ANWSER
Question 1a:
Answer:
Virus-mediated lateral transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells occurs through transduction. In this process, a bacteriophage infects a donor bacterial cell, incorporating bacterial DNA into its capsid instead of viral DNA. When the phage infects a new host cell, it transfers the bacterial DNA, facilitating genetic exchange. Diagrams should show:
1. Phage infecting donor bacterium.
2. Phage packaging bacterial DNA.
3. Phage injecting bacterial DNA into recipient cell.
—
Question 1b:
Answer:
| Conjugation | Transformation |
|——————————————|—————————————-|
| Requires direct cell-to-cell contact. | Does not require cell-to-cell contact. |
| Involves plasmid transfer via pilus. | Involves uptake of free DNA from environment. |
| Donor cell must be F+ or Hfr. | Recipient cell must be competent. |
—
Question 1c:
Answer:
Artificial transformation of a bacterial cell (e.g., *E. coli*) with an antibiotic resistance plasmid (e.g., pUC19) involves:
1. Preparation of competent cells using calcium chloride (CaCl₂).
2. Heat shock (42°C for 30–90 seconds) to allow plasmid uptake.
3. Recovery in nutrient broth.
4. Selection on agar containing the antibiotic (e.g., ampicillin).
—
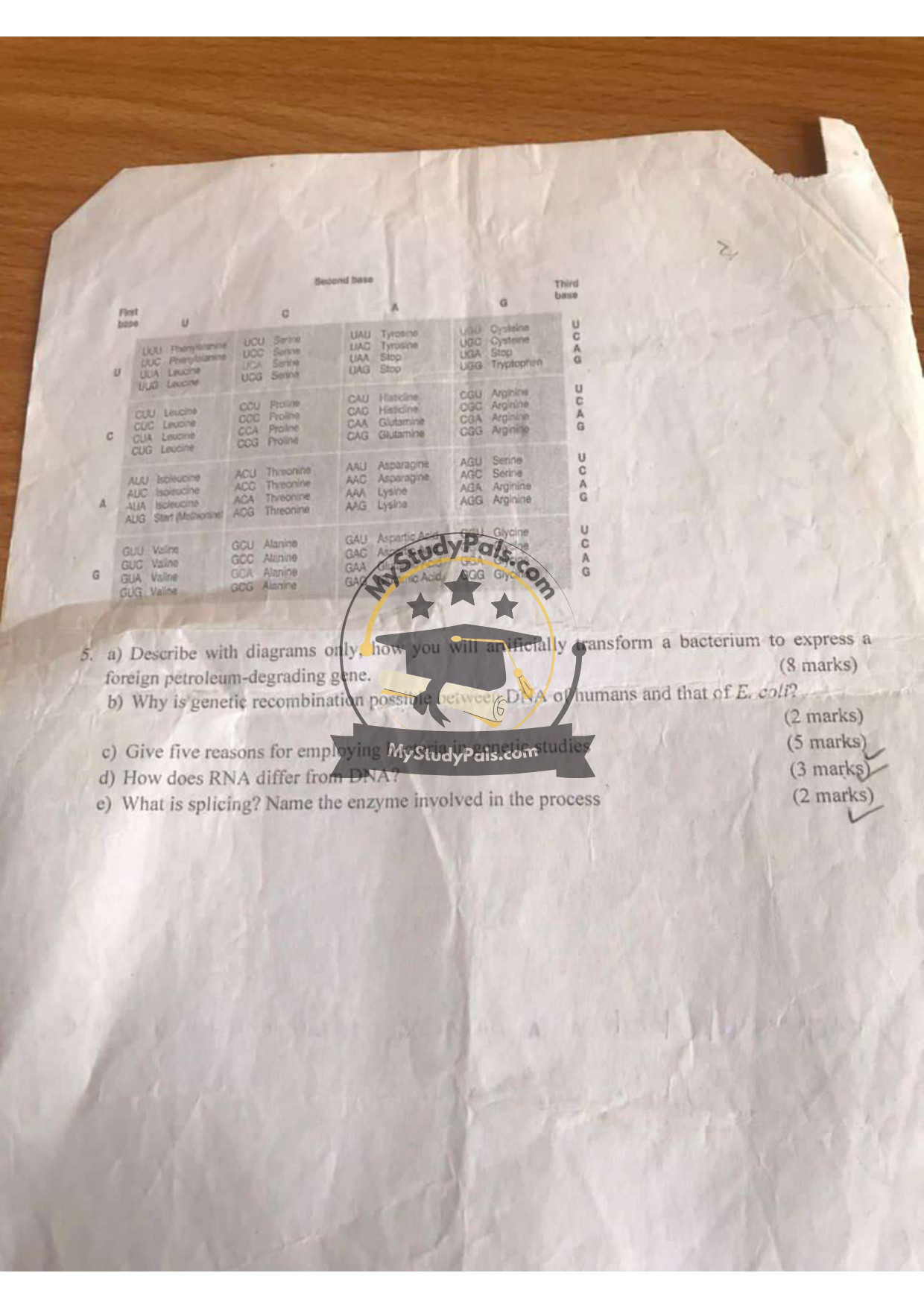
Question 5a:
Answer:
RNA differs from DNA in:
1. Sugar: RNA has ribose; DNA has deoxyribose.
2. Bases: RNA uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
3. Structure: RNA is single-stranded; DNA is double-stranded.
—
Question 5b:
Answer:
The amino acid coded by the start codon (AUG) is methionine.
—
Question 5c:
Answer:
In bacteria, the equivalent amino acid is N-formylmethionine (fMet).
—
Question 5d:
Answer:
Frameshift mutations occur due to insertions or deletions of nucleotides (not in multiples of 3), altering the reading frame.
—
Question 5e:
Answer:
Two DNA repair mechanisms:
1. Excision repair: Damaged bases are removed and replaced.
2. Photoreactivation: UV-induced thymine dimers are repaired by photolyase enzyme.
—
Question 5f:
Answer:
Characteristics of the genetic code:
1. Universal (mostly).
2. Degenerate (multiple codons for one amino acid).
3. Non-overlapping.
4. Commaless.
—
Question 5g:
Answer:
Splicing is the removal of introns from pre-mRNA. The enzyme involved is the spliceosome (comprising snRNPs).
—
Question 6a:
Answer:
Gene expression involves:
1. Transcription: RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA from DNA.
2. Translation: Ribosomes read mRNA to synthesize proteins.
—
Question 6b (enzymes in replication):
Answer:
– Ligase: Seals DNA nicks.
– Helicase: Unwinds DNA.
– DNA polymerase III: Synthesizes new DNA.
– Primase: Synthesizes RNA primers.
– DNA polymerase I: Replaces primers with DNA.
—
Question 7a (DNA structure):
Answer:
DNA is a double helix with:
– Sugar-phosphate backbone.
– Complementary base pairing (A-T, G-C).
– Antiparallel strands (5’→3’ and 3’→5’).
—
Question 7b (mutations):
Answer:
– Silent: No amino acid change (same codon).
– Missense: Amino acid substitution.
– Nonsense: Premature stop codon.
– Somatic: Occurs in non-germ cells.
—
Question 8:
Answer:
Three types of RNA:
1. mRNA: Carries genetic code for translation.
2. tRNA: Transfers amino acids to ribosomes.
3. rRNA: Forms ribosomes’ structural and catalytic core.