(a) Solve : \(7x + 4 < \frac{1}{2}(4x + 3)\).
(b) Salem, Sunday and Shaka shared a sum of N1,100.00. For every N2.00 that Salem gets, Sunday gets 50 kobo and for every N4.00 Sunday gets, Shaka gets N2.00. Find Shaka’s share.
(a) Simplify, without using tables or calculator : \(\frac{\frac{3}{4}(3\frac{3}{8} + 1\frac{5}{8})}{2\frac{1}{8} – 1\frac{1}{2}}\).
(b) Given that \(\log_{10} 2 = 0.3010\) and \(\log_{10} 3 = 0.4771\), evaluate, correct to 2 significant figures and without using tables or calculator, \(\log_{10} 1.125\).
(a) Two functions, f and g, are defined by \(f : x \to 2x^{2} – 1\) and \(g : x \to 3x + 2\) where x is a real number.
(i) If \(f(x – 1) – 7 = 0\), find the values of x.
(ii) Evaluate : \(\frac{f(-\frac{1}{2}) . g(3)}{f(4) – g(5)}\).
(b) An operation, \((\ast)\) is defined on the set R, of real numbers, by \(m \ast n = \frac{-n}{m^{2} + 1}\), where \(m, n \in R\). If \(-3, -10 \in R\), show whether or not \(\ast\) is commutative.
(a) Given that \(5 \cos (x + 8.5)° – 1 = 0, 0° \leq x \leq 90°\), calculate, correct to the nearest degree, the value of x.
(b) The bearing of Q from P is 0150° and the bearing of P from R is 015°. If Q and R are 24km and 32km respectively from P : (i) represent this information in a diagram;
(ii) calculate the distance between Q and R, correct to two decimal places ; (iii) find the bearing of R from Q, correct to the nearest degree.
| Scores | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Frequency | 2 | 5 | 13 | 11 | 9 | 10 |
The table shows the distribution of outcomes when a die is thrown 50 times. Calculate the :
(a) Mean deviation of the distribution ; (b) probability that a score selected at random is at least a 4.
(a) Solve : \((x – 2)(x – 3) = 12\).
(b) 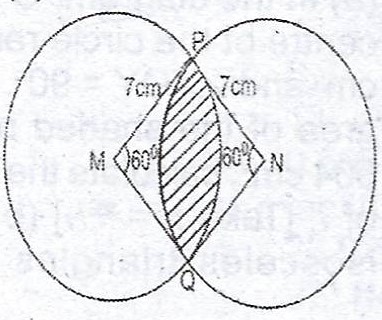 In the diagram, M and N are the centres of two circles of equal radii 7cm. The circle intercept at P and Q. If < PMQ = < PNQ = 60°, calculate, correct to the nearest whole number, the area of the shaded portion. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
In the diagram, M and N are the centres of two circles of equal radii 7cm. The circle intercept at P and Q. If < PMQ = < PNQ = 60°, calculate, correct to the nearest whole number, the area of the shaded portion. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a) 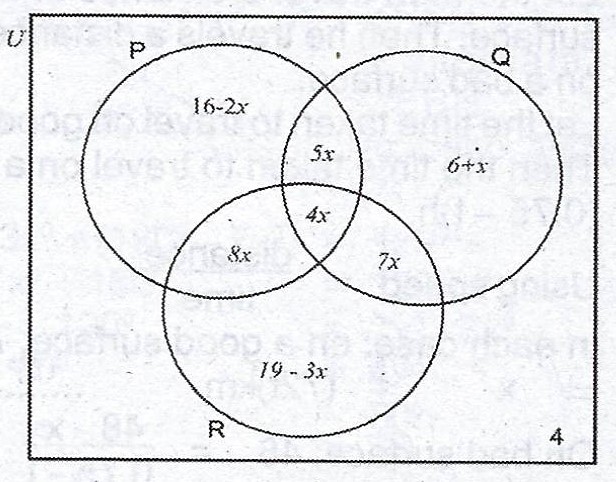
In the Venn diagram, P, Qand R are subsets of the universal set U. If n(U) = 125, find : (i) the value of x ; (ii) n(\(P \cup Q \cap R’\)).
