(a) A cylinder with radius 3.5 cm has its two ends closed, if the total surface area is \(209 cm^{2}\), calculate the height of the cylinder. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(b) 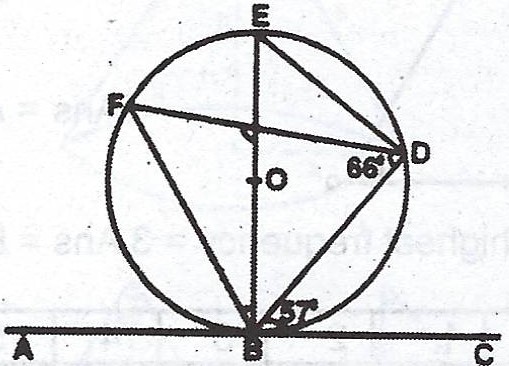 In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle and ABC is a tangent at B. If \(\stackrel\frown{BDF} = 66°\) and \(\stackrel\frown{DBC} = 57°\), calculate, (i) \(\stackrel\frown{EBF}\) and (ii) \(\stackrel\frown{BGF}\).
In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle and ABC is a tangent at B. If \(\stackrel\frown{BDF} = 66°\) and \(\stackrel\frown{DBC} = 57°\), calculate, (i) \(\stackrel\frown{EBF}\) and (ii) \(\stackrel\frown{BGF}\).
(a) With the aid of four- figure logarithm tables, evaluate \((0.004592)^{\frac{1}{3}}\).
(b) If \(\log_{10} y + 3\log_{10} x = 2\), express y in terms of x.
(c) Solve the equations : \(3x – 2y = 21\)
\(4x + 5y = 5\).
(a) Simplify : \(\frac{3\frac{1}{12} + \frac{7}{8}}{2\frac{1}{4} – \frac{1}{6}}\)
(b) If \(p = \frac{m}{2} – \frac{n^{2}}{5m}\) ;
(i) make n the subject of the relation ; (ii) find, correct to three significant figures, the value of n when p = 14 and m = -8.
Out of the 24 apples in a box, 6 are bad. If three apples are taken from the box at random, with replacement, find the probability that :
(a) the first two are good and the third is bad ;
(b) all three are bad ;
(c) all the three are good.
Y is 60 km away from X on a bearing of 135°. Z is 80 km away from X on a bearing of 225°. Find the :
(a) distance of Z from Y ;
(b) bearing of Z from Y.
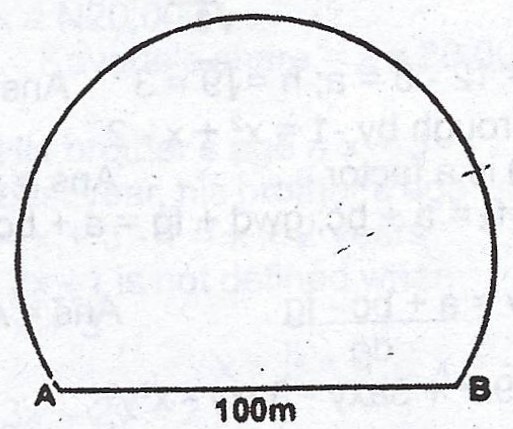
The diagram shows the cross- section of a railway tunnel. If |AB| = 100m and the radius of the arc is 56m, calculate, correct to the nearest metre, the perimetre of the cross- section.
(a) Simplify : \(\frac{x^{2} – 8x + 16}{x^{2} – 7x + 12}\).
(b) If \(\frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{x}, \frac{1}{3}\) are successive terms of an arithmetic progression (A.P), show that \(\frac{2 – x}{x – 3} = \frac{2}{3}\).
(a) Evaluate, without using mathematical tables or calculator, \((3.69 \times 10^{5}) \div (1.64 \times 10^{-3})\), leaving your answer in standard form.
(b) A man invested N20,000 in bank A and N25,000 in bank B at the beginning of the year. Bank A pays simple interest at a rate of y% per annum and B pays 1.5y% per annum. If his total interest at the end of the year from the two banks was N4,600, find the value of y.
(a) If 3, x, y, 18 are the terms of an Arithmetic Progression (A.P), find the values of x and y.
(b)(i) The sum of the second and third terms of a grometric progression is six times the fourth term. Find the two possible values of the common ratio.
(ii) If the second term is 8 and the common ratio is positive, find the first six terms.
(a) Copy and complete the table of values for \(y = 3\sin x + 2\cos x\) for \(0° \leq x \leq 360°\).
| x | 0° | 60° | 120° | 180° | 240° | 300° | 360° |
| y | 2.00 | 2.00 |
(b) Using a scale of 2 cm to 60° on x- axis and 2 cm to 1 unit on the y- axis, draw the graph of \(y = 3 \sin x + 2 \cos x\) for \(0° \leq x \leq 360°\).
(c) Use your graph to solve the equation : \(3 \sin x + 2 \cos x = 1.5\).
(d) Find the range of values of x for which \(3\sin x + 2\cos x < -1\).
(a) 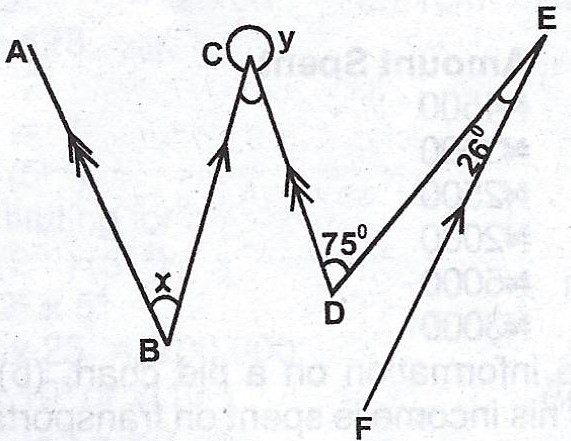
In the diagram, AB // CD and BC // FE. \(\stackrel\frown{CDE} = 75°\) and \(\stackrel\frown{DEF} = 26°\). Find the angles marked x and y.
