(a) Using completing the square method, solve, correct to 2 decimal places, the equation \(3y^{2} – 5y + 2 = 0\).
(b) Given that \(M = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 3 \end{pmatrix}, N = \begin{pmatrix} m & x \\ n & y \end{pmatrix}\) and \(MN = \begin{pmatrix} 2 & 1 \\ 3 & 4 \end{pmatrix}\), find the matrix N.
(a) It takes 8 students two- thirds of an hour to fill 12 tanks with water. How many tanks of water will 4 students fill in one- third of an hour at the same rate?
(b) A chord, 20 cm long, is 12 cm from the centre of the circle. Calculate, correct to one decimal place, the :
(i) angle subtended by the chord at the centre of the circle;
(ii) perimeter of the minor segment cut off by the chord. [Take \(\pi = 3.142\)].
(a) Given that \(\sin x = \frac{5}{13}, 0° < x < 90°\), find \(\frac{\cos x – 2\sin x}{2\tan x}\).
(b) A ladder, LA, leans against a vertical pole at a point L which is 9.6metres above the groung. Another ladder, LB, 12 metres long, leans on the opposite side of the pole and at the same point L. If A and B are 10 metres apart and on the same straight line as the foot of the pole, calculate, correct to 2 significant figures, the :
(i) length of ladder LA (ii) angle which LA makes with the ground.
(a) PQ is a tangent to a circle RST at the point S. PRT is a straight line, < TPS = 34° and < TSQ = 65°.
(i) Illustrate the information in a diagram; (ii) find the value of : (a) < RTS ; (b) < SRP.
(b) 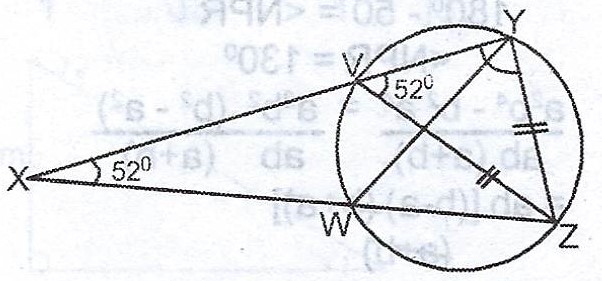
In the diagram, /VZ/ = /YZ/, < YXZ = 20° and < ZVY = 52°. Calculate the size of < WYZ.
| Marks | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Number of students | m + 2 | m – 1 | 2m – 3 | m + 5 | 3m – 4 |
The table shows the distribution of marks scored by some students in a test.
(a) If the mean mark is \(3\frac{6}{23}\), find the value of m.
(b) Find the : (i) interquartile range
(ii) probability of selecting a student who scored at least 4 marks in the test.
(a) Copy and complete the table of values for the equation \(y = 2x^{2} – 7x – 9\) for \(-3 \leq x \leq 6\).
| x | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| y | 13 | -9 | -14 | -12 | 6 |
(b) Using scales of 2cm to 1 unit on the x- axis and 2cm to 4 units on the y- axis, draw the graphs of \(y = 2x^{2} – 7x – 9\) for \(-3 \leq x \leq 6\).
(c) Use the graph to estimate the :
(i) roots of the equation \(2x^{2} – 7x = 26\);
(ii) coordinates of the minimum point of y;
(iii) range of values for which \(2x^{2} – 7x < 9\).
(a) A manufacturing company requires 3 hours of direct labour to process N87.00 worth of raw materials. If the company uses N30,450.00 worth of raw materials, what amount should it budget at N18.25 per hour?
(b) An investor invested Nx in bank M at the rate of 6% simple interest per annum and Ny in bank N at the rate of 8% simple interest per annum. If a total of N8,000,000.00 was invested in the two banks and the investor received a total of N2,320,000.00 as interest from the two banks after 4 years, calculate the:
(i) values of x and y
(ii) interest paid by the second bank.