(b) 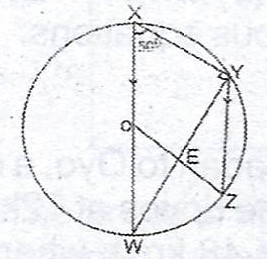 In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle. If WX is parallel to YZ and < WXY = 50°, find the value of (i) , WYZ
In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle. If WX is parallel to YZ and < WXY = 50°, find the value of (i) , WYZ
(ii) < YEZ.
(a) Copy and complete the following table for multiplication modulo 11.
| \(\otimes\) | 1 | 5 | 9 | 10 |
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 9 | 10 |
| 5 | 5 | |||
| 9 | 9 | |||
| 10 | 10 |
Use the table to : (i) evaluate \((9 \otimes 5) \otimes (10 \otimes 10)\);
(ii) find the truth set of :(1) \(10 \otimes m = 2\); (2) \(n \otimes n = 4\)
(b) When a fraction is reduced to its lowest term, it is equal to \(\frac{3}{4}\). The numerator of the fraction when doubled would be 34 greater than the denominator. Find the fraction.
(a) Copy and complete the table of values for the relation \(y = 2 \sin x + 1\)
| x | 0° | 30° | 60° | 90° | 120° | 150° | 180° | 210° | 240° |
270° |
| y | 1.0 | 2.7 | 0.0 | -0.7 |
(b) Using scales of 2 cm to 30° on the x- axis and 2 cm to 1 unit on the y- axis, draw the graph of \(y = 2 \sin x + 1, 0° \leq x \leq 270°\).
(c) Use the graph to find the values of x for which \(\sin x = \frac{1}{4}\).
(a) If \(\frac{3}{2p – \frac{1}{2}} = \frac{\frac{1}{3}}{\frac{1}{4}p + 1}\), find p.
(b) A television set was marked for sale at GH¢ 760.00 in order to make a profit of 20%. The television set was actually sold at a discount of 5%. Calculate, correct to 2 significant figures, the actual percentage profit.
A building contractor tendered for two independent contracts, X and Y. The probabilities that he will win contract X is 0.5 and not win contract Y is 0.3, What is the probability that he will win :
(a) both contracts ;
(b) exactly one of the contracts ;
(c) neither of the contracts?
(a) 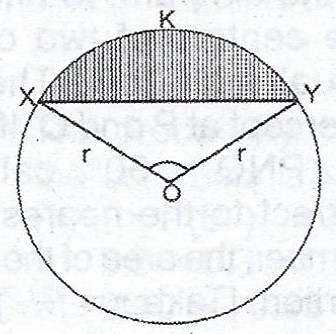
In the diagram, O is the centre of the circle radius r cm and < XOY = 90°.If the area of the shaded part is 504\(cm^{2}\), calculate the value of r. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(b) Two isosceles triangles PQR and PQS are drawn on opposite sides of a common base PQ. If \(< PQR = 66°\) and \(< PSQ = 109°\), calculate the value of \(< RQS\).
(a) Solve the simultaneous equation : \(\frac{1}{x} + \frac{1}{y} = 5 ; \frac{1}{y} – \frac{1}{x} = 1\).
(b) A man drives from Ibadan to Oyo, a distance of 48km in 45 minutes. If he drives at 72 km/h where the surface is good and 48 km/h where it is bad, find the number of kilometers of good surface.
(a) Simplify : \(3\sqrt{75} – \sqrt{12} + \sqrt{108}\), leaving the answer in surd form (radicals).
(b) If \(124_{n} = 232_{five}\), find n.
(a) Without using tables or calculator, simplify : \(\frac{0.6 \times 32 \times 0.004}{1.2 \times 0.008 \times 0.16}\), leaving the answer in standard form (scientific notation).
(b) 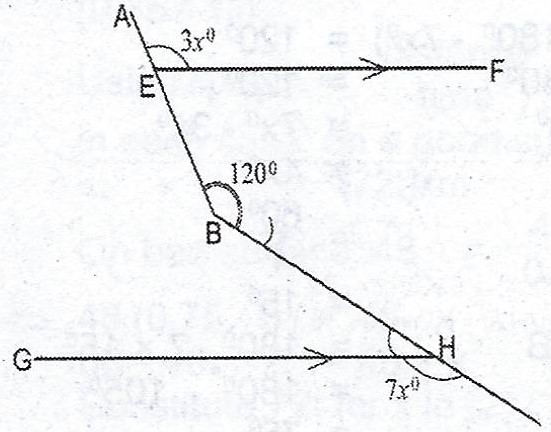
In the diagram, \(\overline{EF}\) is parallel to \(\overline{GH}\). If \(< AEF = 3x°, < ABC = 120°\) and \(< CHG = 7x°\), find the value of \(< GHB\).
