Two fair die are thrown. M is the event described by “The sum of the scores is 10” and N is the event described by “The difference between the scores is 3”.
(a) Write out the elements of M and N.
(b) Find the probability of M or N.
(c) Are M and N mutually exclusive? Give reasons.
(a) 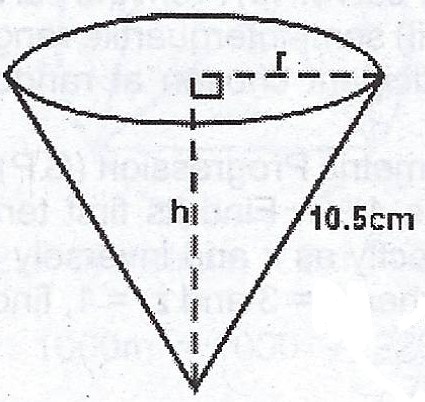
Curved Surface Area = \(\pi rl\)
\(115.5 = \frac{22}{7} \times r \times 10.5\)
\(115.5 = 33r\)
\(r = \frac{115.5}{33} = 3.5 cm\)
(b) 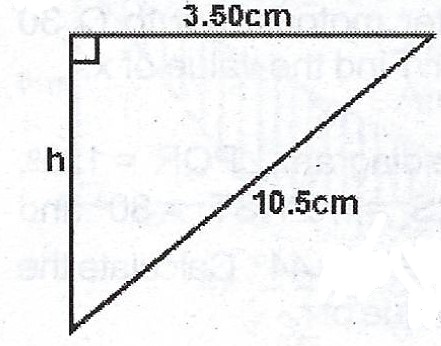
\(\therefore h^{2} + (3.50)^{2} = (10.5)^{2}\)
\(h^{2} = 10.5^{2} – 3.5^{2}\)
\(h^{2} = 98 \implies h = \sqrt{98}\)
\(h = 9.8994 cm \approxeq 9.90 cm\)
(c) Volume of a cone = \(\frac{1}{3} \pi r^{2} h\)
= \(\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times \frac{7}{2} \times \frac{7}{2} \times 9.90\)
= \(\frac{23.1 \times 11}{2}\)
= \(127.05 cm^{3} \approxeq 127 cm^{3}\)
(a) 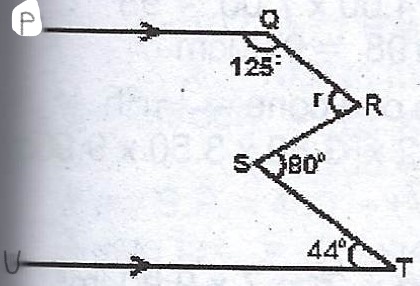
In the diagram, < PQR = 125°, < QRS = r, < RST = 80° and < STU = 44°. Calculate the value of r.
(b) 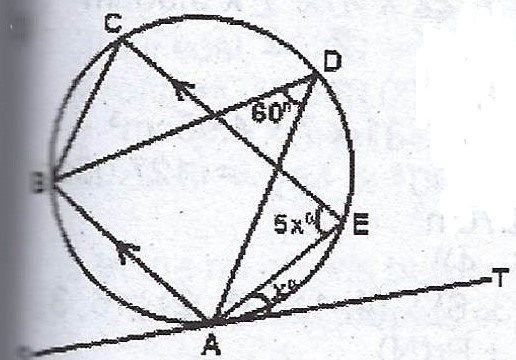 In the diagram TS is a tangent to the circle at A. AB // CE, < AEC = 5x°, < ADB = 60° and < TAE = x. Find the value of x.
In the diagram TS is a tangent to the circle at A. AB // CE, < AEC = 5x°, < ADB = 60° and < TAE = x. Find the value of x.
(a) The angle of depression of a boat from the mid-point of a vertical cliff is 35°. If the boat is 120m from the foot of the cliff, calculate the height of the cliff.
(b) Towns P and Q are x km apart. Two motorists set out at the same time from P to Q at steady speeds of 60 km/h and 80 km/h. The faster motorist got to Q 30 minutes earlier than the other. Find the value of x.
