(a) Simplify : \(\frac{5}{8} of 2\frac{1}{2} – \frac{3}{4} \div \frac{3}{5}\).
(b) A cone and a right pyramid have equal heights and volumes. If the area of the base of the pyramid is \(154 cm^{2}\), find the base radius of the cone. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a) Evaluate : \(2 \div (\frac{64}{125})^{-\frac{2}{3}}\)
(b) The lines \(y = 3x + 5\) and \(y = – 4x – 1\) intersect at a point k. Find the coordinates of k.
(a) Evaluate without using the mathematical table or calculator, \(\log_{10} \sqrt{30} – \log_{10} \sqrt{6} + \log_{10} \sqrt{2}\).
(b) 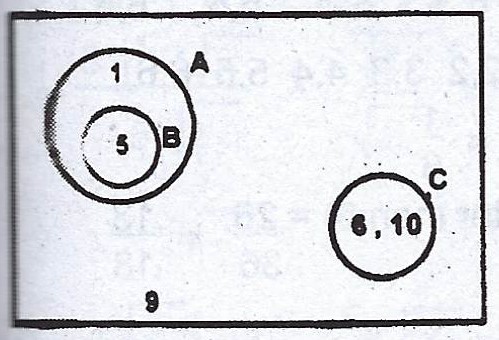
\(U = {1, 2, 3, …, 10} ; A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} ; B = {2, 3, 5}\) and \(C = {6, 8, 10}\). (i) Given that the Venn diagram represents the sets above, copy and fill in the elements.
(ii) Find \(A \cap C\) ; (iii) Find \(A \cap B’\).
(a) Two lines AB and CD intersect at x such that \(\stackrel\frown{CAX}\) is equal to \(\stackrel\frown{BDX}\). If |AX| = 6 cm, |XB| = 4 cm and |CX| = 3 cm, find |XD|.
(b) 
The diagram shows the positions of three points X, Y and Z on a horizontal plane. The bearing of Y from X is 312° and that of Y from Z is 022°. If |XY| = 32 km and |ZY| = 50 km, calculate, correct to one decimal place : (i) |XZ| ; (ii) the bearing of Z from X.
(a) Copy and complete the table of the relation \(y = 2\sin x – \cos 2x\).
| x | 0° | 30° | 60° | 90° | 120° | 150° | 180° |
| y | 0.5 | -1.0 |
Using a scale of 2 cm to 30° on the x- axis and 2 cm to 0.5 unit on the y- axis, draw the graph of \(y = 2\sin x – \cos 2x\), for \(0° \leq x \leq 180°\).
(b) Using the same axes, draw the graph of \(y = 1.25\).
(c) Use your graphs to find the : (i) values of x for which \(2\sin x – \cos 2x = 0\) ; (ii) the roots of the equation \(2\sin x – \cos 2x = 1.25\).
(a) 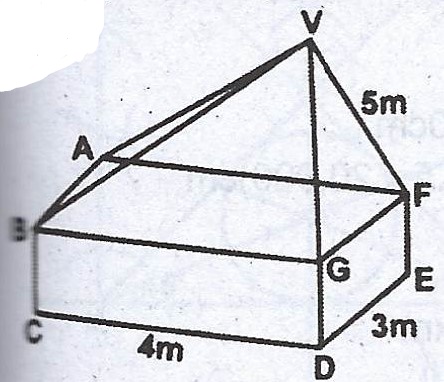
The diagram shows a pyramid standing on a cuboid. The dimensions of the cuboid are 4m by 3m by 2m and the slant edge of the pyramid is 5m. Calculet the volume of the shape.
(b) The 2nd, 3rd and 4th terms of an A.P are x – 2, 5 and x + 2 respectively. Calculate the value of x.
The following table shows the distribution of test scores in a class.
| Scores | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| No of pupils | 1 | 1 | 5 | 3 | \(k^{2} + 1\) | 6 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
(a) If the mean score of the class is 6, find the : (i) value of k (ii) median score.
(b) Draw a bar chart for the distribution.
(c) If a pupil is picked at random, what is the probability that he/ she will score less than 6?