The table shows the marks scored by some candidates in an examination.
| Marks (%) | 0-9 | 10-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70-79 | 80-89 | 90-99 |
| Frequency | 7 | 11 | 17 | 20 | 29 | 34 | 30 | 25 | 21 | 6 |
(a) Construct a cumulative frequency table for the distribution and draw a cumulative frequency curve.
(b) Use the curve to estimate, correct to one decimal place, the :
(i) Lowest mark for distinction if 5% of the candidates passed with distinction ; (ii) probability of selecting a candidate who scored at most 45%.
A water reservoir in the form of a cone mounted on a hemisphere is built such that the plane face of the hemisphere fits exactly to the base of the cone and the height of the cone is 6 times thr radius of its base.
(a) Illustrate this information in a diagram.
(b) If the volume of the reservoir is \(333\frac{1}{3}\pi m^{3}\), calculate, correct to the nearest whole number, the :
(I) volume of the hemisphere ; (II) Total surface area of the reservoir. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)].
(a) Make m the subject of the relations \(h = \frac{mt}{d(m + p)}\).
(b) 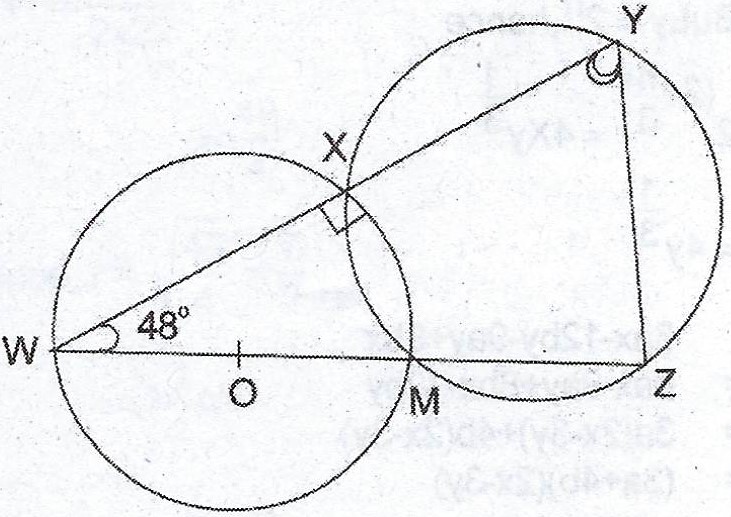
In the diagram, WY and WZ are straight lines, O is the centre of circle WXM and < XWM = 48°. Calculate the value of < WYZ.
(c) An operation \(\star\) is defind on the set X = {1, 3, 5, 6} by \(m \star n = m + n + 2 (mod 7)\) where \(m, n \in X\).
(i) Draw a table for the operation.
(ii) Using the table, find the truth set of : (I) \(3 \star n = 3\) ; (II) \(n \star n = 3\).
(a) Without using Mathematical tables or calculators, simplify : \(\frac{2\tan 60° + \cos 30°}{\sin 60°}\)
(b) From an aeroplane in the air and at a horizontal distance of 1050m, the angles of depression of the top and base of a control tower at an instance are 36° and 41° respectively. Calculate, correct to the nearest meter, the :
(i) height of the control tower ; (ii) shortest distance between the aeroplane and the base of the control tower.
(a) The first term of an Arithmetic Progression (AP) is 8, the ratio of the 7th term to the 9th term is 5 : 8, find the common difference of the AP.
(b) A trader bought 30 baskets of pawpaw and 100 baskets of mangoes for N2,450.00. She sold the pawpaw at a profit of 40% and the mangoes at a profit of 30%. If her profit on the entire transaction was N855.00, find the (i) cost price of a basket of pawpaw ; (ii) selling price of the 100 baskets of mangoes.
(a) Using ruler and a pair of compasses only, construct a :
(i) Trapezium WXYZ such that |WX| = 8 cm, |XY| = 5.5 cm, |YZ| = 8.3 cm, < WXY = 60° and WX // ZY;
(ii) rectangle PQYZ where P and Q are on WX
(b) Measure : (i) |QX| ; (ii) < XWZ.