Out of 120 customers in a shop, 45 bought both bags and shoes. If all the customers bought either bags or shoes and 11 more customers bought shoes than bags:
(a) Illustrate the this information in a diagram;
(b) find the number of customers who bought shoes;
(c) calculate the probability that a customer selected at random bought bags.
If the sixth term of an Arithmetic Progression (A.P) is 37 and the sum of the first six terms is 147, find the
(a) first term;
(b) sum of the first fifteen terms.
(a) The angle of depression of a point P on the ground from the top T of a building is 23.6°. If the distance from P to the foot of the building is 50m, calculate, correct to the nearest metre, the height if the building.
(b) 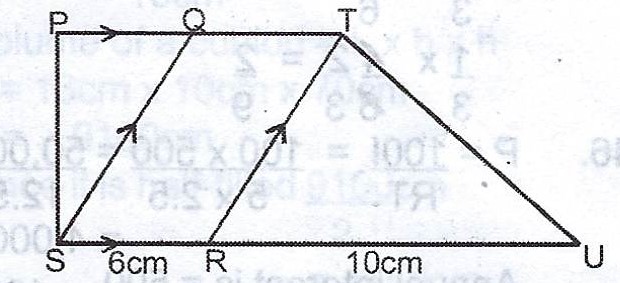
In the diagram, \(PT // SU, QS // TR, /SR/ = 6cm\) and \(/RU/ = 10 cm\). If the area of \(\Delta TRU = 45 cm^{2}\), calculate the area of the trapezium QTUS.
(a) Solve the equation : \(\frac{2}{3}(3x – 5) – \frac{3}{5}(2x – 3) = 3\)
(b) 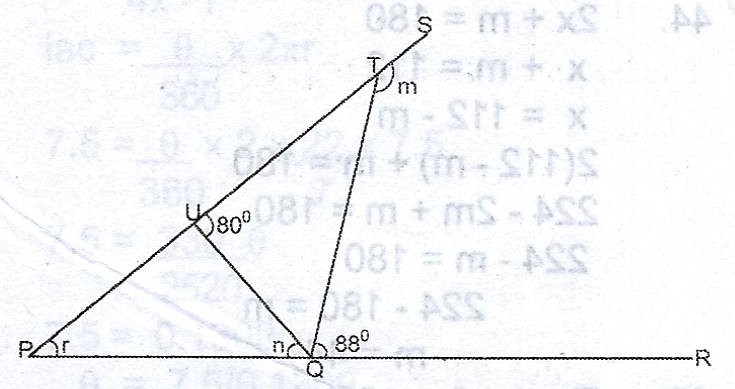
In the diagram, < STQ = m, < TUQ = 80°, < UPQ = r, < PQU = n and < RQT = 88°. Find the value of (m + n).
(a) If \((y – 1)\log_{10}4 = y\log_{10}16\), without using Mathematics tables or calculator, find the value of y.
(b) When I walk from my house at 4km/h, I will get to my office 30mins later than when I walk at 5km/h. Calculate the distance between my house and office.
| Marks | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 |
| Frequency | 1 | 1 | x | 5 | y | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
The frequency distribution shows the marks distribution of a class of 30 students in an examination.
The mean mark of the distribution is 52.
(a) Find the values of x and y.
(b) Construct a group frequency distribution table starting with a lower class limit of 1 and class interval of 10.
(c) Draw a histogram for the distribution
(d) Use the histogram to estimate the mode.
(a) If \(x = \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix}, y = \begin{pmatrix} 5 \\ -2 \end{pmatrix}\) and \(z = \begin{pmatrix} -4 \\ 13 \end{pmatrix}\), find the scalars p and q such that \(px + qy = z\).
(b)(i) Using the scale of 2cm to 2 units on both axis, draw on a graph paper two perpendicular axis x and y for \(-5 \leq x \leq 5, -5 \leq y \leq 5\) respectively.
