The frequency distribution shows tha marks of 100 students in a Mathematics test.
| Marks | 1-10 | 11-20 | 21-30 | 31-40 | 41-50 | 51-60 | 61-70 | 71-80 | 81-90 | 91-100 |
|
No. of Students |
2 | 4 | 9 | 13 | 18 | 32 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 1 |
(a) Draw cumulative frequency curve for the distribution .
(b) Use your curve to estimate : (i) the median ; (ii) the lower quartile ; (iii) the 60th percentile.
K(lat. 60°N, long. 50°W) is a point on the eart’s surface. L is another point due East of K and the third point N is due South of K. The distance KL is 3520km and KN is 10951km.
(a) Calculate: (i) The longitude of L ; (ii) The latitude of N. (Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\) and the radius of the earth = 6400km).
(b) A man was allowed 20% of his income as tax free. He then paid 25 kobo in the naira on the remainder. If he paid N1,200.00 as tax, calculate his total income.
Using a ruler and a pair of compasses only,
(a) Construct : (i) \(\Delta PQR\) such that /PQ/ = 8cm, /PR/ = 7cm and < QPR = 105°. (ii) locus \(L_{1}\) of points equidistant from P and Q. (iii) locus \(l_{2}\) of points equidistant Q and R.
(b)(i) Label the point T where \(l_{1}\) and \(l_{2}\) intersect ; (ii) With centre T and radius /TQ/, construct a circle \(l_{3}\). (iii) Complete quadrilateral PQSR such that /RS/ = /QS/ and /RQ/ = /TS/.
(a) 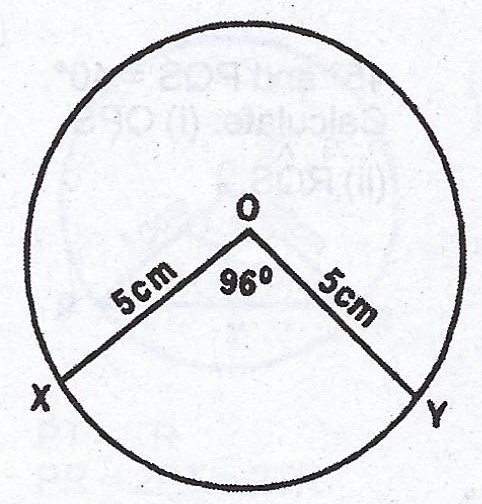
In the diagram, XY is a chord of a circle of radius 5cm. The chord subtends an angle 96° at the centre. Calculate, correct to three significant figures, the area of the minor segment cut-off. (Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)).
(b) 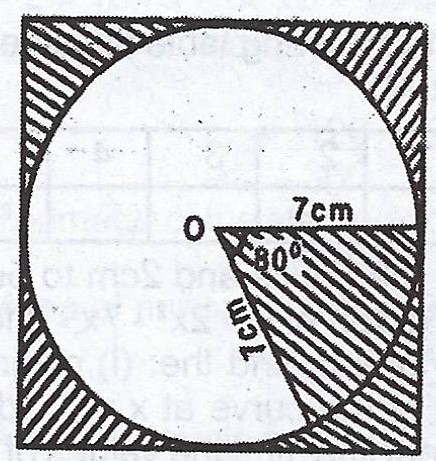 The figure shows a circle inscribed in a square. If a portion of the circle is shaded with some portions of the square, calculate the total area of the shaded portions. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
The figure shows a circle inscribed in a square. If a portion of the circle is shaded with some portions of the square, calculate the total area of the shaded portions. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a) The angles of depression of the top and bottom of a building are 51° and 62° respectively from the top of a tower 72m high. The base of the building is on the same horizontal level as the foot of the tower. Calculate the height of the building correct to 2 significant figures.