A = {2, 4, 6, 8}, B = {2, 3, 7, 9} and C = {x : 3 < x < 9} are subsets of the universal set U = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}. Find
(a) \(A \cap (B’ \cap C’)\) ;
(b) \((A \cup B) \cap (B \cup C)\).
(a) P varies directly as Q and inversely as the square of R. If P = 1 when Q = 8 and R = 2, find the value of Q when P = 3 and R = 5.
(b) An aeroplane flies from town A(20°N, 60°E) to town B(20°N, 20°E). (i) if the journey takes 6 hours, calculate, correct to 3 significant figures, the average speed of the aeroplane. (ii) if it then flies due North from town B to town C, 420 km away, calculate correct to the nearest degree, the latitude of town C. [Take radius of the earth = 6400 km and \(\pi\) = 3.142].
(a) The area of trapezium PQRS is 60\(cm^{2}\). PQ // RS, /PQ/ = 15 cm, /RS/ = 25 cm and < PSR = 60°. Calculate the : (i) perpendicular height of PQRS ; (ii) |PS|.
(b) Ade received \(\frac{3}{5}\) of a sum of money, Nelly \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the remainder while Austin took the rest. If Austin’s share is greater than Nelly’s share by N3,000, how much did Ade get?
The table shows the scores obtained when a fair die was thrown a number of times.
| Score | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Frequency | 2 | 5 | x | 11 | 9 | 10 |
If the probability of obtaining a 3 is 0.26, find the (a) median
(b) standard deviation of the distribution.
(a) The total surface area of two spheres are in the ratio 9 : 49. If the radius of the smaller sphere is 12 cm, find, correct to the nearest \(cm^{3}\), the volume of the bigger sphere.
(b) A cyclist starts from a point X and rides 3 km due West to a point Y. At Y, he changes direction and rides 5 km North- West to a point Z.
(i) How far is he from the starting point, correct to the nearest km? ; (ii) Find the bearing of Z from X, to the nearest degree.
Using ruler and a pair of compasses only,
(a) construct a rhombus PQRS of side 7 cm and < PQR = 60°;
(b) locate point X such that X lies on the locus of points equidistant from PQ and QR and also equidistant from Q and R ;
(c) measure |XR|.
(a) Given that \(\sin x = 0.6, 0° \leq x \leq 90°\), evaluate \(2\cos x + 3\sin x\), leaving your answer in the form \(\frac{m}{n}\), where m and n are integers.
(b) 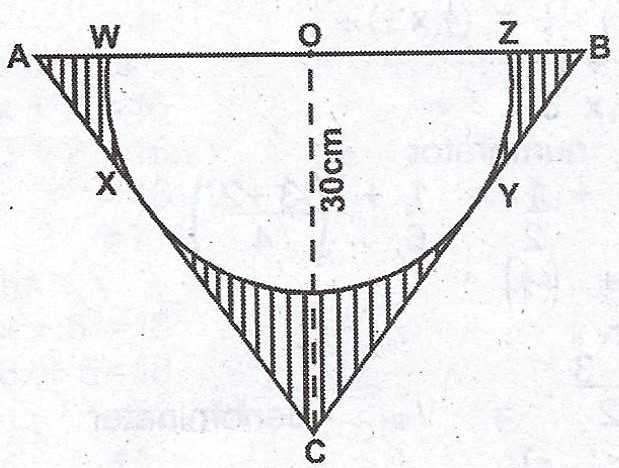
In the diagram, a semi-circle WXYZ with centre O is inscribed in an isosceles triangle ABC. If /AC/ = /BC/, |OC| = 30 cm and < ACB = 130°, calculate, correct to one decimal place, the (i) radius of the circle ; (ii) area oc the shaded portion. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a) Divide \(\frac{x^{2} – 4}{x^{2} + x}\) by \(\frac{x^{2} – 4x + 4}{x + 1}\).