(a) Using a ruler and a pair of compasses only, (i) construct \(\Delta\) XYZ such that |XY| = 8 cm and < YXZ = < ZYX = 45°. (ii) locate a point P inside the triangle equidistant from XY and XZ and also equidistance from YX and YZ. (iii) construct a circle touching the three sides of the triangle (iv) measure the radius of the circle.
(b) The length of the sides of a hexagon are x – 5, 2x, 2x, 2x + 7, 2x and 2x – 1. If the perimeter is 144 cm, find the value of x.
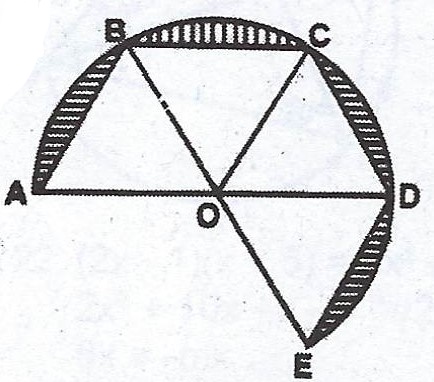
In the diagram, ABCDEO is two- thirds of a circle centre O. The radius AO is 7cm and /AB/ = /BC/ = /CD/ = /DE/. Calculate, correct to the nearest whole number, the area of the shaded portion. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a)(i) If \(4x < 2 + 3x\) and \(x – 8 < 3x\), what range of values of x satisfies both inequalities? ; (ii) Represent your result in (i) on the number line.
(b) A shop is sending out a bill for an amount less than £100. The accountant interchanges the two digits and so overcharges the customer by 45. Given that the sum of the two digits is 9, find how much the bill should be.
(a) A sector of a circle of radius 8cm subtends an angle of 90° at the centre of the circle. If the sector is folded without overlap to form the curved surface of a cone, find the :
(i) base radius ; (ii) height ; (iii) volume of the cone. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(b) A map is drawn to a scale of 1 : 20,000. Use it to calculate the : (i) distance, in kilometres, represented by 4.5 cm on the map ;
Two fair dice are tossed together once.
(a) Draw a sample space for the possible outcomes ;
(b) Find the probability of getting a total : (i) of 7 or 8 ; (ii) less than 4.
(a) In a class of 45 students, 32 offered Physics(P), 28 offered Government(G) and 12 did not offer any of the two subjects. (i) Draw the Venn diagram to represent the information ; (ii) How many students offered both subjects? (iii) What is \(n(P \cup G)\)?
(b) If \(p = \frac{2u}{1 – u}\) and \(q = \frac{1 + u}{1 – u}\) ; express \(\frac{p + q}{p – q}\) in terms of u.
(a) Solve for x and y in the following equations :
\(2x – y = \frac{9}{2}\)
\(x + 4y = 0\)
(b) 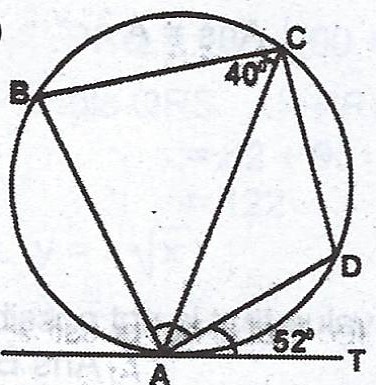
In the diagram, TA is a tangent to the circle at A. If \(\stackrel\frown{BCA} = 40°\) and \(\stackrel\frown{DAT} = 52°\), find \(\stackrel\frown{BAD}\).
(a) A dealer sold a car to a man and made a profit of 15%. The man then sold it to a woman for N120,175.00 at a loss of 5%. How much did the dealer buy the car?
(b) The diameter of the wheel of a car is 36cm. How many revolutions, correct to three significant figures, will it make to cover a distance of 1.05 km? [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a) Simplify : \(\frac{4\frac{2}{9} – 1\frac{13}{15}}{2\frac{1}{5} + \frac{4}{7} \times 2\frac{1}{3}}\)
(b) By rationalising the denominator, simplify : \(\frac{7\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{7}}\), leaving your answer in surd form.