(b) 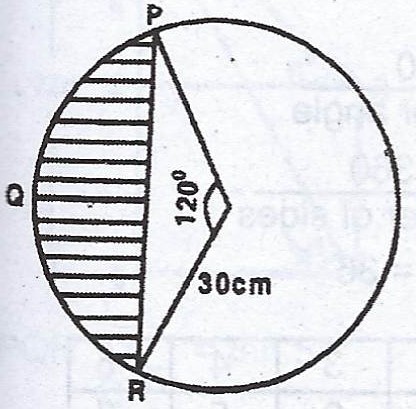 In the diagram, PR is a chord of the circle centre O and radius 30cm, < POR = 120°. Calculate correct to three significant figures : (i) the length of chord PR ; (ii) the length of arc PQR ; (iii) the perimeter of the shaded portion. (Take \(\pi = 3.142\)).
In the diagram, PR is a chord of the circle centre O and radius 30cm, < POR = 120°. Calculate correct to three significant figures : (i) the length of chord PR ; (ii) the length of arc PQR ; (iii) the perimeter of the shaded portion. (Take \(\pi = 3.142\)).
(a) Simplify : \((\frac{x^{2}}{2} – x + \frac{1}{2})(\frac{1}{x – 1})\)
(b) A point P is 40km from Q on a bearing 061°. Calculate, correct to one decimal place, the distance of P to (i) north of Q ; (ii) east of Q.
(c) A man left N5,720 to be shared among his son and three daughters. Each daughter’s share was \(\frac{3}{4}\) of the son’s share. How much did the son receive?
The table shows the marks scored by a group of students in a class test.
| Marks | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Frequency | 1 | 4 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 3 |
(a)(i) Calculate the mean mark ; (ii) Find the median.
(b) If the information were to be represented in a pie chart, what would be the sectorial angle for the mark 2?
(a) The sides of an isosceles triangle triangle are in the ratio \(7 : 5 : 7\). Calculate, correct to the nearest degree, the angle included between the equal sides.
(b) The sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon is 1440°. Calculate : (i) the number of sides ; (ii) the size of one exterior angle of the polygon.
(a) AB is a chord of a circle centre O. If |AB| = 24.2 cm and the perimeter of \(\Delta\) AOB is 52.2 cm, calculate < AOB, correct to the nearest degree.
(b) A rectangular tank 60cm by 80cm by 100cm is half filled with water. How many litres of water is it holding?
(a) In the simultaneous equations : \(px + qy = 5 ; qx + py = -10\); p and q are constants. If x = 1 and y = -2 is a solution of the equations, find p and q.
(b) Solve : \(\frac{4r – 3}{6r + 1} = \frac{2r – 1}{3r + 4}\).
(a) Solve \(\frac{1}{81^{(x – 2)}} = 27^{(1 – x)}\)
(b) Simplify \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{7} – \sqrt{3}} + \frac{1}{\sqrt{7} + \sqrt{3}}\), leaving your answer in surd form.
(a) Copy and complete the table.
\(y = x^{2} – 2x – 2\) for \(-4 \leq x \leq 4\)
| x | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| y | 22 | -2 | 1 | 6 |
(b) Using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x- axis and 2 cm to 5 units on the y- axis, draw the graph of \(y = x^{2} – 2x – 2\).
(c) Use your graph to find : (i) the roots of the equation \(x^{2} – 2x – 2 = 0\) ; (ii) the values of x for which \(x^{2} – 2x – 4\frac{1}{2} = 0\) ; (iii) the equation of the line of symmetry of the curve.
(a)  In the diagram, \(\Delta\) ABD is right-angled at B. |AB| = 3 cm, |AD| = 5 cm, \(\stackrel\frown{ACB}\) = 61° and \(\stackrel\frown{DAC}\) = x°. Calculate, correct to one decimal place, the value of x.
In the diagram, \(\Delta\) ABD is right-angled at B. |AB| = 3 cm, |AD| = 5 cm, \(\stackrel\frown{ACB}\) = 61° and \(\stackrel\frown{DAC}\) = x°. Calculate, correct to one decimal place, the value of x.
(b)  In the diagram, OABCD is a pyramid with a square base of side 2cm and a slant height of 4 cm. Calculate, correct to three significant figures : (i) the vertical height of the pyramid ; (ii) the volume of the pyramid.
In the diagram, OABCD is a pyramid with a square base of side 2cm and a slant height of 4 cm. Calculate, correct to three significant figures : (i) the vertical height of the pyramid ; (ii) the volume of the pyramid.
