaluate without using logarithm tables:
(i) \(\log_{10} 35\); (ii) \(\log_{10} 2.8\).
(b) Given that \(N^{0.8942} = 2.8\), use your result in (a)(ii) to find the value of N.
A, B and C are subsets of the universal set U such that : \(U = {0, 1, 2, 3,…, 12}; A = {x : 0 \leq x \leq 7}; B = {4, 6, 8, 10, 12}; C = {1 < y < 8}\), where y is a prime number.
(a) Draw a venn diagram to illustrate the information given above;
(b) Find: (i) \((B \cup C)’\); (ii) \(A’ \cap B \cap C\).
(a) Copy and complete the following table of values for \(y = 9 \cos x + 5 \sin x\) to one decimal place.
| x | 0° | 30° | 60° | 90° | 120° | 150° | 180° | 210° |
| y | 10.3 | -0.2 | -5.3 | -10.3 |
(b) Using a scale of 2cm to 30° on the x- axis and 2 cm to 1 unit on the y- axis, draw the graph of \(y = 9 \cos x + 5 \sin x\) for \(0° \leq x \leq 210°\).
(c) Use your graph to solve the equation: (i) \(9\cos x + 5\sin x = 0\); (ii) \(9\cos x+ 5\sin x = 3.5\), correct to the nearest degree.
(d) Find the maximum value of y correct to one decimal place.
(a) A shop owner marked a shirt at a price to enable him to make a gain of 20%. During a special sales period, the shirt was sold at 10% reduction to a customer at N864.00. What was the original cost to the shop owner?
(b) A rectangular lawn of length (x + 5) metres is (x – 2) metres wide. If the diagonal is (x + 6) metres, find ;
(i) the value of x ; (ii) the area of lawn.
On a graph sheet, using a scale of 2cm to 2 units on both axes,
(a) Draw the straight line joining points P(-5, 3) and Q(2, 3);
(b) construct the locus L of points equidistant from P and Q;
(c) by construction, locate points R and S on L, such that PRQS forms a rhombus of sides 5cm;
(d) find : (i) coordinates of R and S; (ii) area of the rhombus in cm\(^{2}\).