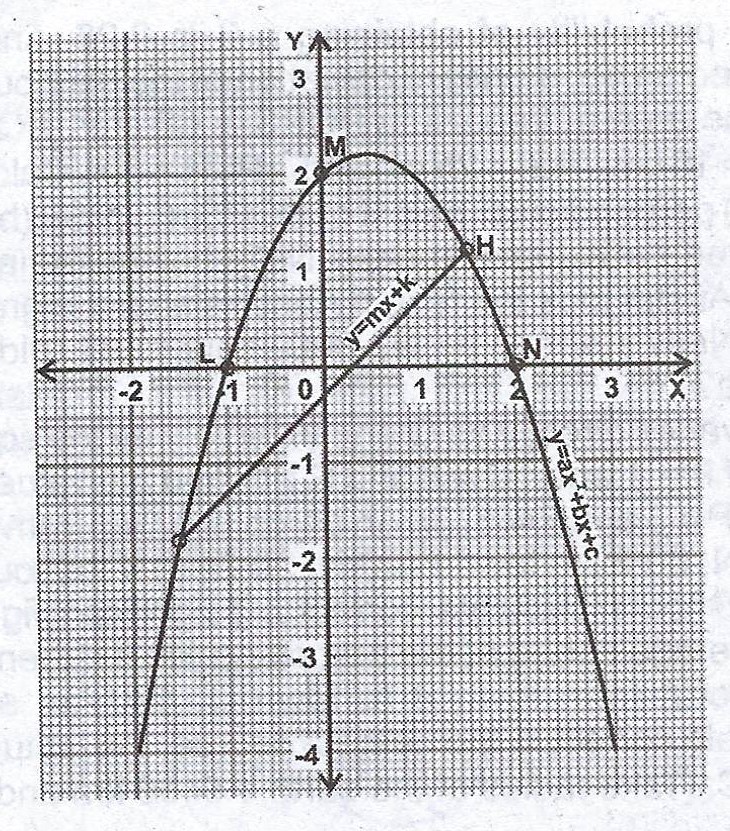
(b) The diagram below shows the graphs of \(y = ax^{2} + bx + c\) and \(y = mx + k\) where a, b, c and m are constants. Use the graph(s) to :
(i) find the roots of the equation \(ax^{2} + bx + c = mx + k\);
(ii) determine the values of a, b and c using the coordinates of points L, M and N and hence write down the equation of the curve;
(iii) determine the line of symmetry of the curve \(y = ax^{2} + bx + c\).
In a class of 40 students, 18 passed Mathematics, 19 passed Accounts, 16 passed Economics, 5 passed Mathematics and Accounts only, 6 Mathematics only, 9 Accounts only, 2 Accounts and Economics only. If each student offered at least one of the subjects,
(a) how many students failed in all subjects?
(b) find the percentage number that failed in at least one of Economics and Mathematics
(c) calculate the probability that a student picked at random failed in Accounts?
A library received $1,300 grant. It spends 10% of the grant on magazine subscriptions, 35% on new books, 15% to repair damaged books, 30% to buy new furniture and 10% to train library staff.
(a) Represent this information on a pie chart.
(b) Calculate, correct to the nearest whole number, the percentage increase of the amount for buying books over that of new furniture.
(a) 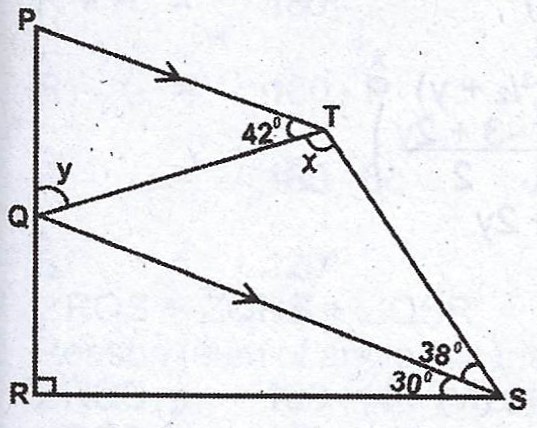
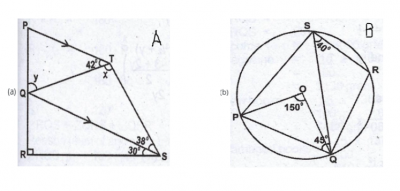
In the diagram, PQRST is a quadrilateral. PT // QS, < PTQ = 42°, < TSQ = 38° and < QSR = 30°. If < QTS = x and < POT = y, find: (i) x ; (ii) y. (SEE THE DIAGRAMS ABOVE)
(b) 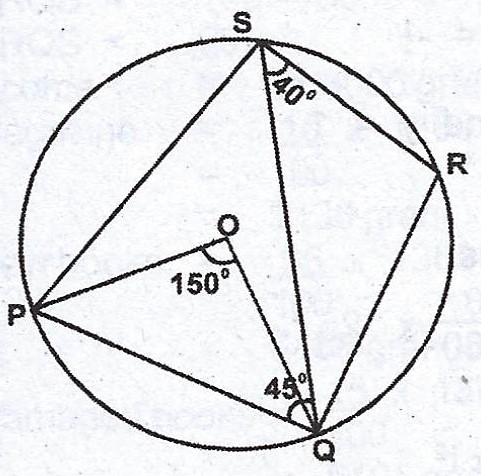
In the diagram, PQRS is a circle centre O. If POQ = 150°, < QSR = 40° and < SQP = 45°, calculate < RQS.