(ii) Draw, on the graph paper, indicating clearly the vertices and their coordinates,
(1) the quadrilateral WXYZ with W(2, 3), X(4, -1), Y(-3, -4) and Z(-3, 2).
(2) the image \(W_{1}X_{1}Y_{1}Z_{1}\) of the quadrilateral WXYZ under an anti-clockwise rotation of 90° about the origin where \(W \to W_{1}, X \to X_{1}, Y \to Y_{1}\) and \(Z \to Z_{1}\).
(a) Copy and complete the table of values for y = 2x\(^{2}\) + x – 10 for -5 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 4.
| x | -5 | -4 | -3 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| y | 5 | -9 | -10 | 0 |
(b) Using scales of 2cm to 1 unit on the x- axis and 2cm to 5 units on the y- axis, Draw the graph of y = 2x\(^{2}\) + x – 10 for -5 \(\leq\) x \(\leq\) 4.
(c) Use the graph to find the solution of :
(i) 2x\(^{2}\) + x = 10
(ii) 2x\(^{2}\) + x – 10 = 2x
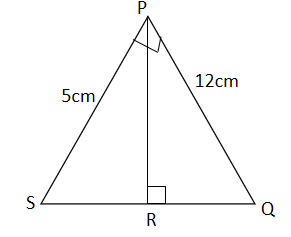
(a) In < PQS, |PQ| = 12 cm, |PS| = 5 cm, < SPQ = < PRQ = 90°, Find, correct to three significant figures, |PR|.
(b) The lengths of two ladders, L and M are 10m and 12m respectively. They are placed against a wall such that each ladder makes angle with the horizontal ground. If the foot of L is 8m from the foot of the wall.
(i) Draw a diagram to illustrate this information; (ii) Calculate the height at which M touches the wall.
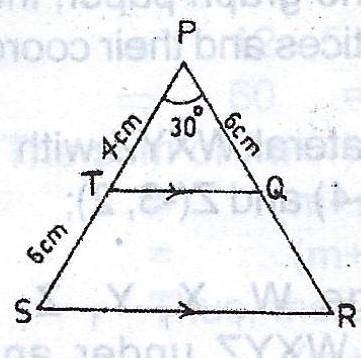
In the diagram, |PT| = 4 cm, |TS| = 6 cm, |PQ| = 6 cm and < SPR = 30°. Calculate, correct to the nearest whole number:
(a) |SR| ;
(b) area of TQRS.
(a) Lamin bought a book for N300.00 and sold it to Bola at a profit of x%. Bola then sold the same book at a profit of x%. If James paid \(N(6x + \frac{3}{4})\) more for the book than Lamin paid, find the value of x.
(b) Find the range of values of x which satisfies the inequality \(3x – 2 < 10 + x < 2 + 5x\).
(a) Find the equation of the line passing through the points (2, 5) and (-4, -7).
(b) Three ships P, Q and R are at sea. The bearing of Q from P is 030° and the bearing of P and R is 300°. If |PQ| = 5 km and |PR| = 8 km,
(i) Illustrate the information in a diagram.
(ii) Calculate, correct to three significant figures, the:
(1) distance between Q and R
(2) bearing of R from Q.
In a road worthiness test on 240 cars, 60% passed. The number that failed had faults in Clutch, Brakes and Steering as follows: Clutch only – 28, Clutch and Steering – 14; Clutch, Steering and Brakes – 8; Clutch and Brakes – 20; Brakes and Steering only – 6. The number of cars with faults in Steering only is twice the number of cars with faults in Brakes only.
(a) Draw a Venn Diagram to illustrate this information.
(b) How many cars had : (i) Faulty Brakes? (ii) Only one fault?
(a) If the mean of m, n, s, p and q is 12, calculate the mean of (m + 4), (n – 3), (s + 6), (p – 2) and (q + 8).
(b) In a community of 500 people, the 75th percentile age is 65 years while the 25th percentile age is 15 years. How many of the people are between 15 and 65 years?