The table shows the age distributions of the members of a club.
| Age (years) | 10-14 | 15-19 | 20-24 | 25-29 | 30-34 | 35-39 |
| Frequency | 7 | 18 | 25 | 17 | 9 | 4 |
(a) Calculate, correct to one decimal place, the mean age.
(b) (i) Draw a histogram to illustrate the information.
(ii) Use the histogram to estimate the modal age .
(c) If a member is selected at random, what is the probability that he/she is in the modal class?
The sketch shows a plot of land .
(a) Using a scale of 1 cm to 10m, draw an accurate diagram of the plot ;
(b) Construct : (i) The locus \(l_{1}\) of points equidistant from AC and BC ; (ii) the locus \(l_{2}\) of points 60m from A.
(c) A tree T inside the plot is on both \(l_{1}\) and \(l_{2}\). Locate T and find |TC| in metres.
(d) A flagpole, P is to be placed such that it it is nearer AC than BC and more than 60m from A. Shade the regions where P can be located.
(a) Find the smallest integer that satisfies the inequality \(x + 8 < 4x – 15\).
(b) A sales girl is paid a monthly salary of N2,500 in addition to a commission of 5 kobo in the naira on all sales made by her during the month. If her sales for a month amounts to N200,000.00, calculate her income for that month.
(c) 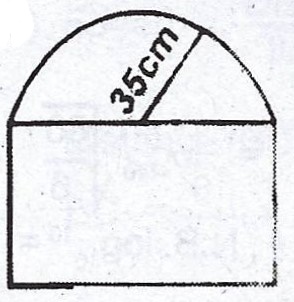 The diagram shows a window consisting of a rectangular and semi- circular parts. The radius of the semi- circular part is 35 cm and the height of the rectangular part is 50 cm. Find the area of the window. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
The diagram shows a window consisting of a rectangular and semi- circular parts. The radius of the semi- circular part is 35 cm and the height of the rectangular part is 50 cm. Find the area of the window. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a) A plane flies due East from A(lat. 53°N, long. 25°E) to a point B(lat. 53°N, long. 85°E) at an average speed of 400 km/h. The plane then flies South from B to a point C 2000km away. Calculate, correct to the nearest whole number :
(a) the distance between A and B.
(b) the time the plane takes to reach point B ;
(c) the latitude of C.
[Take radius of the earth = 6400km; \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a) A regular polygon of n sides is such that each interior angle is 120° greater than the exterior angle. Find :
(i) the value of n ; (ii) the sum of all the interior angles.
(b) A boy walks 6km from a point P to a point Q on a bearing of 065°. He then walks to a point R, a distance of 13km, on a bearing of 146°.
(i) Sketch the diagram of his movement. (ii) Calculate, correct to the nearest kilometre, the distance PR.
(a) Without using mathematical table or calculator, evaluate : \(\sqrt{\frac{0.18 \times 12.5}{0.05 \times 0.2}}\).
(b) Simplify : \(\frac{8 – 4\sqrt{18}}{\sqrt{50}}\).
(c) x, y and z are related such that x varies directly as the cube of y and inversely as the square of z. If x = 108 when y = 3 and z = 4, find z when x = 4000 and y = 10.
(a) 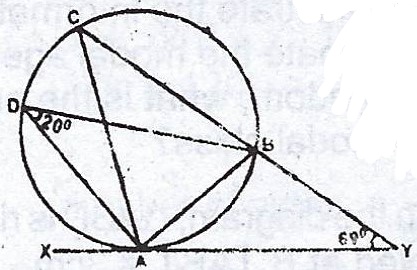
In the diagram, A, B, C and D are points on the circumference of a circle. XY is a tangent at A. Find : (i) < CAX ; (ii) < ABY.
(b) If (m + 1) and (m – 3) are factors of \(m^{2} – km + c\), find the values of k and c.
(a) Two fair die are thrown once. Find the probabitlity of getting : (i) the same digit ; (ii) a total score greater than 5.
(b) Given that \(x = \cos 30°\) and \(y = \sin 30°\), evaluate without using a mathematical table or calculator : \(\frac{x^{2} + y^{2}}{y^{2} – x^{2}}\).