(b) 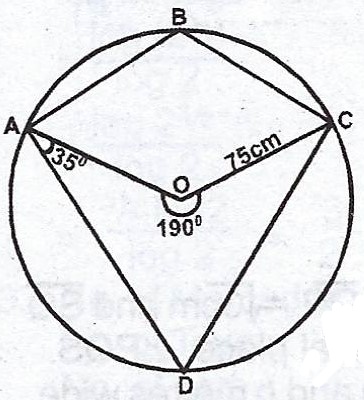
The diagram shows a circle ABCD with centre O and radius 7 cm. The reflex angle AOC = 190° and < DAO = 35°. Find :
(i) < ABC ; (ii) < ADC.
(c) Using the diagram in (b) above, calculate, correct to 3 significant figures, the length of : (i) arc ABC ; (ii) the chord AD. [Take \(\pi = 3.142\)].
(a) Using ruler and a pair of compasses only, construct :
(i) a quadrilateral PQRS such that /PQ/ = 7 cm, < QPS = 60°, /PS/ = 6.5 cm, < PQR = 135° and /QS/ = /QR/ ;
(ii) locus, \(l_{1}\) of points equidistant from P and Q ;
(iii) locus, \(l_{2}\) of points equidistant from P and S.
(b)(i) Label the point T where \(l_{1}\) and \(l_{2}\) intersect. (ii) With center T and radius /TP/, construct a circle \(l_{3}\).
(a) The triangle ABC has sides AB = 17m, BC = 12m and AC = 10m. Calculate the :
(i) largest angle of the triangle ; (ii) area of the triangle.
(b) From a point T on a horizontal ground, the angle of elevation of the top R of a tower RS, 38m high is 63°. Calculate, correct to the nearest metre, the distance between T and S.
The ages, in years, of 50 teachers in a school are given below :
21 37 49 27 49 42 26 33 46 40 50 29 23 24 29 31 36 22 27 38 30 26 42 39 34 23 21 32 41 46 46 31 33 29 28 43 47 40 34 44 26 38 34 49 45 27 25 33 39 40
(a) Form a frequency distribution table of the data using the intervals : 21 – 25, 26 – 30, 31 – 35 etc.
(b) Draw the histogram of the distribution
(c) Use your histogram to estimate the mode
(d) Calculate the mean age.
(a) Solve, correct to two decimal places, the equation \(4x^{2} = 11x + 21\).
(b) A man invests £1500 for two years at compound interest. After one year, his money amounts to £1560. Find the :
(i) rate of interest ; (ii) interest for the second year.
(c) A car costs N300,000.00. It depreciates by 25% in the first year and 20% in the second year. Find its value after 2 years.
(a) If \(2^{x + y} = 16\) and \(4^{x – y} = \frac{1}{32}\), find the value of x and y.
(b) P, Q and R are related in such a way that \(P \propto \frac{Q^{2}}{R}\). When P = 36, Q = 3 and R = 4. Calculate Q when P = 200 and R = 2.
(a) A rectangular field is l metres long and b metres wide. Its perimeter is 280 metres. If the length is two and a half times the breadth, find the values of l and b.
(b) The base of a pyramid is a 4.5 metres rectangle. The height of the pyramid is 4 metres. Calculate its volume.
(a) A pentagon is such that one of its exterior sides is 60°. Two others are (90 – m)° each while the remaining angles are (30 + 2m)° each. Find the value of m.
(b) 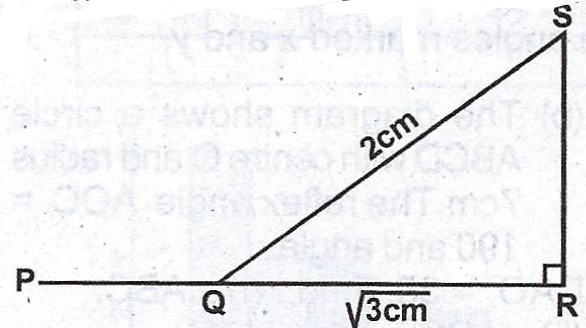
In the diagram, PQR is a straight line, \(\overline{QR} = \sqrt{3} cm\) and \(\overline{SQ} = 2 cm\). Calculate, correct to one decimal place, < PQS.
The table below shows how a man spends his income in a month.
| Items | Amount Spent |
| Food | N4500 |
| House Rent | N3000 |
| Provisions | N2500 |
| Electricity | N2000 |
| Transportation | N5000 |
| Others | N3000 |
(a) Represent the information on a pie chart.
(b) What percentage of his income is spent on transportation?
(a) Solve the inequality : \(\frac{2}{5}(x – 2) – \frac{1}{6}(x + 5) \leq 0\).
(b) Given that P = \(\frac{x^{2} – y^{2}}{x^{2} + xy}\),
(i) express P in its simplest form ; (ii) find the value of P if x = -4 and y = -6.
(a) Without using calculator or tables, find the value of \(\log 3.6\) given that \(\log 2 = 0.3010, \log 3 = 0.4771\) and \(\log 5 = 0.6990\).
(b) If all numbers in the equation \(\frac{y}{y + 101} = \frac{11}{10010}\) are in base two, solve for y.