A sector of a circle with radius 21 cm has an area of 280\(cm^{2}\).
(a) Calculate, correct to 1 decimal place, the perimeter of the sector.
(b) If the sector is bent such that its straight edges coincide to form a cone, calculate, correct to the nearest degree, the vertical angle of the cone. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a) Make q the subject of the relation \(t = \sqrt{\frac{pq}{r} – r^{2}q}\).
(b) If \(9^{(1 – x)} = 27^{y}\) and \(x – y = -1\frac{1}{2}\), find the value of x and y.
(a) Simplify : \(\frac{\frac{1}{2} of \frac{1}{4} \div \frac{1}{3}}{\frac{1}{6} – \frac{3}{4} + \frac{1}{2}}\).
(b) Given that \(\sqrt{x} = 10^{\bar{1}.6741}\), without using calculators, find the value of x.
(a)  In the diagram, /PQ/ = 6 cm, /QR/ = 13 cm, /RS/ = 5 cm and < RSQ is a right- angled triangle. Calculate, correct to one decimal place, /PS/.
In the diagram, /PQ/ = 6 cm, /QR/ = 13 cm, /RS/ = 5 cm and < RSQ is a right- angled triangle. Calculate, correct to one decimal place, /PS/.
(b)  The diagram show a wooden structure in the form of a cone mounted on a hemispherical base. The vertical height of the cone is 24 cm and the base radius 7 cm. Calculate, correct to 3 significant figures, the surface area of the structure. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
The diagram show a wooden structure in the form of a cone mounted on a hemispherical base. The vertical height of the cone is 24 cm and the base radius 7 cm. Calculate, correct to 3 significant figures, the surface area of the structure. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a) Copy and complete the table of values for \(y = 1 – 4\cos x\).
| x | 0° | 30° | 60° | 90° | 120° | 150° | 180° | 210° | 240° | 270° |
300° |
| y | -3.0 | 1.0 | 4.5 | -1.0 |
(b) Using a scale of 2cm to 30° on the x- axis and 2cm to 1 unit on the y- axis, draw the graph of \(y = 1 – 4\cos x\) for \(0° \leq x \leq 360°\).
(c) Use the graph to : (i) solve the equation \(1 – 4\cos x = 0\) ; (ii) find the value of y when x = 105° ; (iii) find x when y = 1.5.
(a) 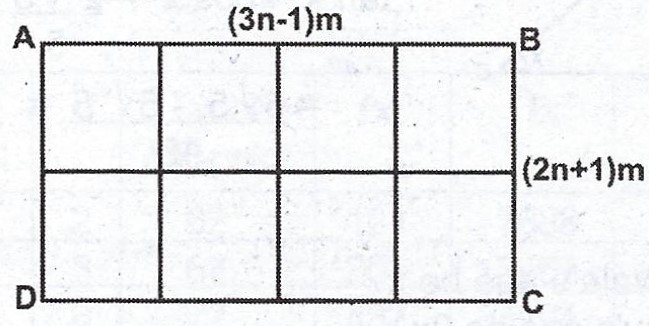
In the diagram, ABCD is a rectangular garden (3n – 1)m long and (2n + 1)m wide. A wire mesh 135m long is used to mark its boundary and to divide it into 8 equal plots. Find the value of n.
(b) A cylinder with base radius 14 cm has the same volume as a cube of side 22 cm. Calculate the ratio of the total surface area of the cylinder to that of the cube. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)]