In a college, the number of absentees recorded over a period of 30 days was as shown in the frequency distribution table
| Number of absentees | 0-4 | 5-9 | 10-14 | 15-19 | 20-24 |
| Number of Days | 1 | 5 | 10 | 9 | 5 |
Calculate the : (a) Mean
(b) Standard deviation , correct to two decimal places.
(a) The 3rd and 8th terms of an arithmetic progression (A.P) are -9 and 26 respectively. Find the : (i) common difference ; (ii) first term.
(b) 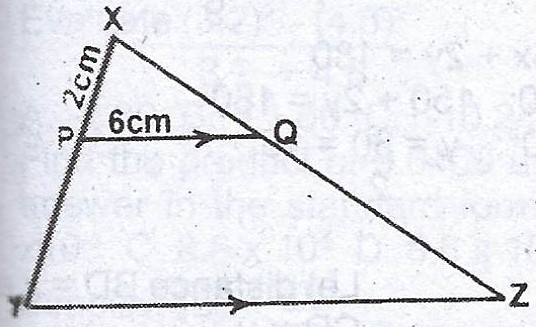
In the diagram \(\overline{PQ} || \overline{YZ}\), |XP| = 2cm, |PY| = 3 cm, |PQ| = 6 cm and the area of \(\Delta\) XPQ = 24\(cm^{2}\).Calculate the area of the trapezium PQZY.
(a) 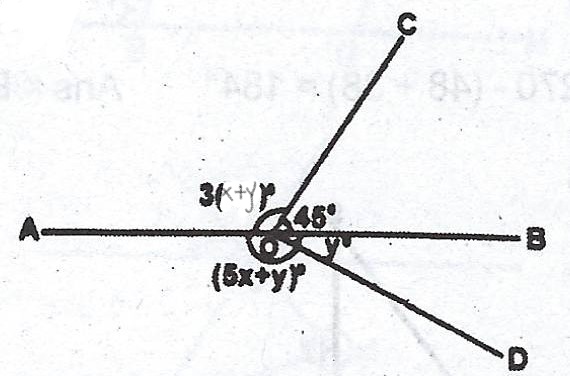
In the diagram, AOB is a straight line. < AOC = 3(x + y)°, < COB = 45°, < AOD = (5x + y)° and < DOB = y°. Find the values of x and y.
(b) From two points on opposite sides of a pole 33m high, the angles of elevation of the top of the pole are 53° and 67°. If the two points and the base are on te same horizontal level, calculate, correct to three significant figures, the distance between the two points.
(a) Simplify : \(\frac{x^{2} – y^{2}}{3x + 3y}\)
(b) 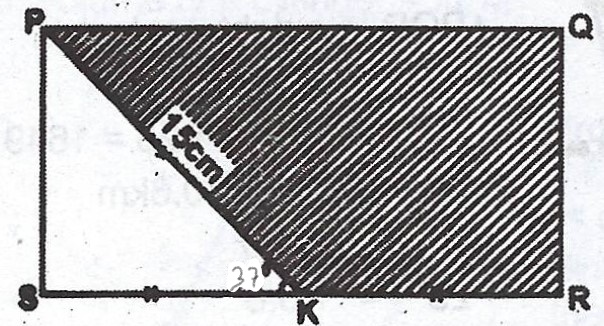
In the diagram, PQRS is a rectangle. /PK/ = 15 cm, /SK/ = /KR/ and <PKS = 30°. Calculate, correct to three significant figures : (i) /PS/ ; (ii) /SK/ and (iii) the area of the shaded portion.
(a) Using a ruler and a pair of compasses only, construc :
(i) a triangle PQR such that /PQ/ = 10 cm, /QR/ = 7 cm and < PQR = 90° ; (ii) the locus \(l_{1}\) of points equidistant from Q and R ; (iii) the locus \(l_{2}\) of points equidistant from P and Q.
(b) Locate the point O equidistant from P, Q and R.
(c) With O as centre, draw the circumcircle of the triangle PQR.
(d) Measure the radius of the circumcircle.

